
a.
Prepare all general journal entries for the given transactions.
a.
Explanation of Solution
Journal:
Journal is the method of recording monetary business transactions in chronological order. It records the debit and credit aspects of each transaction to abide by the double-entry system.
Rules of Debit and Credit:
Following rules are followed for debiting and crediting different accounts while they occur in business transactions:
- Debit, all increase in assets, expenses and dividends, all decrease in liabilities, revenues and stockholders’ equities.
- Credit, all increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equities, all decrease in assets, expenses.
Prepare journal entries:
| Event | Account Titles and Explanation | Debit ($) | Credit($) |
| 1. | Petty Cash | 250 | |
| Cash | 250 | ||
| ( To record the establishment of fund) | |||
| 2. | No Entry | ||
| 3. | Meals Expense | 120 | |
| Postage Expense | 21 | ||
| Delivery Expense | 93 | ||
| Cash Short and Over | 3 | ||
| Cash (1) | 237 | ||
| (To record the recognition of expenses) |
Table (1)
To record the establishment of fund:
- Petty cash is an asset account and it is increased. Therefore debit petty cash fund by $250.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account by $250.
To record the recognition of expenses:
- Meals expense of $120, postage expense of $ 21, Delivery expense of $93, cash short and over of $3 are a component of
stockholders’ equity and it is decreased. Therefore debit it by $ 237. - Cash is an asset and it is decreased. Therefore, credit cash account by $237.
Note:
Working note:
Calculate the amount of cash:
Note: Event 2 (reimbursement of employees) is not affected because, these are the expenses paid by the employer on behalf of the employee and Event 3 (Replenishment of fund) is also not affected by any of the transaction because, it is the constant fund that remains in the petty cash box to meet minor business expenses and it has to be periodically replenished to ensure sufficient availability of fund.
b.
Explain the way in which the cash short and over account will affect the income statement.
b.
Explanation of Solution
The cash short will be stated as miscellaneous expense on the income statement.
c.
Identify the type of event depicted in each journal entry.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Assets exchange transaction:
Transaction that has two asset accounts is called as assets exchange transaction. Assets exchange transaction increases the value of one asset account, and decreases the value of another asset account. The increased asset account is recorded with the debit entry, and decreased asset account is recorded with the credit entry.
Assets use transaction:
Transaction that reduces the value of assets account is called as assets use transaction. Asset use transaction decreases the value of assets account and also decreases the corresponding liabilities and stockholder’s equity account. The decreased asset account is recorded with credit entry.
Three Events are identified as follows:
| Event Number | Type of Event |
| 1. | Asset Exchange Transaction |
| 2. | No Effect |
| 3. | Asset Use Transaction |
Table (2)
- In event number 1, the company established petty cash fund by issuing check of $250. It is an Asset exchange transaction as it decreases the cash (asset account) by $250 and increases the petty cash (asset account) by $ 250. Asset exchange transaction affects only the composition of assets and the total amount of assets remains unaffected.
- In event number 3, Company has recognised expenses by decreasing the cash account. It is an Asset use transaction as it decreases the total amount of assets (cash) by $237 and increases the expenses account by $237.
Note: Event 2 (reimbursement of employees) is not affected because, these are the expenses paid by the employer on behalf of the employee and Event 3(Replenishment of fund) is also not affected by any of the transaction because, it is the constant fund that remains in the petty cash box to meet minor business expenses and it has to be periodically replenished to ensure sufficient availability of fund.
d.
Show the effects of the events on the financial statements and indicate whether item is an operating activity (OA), Investing activity (IA), financing activity (FA) or use NA to show that the account is not affected by the event.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Financial statements:
Financial statements are condensed summary of transactions communicated in the form of reports for the purpose of decision making. The financial statements reports, and shows the financial status of the business. The financial statements consist of the
Three events are recorded as follows:
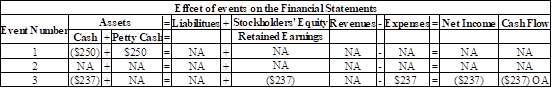
Figure (1)
Note: Event 2 (reimbursement of employees) is not affected because, these are the expenses paid by the employer on behalf of the employee and Event 3 (Replenishment of fund) is not recorded on the financial statements because, it is the constant fund that remains in the petty cash box to meet minor business expenses and it has to be periodically replenished to ensure sufficient availability of fund.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamental Financial Accounting Concepts

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





