
Concept explainers
Alternative cost flows
Montoure Company uses a perpetual inventory system. It entered into the following calendar-year purchases and sales transactions. (For specific identification, units sold consists of 600 units from beginning inventory, 300 from the February 10 purchase, 200 from the March 13 purchase, 50 from the August 21 purchase, and 250 from the September 5 purchase.)
| Date | Activities | Units Acquired at Cost | Units Sold at Retail |
| Jan. 1 | Beginning inventory..... | 600 units @ $45.00 per unit | |
| Feb. 10 | Purchase.................... | 400 units @ $42.00 per unit | |
| Mar. 13 | Purchase.................... | 200 units @ $27.00 per unit | |
| Mar. 15 | Sales....................... | 800 units @ $ 75.00 per unit | |
| Aug. 21 | Purchase................. | 100 units @ $50.00 per unit | |
| Sep. 5 | Purchase.................... | 500 units @ $46.00 per unit | |
| Sep.10 | Sales....................... | 600 units @ $75.00 per unit | |
| Total....................... | 1,800 units | 1,400 units |
Required
- 1. Compute cost of goods available for sale and the number of units available for sale.
- 2. Compute the number of units in ending inventory.
- 3. Compute the cost assigned to ending inventory using (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification (Round all amounts to cents.)
- 4. Compute gross profit earned by the company for each of the four costing methods in part 3.
- 5. If the company’s manager earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit, which method of inventory costing will the manager likely prefer?
1.
Ascertain the cost of goods available for sale, and the number of units available for sales.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the cost of goods available for sale, and the number of units available for sales as follows:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 600 | 45 | 27,000 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| February 10 | 400 | 42 | 16,800 |
| March 13 | 200 | 27 | 5,400 |
| August 21 | 100 | 50 | 5,000 |
| September 5 | 500 | 46 | 23,000 |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 1,800 | 77,200 |
Table (1)
Therefore, the number of units available for sales is 1,800 units, and the cost of goods available for sale is $77,200.
2.
Ascertain the number of units in ending inventory.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the number of units in ending inventory as follows:
| Details | Number of Units |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 1,800 |
| Less: Sales: | |
| March 15 | 800 |
| September 10 | 600 |
| Ending Inventory | 400 |
Table (2)
Therefore, the number of units in ending inventory is 400.
3.
Ascertain the cost assigned to ending inventory under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual inventory system: The method or system of maintaining, recording, and adjusting the inventory perpetually throughout the year, is referred to as perpetual inventory system.
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In this method, items purchased initially are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the recent cost for the remaining unsold items.
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In this method, items purchased recently are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the initial cost for the remaining unsold items.
Weighted-average Cost Method: In this method, the inventories are priced at the average rate of goods available for sales.
Specific identification method: Specific identification method identifies the cost of each item in ending inventory by separating purchases. In this method, the value of ending inventory is computed based on the lower of cost or market value.
Ascertain the cost assigned to ending inventory under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification as follows:
(a) FIFO
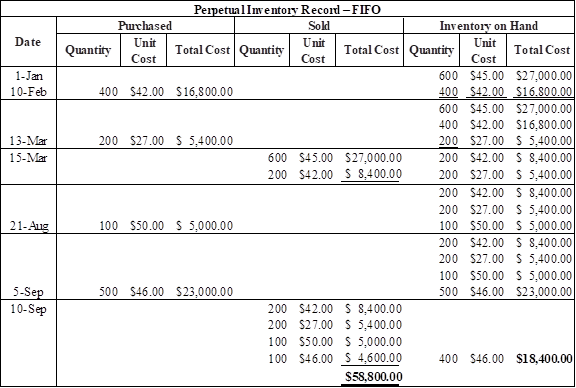
Table (3)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under FIFO is $18,400.
(b) LIFO

Table (4)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under LIFO is $18,000.
(c) Weighted average method:
Refer working note 1 and 2 for calculation of weighted average cost

Table (5)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under weighed average method is $17,760.
Working note:
Calculate the weighted average cost of inventory after March 13purchase
Calculate the weighted average cost of inventory after September 5 purchase
(d) Specific identification method:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Cost of goods available for sale (refer table 1) | 77,200 | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | |||
| Beginning inventory | 600 | 45 | 27,000 |
| February 10 | 300 | 42 | 12,600 |
| March 13 | 200 | 27 | 5,400 |
| August 21 | 50 | 50 | 2,500 |
| September 5 | 250 | 46 | 11,500 |
| Ending inventory | 18,200 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under specific identification method is $18,200.
4.
Ascertain the gross profit earned by the company for the each of the given methods.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the gross profit earned by the company for the each of the given methods as follows:
| Particulars | FIFO | LIFO | Specific Identification | Weighted Average |
| Sales | $ 105,000 | $ 105,000 | $105,000 | $ 105,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | $ 58,800 | $ 59,200 | $ 59,000 | $ 59,440 |
| Gross profit | $ 46,200 | $ 45,800 | $46,000 | $ 45,560 |
Table (7)
5.
Identify the inventory method which is preferred by the manager, if company’s manger earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the inventory method which is preferred by the manager, if company’s manger earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit as follows:
In this case, gross profit under FIFO method ($46,200) is more than the other three methods. Hence, the manager of Company would likely to prefer the FIFO method.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Cornerstones of Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337690881Author:Jay Rich, Jeff JonesPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning





