
Concept explainers
Explanation of Solution
Database is the organized collection of associated data elements which is used to have the record the things or items of interest.
- It is often defined as the structure to hold the data.
- It contains the elements like schemas, views, tables (which are linked through foreign keys), queries and many other elements.
- Database and database management are interdependent.
Entity:
The basic block for building the data collected about person, place, event, or thing is called as entity.
- Entities denote attributes that can have many instances.
- Entity is about the gathering of the information about the place, person, or thing. For example: a patient, a musician, and so on.
- To locate the information in the entity, they have a name, short description about what they are and identifier.
- Identifiers are used to find each and every specific instance of an entity.
- So, it is the purpose of having identifiers with unique values.
Example:
The example of an entity is given below:
- STUDENT – the student is the person name that collects the details of student information. So the STUDENT acts as the entity.
- EMPLOYEE - the employee is the person name that collects the details of employee information. So the EMPLOYEE acts as the entity.
Attribute:
- The data are organized in tables, which consist of rows and columns is called as attributes.
- A data in a row or column of a table are called fields.
- In a database table, column fields are also referred as attributes of a database object.
- For example: In a customer table, “cust_id”, “cust_name”, “cust_addr” and “mobile_no” are the attributes.
Field:
- Relational database is a database, which organizes data according to the relational model as table and table consists of rows and columns.
- The table is also called data file.
- Group of related row is called record which is also called database object or entity.
- Often, the group of related column is called field.
- Group of records is called table.
Relational database:
- Relational database is a set of multiple data organized by tables, records, and columns and it creates the relationship between the database tables.
- The individual value in table provides the link from one table to another.
Storage of data in relational database:
- Relational database is a database which organizes data according to the relational model as table and table consists of rows and columns.
- A data in a row or column of a table is called fields.
- Fields in a database table are also referred as attributes of a database object.
- Group of related fields is called record which is also called database object or entity.
- Group of records are called table
- Storing data in relational database offers the following advantages:
- The data stored in this can be retrieved quickly and easily by the computer.
- The data stored in relational database can be displayed in any order.
- For example, to get information about songs from a music CD, the information about a particular artist, songs, and song title can be displayed individually in any order.
Role of Entity-relationship diagram in database:
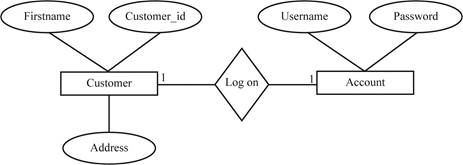
An entity-relationship diagram represents the important elements of database in a graphical form.
- Entity-relationship (ER) diagram is the technique used to design the relational database.
- ER diagram is useful to create the data model, which serves business process. Additionally, the diagram ensures whether data is accurate, well-formed and easy for retrieval.
- An Entity-relationship diagram is represented in the graphical form that shows only important elements such as:
- Record types
- Attributes
- Relationship between entities
- For example, consider the following diagram:
- The rectangular box represents the entities such as Customer and Account.
- The oval symbol represents the attributes such as Firstname, Customer _id, Address, Username and Password.
- The diamond symbol represents the relationship between two entities.
- Here, it shows the one-to-one relationship between the Customer and Account.
- The relationship shows that one customer is allowed to access the one account.
- Here, it shows the one-to-one relationship between the Customer and Account.
Role of normalization in database:
Normalization is a process of dividing the tables by more than one idea into set of tables such that each and every table contains only one idea.
Nature and purpose of normalization process in database:
The nature and purpose of normalization process in database is given below:
- The normalization process helps to minimize the data redundancy and dependency in database.
- It is a method to remove all inconsistencies and bring the database to consistent state.
The normalization process obeys the following rules.
- Select the source of data and transform into an unnormalized table (UNF).
- Convert the unnormalized table into first normal form (1NF).
- Convert the first normal form data into second normal form (2NF).
- Convert the second normal form data into third normal form (3NF).
In some cases, the data in third normal form may be inconsistencies state. For this case, we may perform the following transformations. There are,
- Convert the third normal form data into Boyce-Codd normal form (BCNF).
- Convert the Boyce-Codd normal form data into fourth normal form (4NF).
- Convert fourth normal form data into fifth normal form (5NF).
Non-relational database management system:
- A non-relational database gives a
mechanism for storing and recovery of data that is modeled in means other than the tabular relationships used in relational databases. - The non-relational databases are gradually used in big data and real time web applications.
Difference between relational DBMS and non-relational DBMS:
| Relational DBMS | Non-relational DBMS |
| The relational DBMS works with structured data. | The non-relational DBMS works with semi-structured data. |
| It supports joins. | It does not contain join, so it will work fast. |
| The relationship in RDBMS via constraints. | It supports documents with different fields. |
| It is built-in data integrity. | Huge data stores |
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Essentials of MIS (12th Edition)
- I need help to solve a simple problem using Grover’s algorithm, where the solution is not necessarily known beforehand. The problem is a 2×2 binary sudoku with two rules: • No column may contain the same value twice. • No row may contain the same value twice. Each square in the sudoku is assigned to a variable as follows: We want to design a quantum circuit that outputs a valid solution to this sudoku. While using Grover’s algorithm for this task is not necessarily practical, the goal is to demonstrate how classical decision problems can be converted into oracles for Grover’s algorithm. Turning the Problem into a Circuit To solve this, an oracle needs to be created that helps identify valid solutions. The first step is to construct a classical function within a quantum circuit that checks whether a given state satisfies the sudoku rules. Since we need to check both columns and rows, there are four conditions to verify: v0 ≠ v1 # Check top row v2 ≠ v3 # Check bottom row…arrow_forward1 Vo V₁ V3 V₂ V₂ 2arrow_forward1 Vo V₁ V3 V₂ V₂ 2arrow_forward
- Preparing for a testarrow_forward1 Vo V₁ V3 V₂ V₂ 2arrow_forwardI need help to solve a simple problem using Grover’s algorithm, where the solution is not necessarily known beforehand. The problem is a 2×2 binary sudoku with two rules: • No column may contain the same value twice. • No row may contain the same value twice. Each square in the sudoku is assigned to a variable as follows: We want to design a quantum circuit that outputs a valid solution to this sudoku. While using Grover’s algorithm for this task is not necessarily practical, the goal is to demonstrate how classical decision problems can be converted into oracles for Grover’s algorithm. Turning the Problem into a Circuit To solve this, an oracle needs to be created that helps identify valid solutions. The first step is to construct a classical function within a quantum circuit that checks whether a given state satisfies the sudoku rules. Since we need to check both columns and rows, there are four conditions to verify: v0 ≠ v1 # Check top row v2 ≠ v3 # Check bottom row…arrow_forward
- I need help to solve a simple problem using Grover’s algorithm, where the solution is not necessarily known beforehand. The problem is a 2×2 binary sudoku with two rules: • No column may contain the same value twice. • No row may contain the same value twice. Each square in the sudoku is assigned to a variable as follows: We want to design a quantum circuit that outputs a valid solution to this sudoku. While using Grover’s algorithm for this task is not necessarily practical, the goal is to demonstrate how classical decision problems can be converted into oracles for Grover’s algorithm. Turning the Problem into a Circuit To solve this, an oracle needs to be created that helps identify valid solutions. The first step is to construct a classical function within a quantum circuit that checks whether a given state satisfies the sudoku rules. Since we need to check both columns and rows, there are four conditions to verify: v0 ≠ v1 # Check top row v2 ≠ v3 # Check bottom row…arrow_forwardI need help to solve a simple problem using Grover’s algorithm, where the solution is not necessarily known beforehand. The problem is a 2×2 binary sudoku with two rules: • No column may contain the same value twice. • No row may contain the same value twice. Each square in the sudoku is assigned to a variable as follows: We want to design a quantum circuit that outputs a valid solution to this sudoku. While using Grover’s algorithm for this task is not necessarily practical, the goal is to demonstrate how classical decision problems can be converted into oracles for Grover’s algorithm. Turning the Problem into a Circuit To solve this, an oracle needs to be created that helps identify valid solutions. The first step is to construct a classical function within a quantum circuit that checks whether a given state satisfies the sudoku rules. Since we need to check both columns and rows, there are four conditions to verify: v0 ≠ v1 # Check top row v2 ≠ v3 # Check bottom row…arrow_forwardDon't use ai to answer I will report you answerarrow_forward
- You can use Eclipse later for program verification after submission. 1. Create an abstract Animal class. Then, create a Cat class. Please implement all the methods and inheritance relations in the UML correctly: Animal name: String # Animal (name: String) + getName(): String + setName(name: String): void + toString(): String + makeSound(): void Cat breed : String age: int + Cat(name: String, breed: String, age: int) + getBreed(): String + getAge (): int + toString(): String + makeSound(): void 2. Create a public CatTest class with a main method. In the main method, create one Cat object and print the object using System.out.println(). Then, test makeSound() method. Your printing result must follow the example output: name: Coco, breed: Domestic short-haired, age: 3 Meow Meowarrow_forwardautomata theory can please wright the exact language it know for example say it knows strings start 0 and end with 1 this is as example also as regular expressionarrow_forwardI would like help to resolve the following case, thank youarrow_forward
 Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Database System ConceptsComputer ScienceISBN:9780078022159Author:Abraham Silberschatz Professor, Henry F. Korth, S. SudarshanPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON
Starting Out with Python (4th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780134444321Author:Tony GaddisPublisher:PEARSON Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON
Digital Fundamentals (11th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780132737968Author:Thomas L. FloydPublisher:PEARSON C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON
C How to Program (8th Edition)Computer ScienceISBN:9780133976892Author:Paul J. Deitel, Harvey DeitelPublisher:PEARSON Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Database Systems: Design, Implementation, & Manag...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337627900Author:Carlos Coronel, Steven MorrisPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersComputer ScienceISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





