
a.
To identify: The factors which affect the cost of money or general level interest rate.
Interest Rate:
A rate at which a borrower is ready to pay and the depositor is ready to receive the money is known as the interest rate.
a.
Answer to Problem 21IC
The factors that affects the general level of interest rate or the cost of money are as follows:
- Production opportunities
- Time preferences
- Risk
- Inflation
Explanation of Solution
- Production opportunities for a company are the main factor, which affects the cost of money as it leads to the higher production.
- The consumption of the product by the customer in the duration of a period, affect the cost of money.
- The concept of higher risk lead to higher return and lower risk leads to lower return mainly affects the interest rate. Hence, is also a factor which affects the interest rate.
- Inflation refers to the rise in price in the market. Due to increase in the price of products the money supply also increase which refers that the inflation is the main factor that affects the cost of money.
Hence, there are various factors such as production opportunities, time preferences, risk and inflation which affect the cost of money and interest rate.
b.
To explain: The real risk-free rate and nominal risk-free rate and their measurement.
b.
Answer to Problem 21IC
Real Risk-Free Rate:
A
The measurement of real risk-free rate is difficult as it is measured withthe help of Treasury bond index.
Nominal Risk-Free Rate:
A combination of real risk-free rate and inflation premium is the nominal risk-free rate.
A formula is used for the measurement of nominal risk-free rate,
Where,
- r is the nominal risk-free rate.
- r* is the real risk-free rate.
- IP is inflation premium.
Explanation of Solution
- The real risk-free rate is the interest rate which is mainly attached to the short-term Treasury securities.
- The real risk-free rate is the rate which is lowest interest rate and is expected by the investors on their investments.
- The real risk-free rate and inflation premium combined are known as nominal risk-free rate. The inflation premium refers the compensation by the issuer for the inflation risk.
Hence, the real risk-free rate is the interest rate which is the at least interest expected by the investors and the nominal risk-free rate is the combination of real risk-free rate and the compensation of inflation risk.
c.
To explain: The inflation premium, default risk premium, liquidity premium and maturity risk premium.
Interest Rate:
A rate at which a borrower is ready to pay and the depositor is ready to receive the money is known as the interest rate.
c.
Answer to Problem 21IC
Inflation Premium:
Inflation refers a financial term which indicates the generally raised price level of goods and services in the market and currency’s decreased level of
Default Risk Premium:
A premium which is paid by the borrower to its lender in the form of compensation of lender’s money in the regards of default risk is known as default risk premium.
Liquidity Premium:
A premium which is paid by the borrower to its lender in the form of compensation of short-term or long-term liquidation of investment is known as maturity risk premium.
Maturity Risk Premium:
A premium which is paid by the borrower to its lender in the form of compensation of interest rate uncertainty in the regards of maturity risk is known as maturity risk premium.
The premium which is required for the calculation of interest rates on:
(1) Short-term U.S. Treasury Securities:
There is no as such risk in U.S. Treasury securities. The interest rate which is offered on the securities is real risk-free rate which is measured with the help of Treasury index.
(2) Long-term U.S. Treasury Securities:
The inflation risk is the main risk which is there on the long-term Treasury securities. The inflation premium is included with the interest rate of long-term Treasury securities.
(3)Short-term Corporate Securities:
The inflation premium, default risk premium and liquidity premiums are included in the interest rates of short-term corporate securities.
(4)Long-term Corporate Securities:
The inflation premium, default risk premium, liquidity premium and maturity risk premium is included in the interest rates of long-term corporate securities.
Explanation of Solution
- The inflation premium is an average inflation over a period of investment and it is connected with the interest rates of Long-term U.S. Treasury securities and both the type of corporate securities as the inflation risk is there with these securities.
- Default risk premium refers the expected default that can happen because of investment. The Treasury securities have no default risk. Hence, the default risk premium is connected with the interest rates of corporate securities.
- The liquidity premium is the premium which refers the conversion of investment into cash at a shorter period. The short-term and long-term corporate securities include the liquidity premium as there is a liquidity risk with it.
- The maturity risk premium was the consideration of price at the time of maturity of the securities. The long-term corporate securities have the maturity risk premium in their interest rates as the maturity payment risk or less payment risk is there.
Hence, the different securities have the different premium requirements according to their risk availability.
d.
To explain: The term structure of interest rate and the yield curve.
Yield:
Yield is the percentage of the securities at which the return is provided by the company to its investors. Yield can be used in the form of dividend and interest.
d.
Answer to Problem 21IC
Term Structure of Interest Rate:
The term structure represents the connection between the interest rates at the different time period.
Yield Curve:
The graphical representation of expected which return, provided by the company to its investors during the years is known as the yield curve.
Explanation of Solution
- The term structure helps in the presentation of the volatility of the curve.
- To make the various investment-related decisions, the term structure of interest rate and yield curve helps.
Hence, the term structure of interest rate and yield curve are the representation of the relationship between the interest rates and term.
e.
To identify: The interest rate of securities: 1-year, 10-year, and 20-year Treasury bond and draw a curve to identify whether it is upward-sloping or not.
e.
Explanation of Solution
The items required for the calculation of interest rates on Treasury bonds are risk-free rate, inflation premium, and market risk premium.
Compute the interest rate on 1-year:
Given,
The real risk-free rate is 3%.
The inflation premium is 5%.
The formula to calculate the interest rate,
- Wherer is the interest rate.
- r* is the real risk-free rate.
- IP is inflation premium.
Substitute 3% for r* 5% for IP.
The interest rate on 1-year Treasury security is 8%.
Compute the interest rate on 10-year:
Given,
The real risk-free rate is 3%.
The average inflation premium is 7.5%.
The maturity risk premium is 0.14%.
The formula to calculate the interest rate,
- Wherer is the interest rate.
- r* is the real risk-free rate.
- IP is inflation premium.
- MRP is maturity risk premium.
Substitute 3% for r*, 7.5% for IP and 0.14 for MRP.
The interest rate on 10-years Treasury security is 10.64%.
Compute the interest rate on 20-year:
Given,
The real risk-free rate is 3%.
The average inflation premium is 7.75%.
The maturity risk premium is 0.26%.
The formula to calculate the interest rate,
Where,
- r is the interest rate.
- r* is the real risk-free rate.
- IP is inflation premium.
- MRP is maturity risk premium.
Substitute 3% for r*, 7.75% for IP and 0.26 for MRP.
The interest rate on 20-years Treasury security is 11.01%.
Working note:
Computation of average inflation premium at 10-year Treasury securities,
The inflation premium is 7.5%.
Compute the maturity risk premium at 10-year Treasury securities.
| Year | Workings |
Maturity Risk Premium (%) |
| 1 | 0 | |
| 2 | 0.10 | |
| 3 |
| 0.11 |
| 4 |
| 0.121 |
| 5 |
| 0.1331 |
| 6 |
| 0.14641 |
| 7 |
| 0.161051 |
| 8 |
| 0.1772 |
| 9 |
| 0.195 |
| 10 |
| 0.2145 |
| Total | 1.358261 | |
| Average Maturity Risk Premium |
| 0.136 or 0.14 |
Table (1)
The average maturity risk premium is 0.14%.
Computation of average inflation premium at 20-year Treasury securities,
The inflation premium is 7.75%.
Compute the maturity risk premium at 20-year treasury securities.
| Year | Workings |
Maturity Risk Premium (%) |
| 1 | 0 | |
| 2 | 0.10 | |
| 3 |
| 0.11 |
| 4 |
| 0.121 |
| 5 |
| 0.1331 |
| 6 |
| 0.14641 |
| 7 |
| 0.161051 |
| 8 |
| 0.1772 |
| 9 |
| 0.195 |
| 10 |
| 0.2145 |
| 11 |
| 0.2359 |
| 12 |
| 0.2595 |
| 13 |
| 0.2855 |
| 14 |
| 0.3141 |
| 15 |
| 0.3456 |
| 16 |
| 0.3801 |
| 17 |
| 0.4182 |
| 18 |
| 0.4600 |
| 19 |
| 0.506 |
| 20 |
| 0.557 |
| Total | 5.120616 | |
| Average Maturity Risk Premium |
| 0.26 |
Table (2)
The average maturity risk premium is 0.26%.
Statement to show the interest rates:
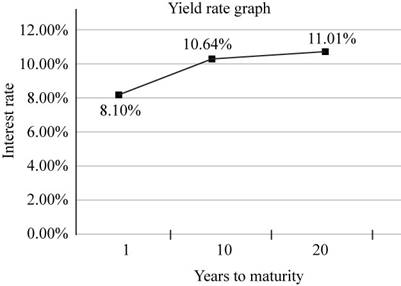
Fig 1
- Thex-axis represents the maturity years.
- They-axis represents the interest rate with the respective maturity years.
- The yield curve is upward sloping.
Hence, the interest rate at 1-year maturity is 8%, at 10-year maturity is 10.64% and at 20-year maturity, 11.01% and the curve which represent with the help of interest rates is upward sloping.
f.
To explain: The performance of U.S. Treasury securities, AAA-rated securities, and BB-rated securities.
f.
Answer to Problem 21IC
Statement to show the interest rates of the securities at a particular maturity,
| Years to Maturity |
U.S. Treasury Yield Rates (%) |
AAA-rated Yield Rates (%) |
BB-rated Yield Rates (%) |
| 1 | 8 | 8.56 | 9.05 |
| 10 | 10.64 | 11.10 | 11.85 |
| 20 | 11.01 | 12.05 | 12.48 |
Table (3)
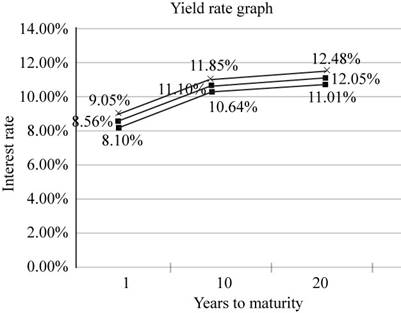
Fig 2
- The lower curve shows the yields of U.S. Treasury securities, middle curve shows the yields of AAA-rated securities and higher curve shows the yields of SS-rated securities.
- The U.S. Treasury curve is the lowest as it doesn’t include the liquidity and default premium.
- AAA-rated securities include a lower rate of liquidity premium and default risk premium.
- BB-rated securities include the higher rate of liquidity premium than AAA-rated securities.
Explanation of Solution
- The interest rate of securities which includes the risk-free rate and inflation premium only is the treasury security bonds.
- The interest rates which includes the risk-free rate, inflation premium, liquidity premium, maturity risk premium and default risk premium has the higher interest rate and the curveis also higher than other securities.
Hence, the U.S. Treasury securities curve is lower, AAA-rated is medium and BB- rated curve is higher.
g.
To describe: The pure expectation theory and its implication in the regards of the term structure.
g.
Answer to Problem 21IC
Expectation Theory: Expectation theory estimates the future interest without taking into consideration of maturity risk.
The maturity risk doesn’t consider in that case. The interest rate on long-term securities is calculated without considering the maturity risk.
Explanation of Solution
- According to the expectation theory, the yield curve of investment totally depends upon the future expectation of investors.
- The short-term securities have not defaulted risk premium and interest on long-term securities is the weighted average of securities.
Hence, the interest is calculated without taking into consideration default risk premium.
h.
To identify: The interest rate on 1-year securities after 1 year and interest rate on 3-year securities after 2 years from now with the use of the geometric average method.
h.
Explanation of Solution
Compute the interest rate on 1-years securities after 1 year.
Given,
The yield for 2 years is 6.20%.
The yield for 1 year is 6%.
The formula to compute the rate,
Substitute 0.062 for yield for year 2, 0.060 for yield for year 1, 1 for a number of years and 1 for years from now.
The rate is 6.40%.
Compute the interest rate on 3-years securities after 2years.
Given,
The yield for 5 years is 6.50%.
The yield for 2years is 6.2%.
The formula to compute the rate,
Substitute 0.065 for yield for year 5, 0.062 for yield for year 2, 3 for a number of years and 2 for years from now.
Simplify the above equation,
The rate is 6.70%.
Hence, the interest rate on1-years securities after 1 year is 6.40% and at 3-years securities after 2 years is 6.70%.
i.
To explain: The effect of macroeconomic factors on interest rate and the reason of securities have the low-interestrate.
i.
Answer to Problem 21IC
- The Federal Reserve policy mainly affects the interest rate on short-term and long-term securities. The federal trade the short-term securities which would result in the increment of the money supply.
- Federal budget deficits and surplus increase the interest rate to balance the budget, the government would issue the investment securities and increase the interest on that and interest rates would increase.
- The corporations require fund for their business and increase the demand for the product. The increase in demand of the product leads to increase in nominal interest rate.
Explanation of Solution
- The increase in money supply results to increase in inflation and high inflation is not good for the economy.
- To attract the outside borrowers it is necessary not to fix the less interest rate which increases the investments.
Hence, the international factors, businesses, Federal Reserve policies and federal budget deficits are the main factors of
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
FUND.OF FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT(LL)FDS
- QUESTION 1 Examine the information provided below and answer the following question. (10 MARKS) The hockey stick model of start-up financing, illustrated by the diagram below, has received a lot of attention in the entrepreneurial finance literature (Cumming & Johan, 2013; Kaplan & Strömberg, 2014; Gompers & Lerner, 2020). The model is often used to describe the typical funding and growth trajectory of many startups. The model emphasizes three main stages, each of which reflects a different phase of growth, risk, and funding expectations. Entrepreneur, 3 F's Debt(banks & microfinance) Research Business angels/Angel Venture funds/Venture capitalists Merger, Acquisition Grants investors PO Public market Growth (revenue) Break even point Pide 1st round Expansion 2nd round 3rd round Research commercial idea Pre-seed Initial concept Seed Early Expansion Financial stage Late IPO Inception and prototype Figure 1. The hockey stick model of start-up financing (Lasrado & Lugmayr, 2013) REQUIRED:…arrow_forwardcritically discuss the hockey stick model of a start-up financing. In your response, explain the model and discibe its three main stages, highlighting the key characteristics of each stage in terms of growth, risk, and funding expectations.arrow_forwardSolve this problem please .arrow_forward
- Take value of 1.01^-36=0.699 . step by steparrow_forwardsolve this question.Pat and Chris have identical interest-bearing bank accounts that pay them $15 interest per year. Pat leaves the $15 in the account each year, while Chris takes the $15 home to a jar and never spends any of it. After five years, who has more money?arrow_forwardWhat is corporate finance? explain all thingsarrow_forward
