
Concept explainers
a.
Use a horizontal statements model to show the effect of the transactions on the elements of financial statements.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Financial Statements:
Financial statements are complete record of all the financial transactions that take place in the business during a particular financial year. They report important financial information such as assets, liabilities, revenues and expenses of the company to the internal and external users for taking necessary decision. They help them to know the financial status of the business for a particular period.
Record the transactions in a horizontal statements model:
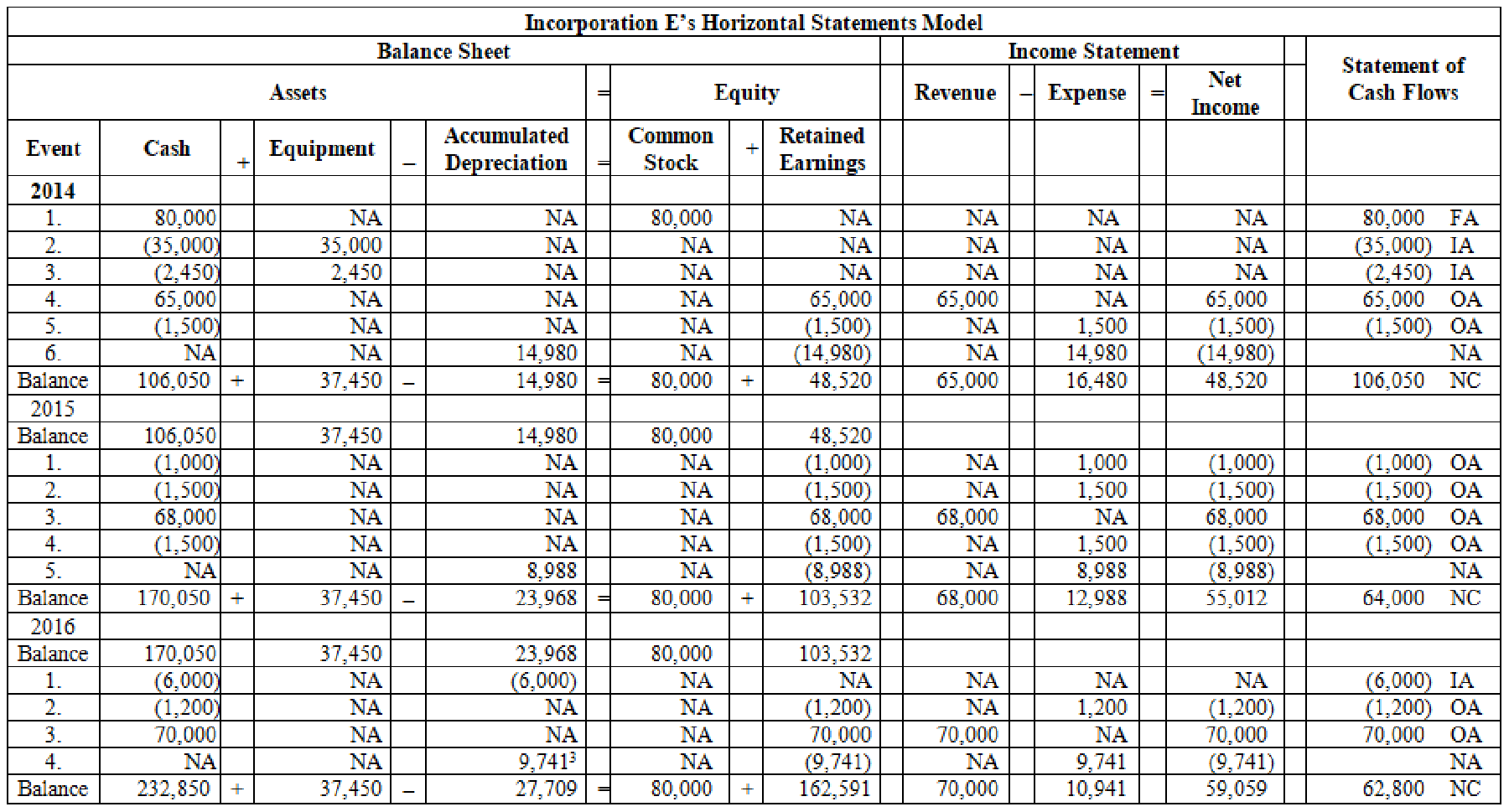
Table (1)
Working note 1: Determine the
Useful life = 5 years
Working note 2: Calculate the depreciation expense using Double-declining-balance method.
Calculate the depreciation expense for 2014.
Working note 3: Calculate the depreciation expense for 2015.
Working note 4: Calculate the depreciation expense for 2016.
b.
Use a vertical model to present financial statements for 2014, 2015, and 2016.
b.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement:
Income statement is a financial statement that shows the net income or net loss by deducting the expenses from the revenues and vice versa.
Statement of changes in stockholders' equity:
Statement of changes in stockholders' equity records the changes in the owners’ equity during the end of an accounting period by explaining about the increase or decrease in the capital reserves of shares.
Balance sheet summarizes the assets, the liabilities, and the
Statement of
Statement of cash flow is a financial statement that shows the cash and cash equivalents of a company for a particular period of time. It shows the net changes in cash, by reporting the sources and uses of cash as a result of operating, investing, and financing activities of a company.
Use a vertical model to present financial statements for 2014, 2015, and 2016 as follows:
| Incorporation E | |||
| Financial Statements | |||
| For the year ended December 31 | |||
| Income Statements | |||
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |
| Service Revenue | $65,000 | $68,000 | $70,000 |
| Expenses: | |||
| Maintenance Expense | 0 | (2,500) | 0 |
| Computer Service Expense | (1,500) | (1,500) | (1,200) |
| Depreciation Expense | (14,980) | (8,988) | (9,741) |
| Total Expenses | (16,480) | (12,988) | (10,941) |
| Net Income | $48,520 | $55,012 | $59,059 |
| Statement of Changes in Stockholder's Equity | |||
| Beginning Common Stock | 0 | $80,000 | $80,000 |
| Add: Stock Issued | 80,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Ending Common Stock | 80,000 | 80,000 | 80,000 |
| Beginning | 0 | 48,520 | 103,532 |
| Add: Net Income | 48,520 | 55,012 | 59,059 |
| Ending Retained Earnings | 48,520 | 103,532 | 162,591 |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $128,520 | $183,532 | $242,591 |
Table (2)
| Incorporation E | |||
| Financial Statements | |||
| Balance Sheet as of December 31 | |||
| 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | |
| Assets | |||
| Cash | $106,050 | $170,050 | $232,850 |
| Computer | 37,450 | 37,450 | 37,450 |
| Less: | (14,980) | (23,968) | (27,709) |
| Total Assets | $128,520 | $183,532 | $242,591 |
| Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Stockholders’ Equity | |||
| Common Stock | 80,000 | 80,000 | 80,000 |
| Retained Earnings | 48,520 | 103,532 | 162,591 |
| Total Stockholders’ Equity | $128,520 | $183,532 | $242,591 |
| Total Liabilities and Stockholders' Equity | $128,520 | $183,532 | $242,591 |
Table (3)
| Incorporation E | |||
| Statement of Cash Flows | |||
| For the Year Ended December 31 | |||
| Particulars | 2014 (in $) | 2015 (in $) | 2016 (in $) |
| Cash Flows From Operating Activities: | |||
| Inflow from revenue | 65,000 | 68,000 | 70,000 |
| Outflow for expenses | (1,500) | (4,000) | (1,200) |
| Net Cash Flow from operating activities | 63,500 | 64,000 | 68,800 |
| Cash Flows From Investing Activities: | |||
| Outflow to purchase Computer | (37,450) | 0 | (6,000) |
| Net Cash Flow from investing activities | (37,450) | 0 | (6,000) |
| Cash Flows From Financing Activities: | |||
| Inflow from stock issue | 80,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Net Cash Flow from financing activities | 80,000 | 0 | 0 |
| Net Increase in Cash | 106,050 | 64,000 | 62,800 |
| Add: Beginning Cash Balance | 0 | 106,050 | 170,050 |
| Ending Cash Balance | $106,050 | $170,050 | $232,850 |
(Table 4)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
SURVEY OF ACCOUNTING-ACCESS
- I need assistance with this financial accounting problem using valid financial procedures.arrow_forwardAccounting problemarrow_forwardRoyal Designs creates custom furniture. During November, it had applied an overhead of $162,000. Overhead is applied at the rate of 80% of direct labor cost. Direct labor wages average $32 per hour. How many direct labor hours did Royal Designs have for the month of November?arrow_forward
- Please explain the solution to this general accounting problem using the correct accounting principles.arrow_forwardWhich circumstances require modified nominal account treatment? A. Nominal accounts never need modification B. Standard closing entries always suffice C. Special purpose entities demand unique closing procedures D. Year-end procedures remain constant. MCQarrow_forwardAssume that a company produced 12,000 units and sold 9,500 units during its first year of operations.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





