
Concept explainers
Perpetual: Alternative cost flows
Aloha Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year purchases and sales transactions. (For specific identification, the May 9 sale consisted of 80 units from beginning inventory and 100 units from the May 6 purchase; the May 30 sale consisted of 200 units from the May 6 purchase and 100 units from the May 25 purchase.)
| Date | Activities | Units Acquired at Cost | Units Sold at Retail |
| May 1 | Beginning inventory .......... | 150 units @ $300.00 per unit | |
| May 6 | Purchase.................... | 350 units @ $350.00 per unit | |
| May 9 | Sales....................... | 180 units @ $ 1,200.00 per unit | |
| May 17 | Purchase................... | 80 units @ $450.00 per unit | |
| May 25 | Purchase.................... | 100 units @ $458.00 per unit | |
| May 30 | Sales....................... | 300 units @ $1,400.00 per unit | |
| Total........................ | 680 units | 480 units |
Required
- 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale.
- 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory.
- 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification (Round all amounts to cents.)
- 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3.
Analysis Component
5. If the company’s manager earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit, which method of inventory costing will the manager likely prefer?
1.
Ascertain the cost of goods available for sale, and the number of units available for sales.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the cost of goods available for sale, and the number of units available for sales as follows:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 150 | 300 | 45,000 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| May 6 | 350 | 350 | 122,500 |
| May 17 | 80 | 450 | 36,000 |
| May 25 | 100 | 458 | 45,800 |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 680 | 249,300 |
Table (1)
Therefore, the number of units available for sales is 680 units, and the cost of goods available for sale is $246,300.
2.
Ascertain the number of units in ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the number of units in ending inventory as follows:
| Details | Number of Units |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 680 |
| Less: Sales: | |
| May 9 | 180 |
| May 30 | 300 |
| Ending Inventory | 200 |
Table (2)
Therefore, the number of units in ending inventory is 200.
3.
Ascertain the cost assigned to ending inventory under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual inventory system: The method or system of maintaining, recording, and adjusting the inventory perpetually throughout the year, is referred to as perpetual inventory system.
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In this method, items purchased initially are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the recent cost for the remaining unsold items.
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In this method, items purchased recently are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the initial cost for the remaining unsold items.
Weighted-average Cost Method: In this method, the inventories are priced at the average rate of goods available for sales.
Specific identification method: Specific identification method identifies the cost of each item in ending inventory by separating purchases. In this method, the value of ending inventory is computed based on the lower of cost or market value.
Ascertain the cost assigned to ending inventory under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification as follows:
(a) FIFO

Table (3)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under FIFO is $88,800.
(b) LIFO

Table (4)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under LIFO is 62,500.
(c) Weighted average method:
Refer working note 1 and 2 for calculation of weighted average cost
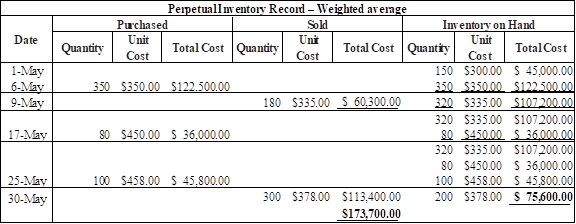
Table (5)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under weighed average method is $75,600.
Working note:
Calculate the weighted average cost of inventory after May 6 purchase
Calculate the weighted average cost of inventory after May 25 purchase
(d) Specific identification method:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Cost of goods available for sale | 249,300 | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | |||
| Beginning inventory | 80 | 300 | 24,000 |
| May 6 | 300 | 350 | 105,000 |
| May 25 | 100 | 458 | 45,800 |
| Ending inventory | 74,500 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under specific identification method is $74,500.
4.
Ascertain the gross profit earned by the company for the each of the given methods.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the gross profit earned by the company for the each of the given methods as follows:
| Particulars | FIFO | LIFO | Specific Identification | Weighted Average |
| Sales | $ 636,000 | $ 636,000 | $ 636,000 | $ 636,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | $ 160,500 | $ 186,800 | $ 173,700 | $ 174,800 |
| Gross profit | $ 475,500 | $ 449,200 | $ 462,300 | $ 461,200 |
Table (7)
5.
Identify the inventory method which is preferred by the manager, if company’s manger earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the inventory method which is preferred by the manager, if company’s manger earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit as follows:
In this case, gross profit under FIFO method ($475,500) is more than the other three methods. Hence, the manager of Company would likely to prefer the FIFO method.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- 4. A purchase of equipment for cash will:A. Increase assetsB. Decrease total assetsC. Have no effect on assetsD. Increase liabilitiesarrow_forwardWhen a company collects cash from a customer in advance, it should:A. Recognize revenue immediatelyB. Record a liabilityC. Record it as equityD. Ignore it until revenue is earnedarrow_forwardThe journal entry to record the purchase of office supplies on account would include:A. Debit Supplies, Credit CashB. Debit Supplies, Credit Accounts PayableC. Debit Cash, Credit SuppliesD. Debit Accounts Payable, Credit Suppliesarrow_forward
- 7. Which of the following is an adjusting entry?A. Payment of salariesB. Depreciation expenseC. Purchase of suppliesD. Payment of rent in advancearrow_forward5. What is the normal balance of the Dividends account?A. DebitB. CreditC. Zero balanceD. Depends on the type of dividendarrow_forward6. Which of the following transactions decreases stockholders' equity?A. Issuing sharesB. Paying dividendsC. Earning net incomeD. Receiving customer paymentsarrow_forward
- Accounting?arrow_forward9. If a company fails to adjust for accrued interest expense, what is the effect on the financial statements?A. Assets overstatedB. Liabilities understatedC. Revenues understatedD. Equity overstated need helllparrow_forward9. If a company fails to adjust for accrued interest expense, what is the effect on the financial statements?A. Assets overstatedB. Liabilities understatedC. Revenues understatedD. Equity overstatedarrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning  Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning





