
Interpretation:
The reaction which occurs faster in each of the given reactions is to be determined and the reason is to be explained.
Concept introduction:
Alkyl iodides are several times more reactive than alkyl bromides. These reactivity differences can be related to the carbon-halogen bond strength and the basicity of the halide anion. Alkyl iodides have the weakest carbon-halogen bond and require the lowest activation energy to break.
Regarding basicity of the halide leaving the group, iodide is the weakest base. Generally, it is true that, the less basic the leaving group, the smaller the energy requirement for cleaving its bond to carbon and the faster the rate.
Alkyl groups that are adjacent to the carbon atom to the point of nucleophilic attack decrease the rate of the
Protic solvents having
In
Answer to Problem 27P
Solution:
a)
b)
c) Cyclohexyl chloride reacts faster than hexyl chloride by the
d) Tert-butyl bromide reacts faster than
e) sec-butyl bromide reacts faster than isobutyl bromide by the
f) The reaction of
g) The reaction of
Explanation of Solution
a)
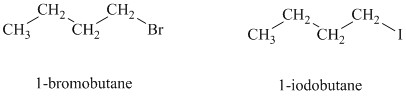
Both the given
b)
Both the given alkyl halides are primary alkyl halides. The reagent is sodium iodide in acetone. Both these suggest an
c)
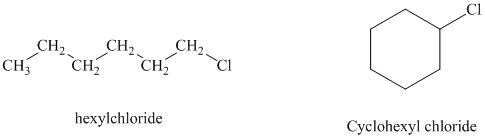
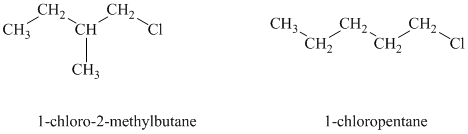
Hexyl chloride is a primary alkyl halide whereas cyclohexyl chloride is a secondary alkyl halide. The solvent is ethanol, which is a polar protic solvent. The nucleophile is the azide ion, which is a good nucleophile. Solvation of the azide ion by ethanol reduces the rate of bimolecular substitution. Polar protic solvents favor
d)

The solvent is ethanol, which is a polar protic solvent. It favors the
e)
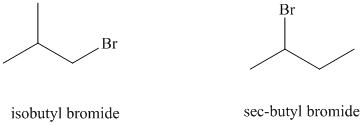
The solvent is aqueous formic acid, which is a polar protic solvent. It favors the
f)
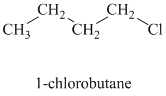
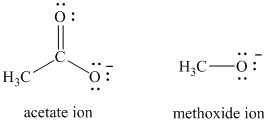
As long as the nucleophilic atom is the same, the more basic the nucleophile, the more reactive it is. The methoxide ion is more basic and more nucleophilic than the acetate ion. Thus, the reaction of
g)
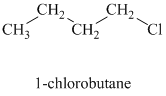
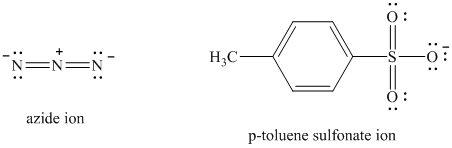
Comparing the nucleophilic atoms, the azide ion is more nucleophilic than the p-toluene sulfonate ion since nitrogen is less electronegative than oxygen. Thus, the reaction of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
ORGANIC CHEMISTRY (LOOSELEAF)-PACKAGE
- For the reaction: CO2(g) + H2(g) --> CO (g) + H2O (g) Kc= 0.64 at 900 degrees celcius. if initially you start with 1.00 atmoshpere of carbon dioxide and 1 atmoshpere of hydrogen gas, what are the equilibrium partial pressuses of all species.arrow_forwardCan I please get this answered? With the correct number of significant digits.arrow_forwardDraw the Hofmann product of the dehydroiodination of this alkyl iodide. ☐ : + Explanation Check esc F1 2 3 I 88 % 5 F5 I. X © tBuOK Click and drag to sta drawing a structure. © 2025 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Te BI BB F6 W E R Y S H Karrow_forward

 Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305580350Author:William H. Brown, Brent L. Iverson, Eric Anslyn, Christopher S. FootePublisher:Cengage Learning

