
In Problems 1–3, set up definite
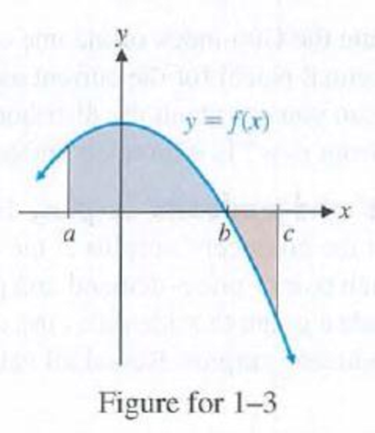
1. Interval [a, b]
The definite integral that represents the indicated shaded area.
Answer to Problem 1RE
The definite integral
Explanation of Solution
Theorem used:
If f and g are continuous and
Calculation:
The given function is
From the given figure, it is observed that the indicated area is bounded by the graph of the function
Also, it is noted that the function
By the above mentioned theorem, the area of the shaded region can be computed by the definite integral
Thus, the definite integral
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Calculus for Business, Economics, Life Sciences, and Social Sciences (14th Edition)
- Find all solutions of cos(x + 1) = cos(x − 1) = Π - - = 1 in the interval [0, 2π). 6arrow_forwardSolve the equation 2 cos 2x + √√3 = 0 for 0 ≤ 0 < 2π.arrow_forwardConsider y (t) — y" (t) − y' (t) + y(t) = 0 (a) Denote new variables x1(t) := y(t), x2(t) := y' (t), x3(t) = y"(t) and solve the following system 0 1 0 x1(t) X' (t) = 0 1 X(t), X(t) = x2(t) -1 1 1 x3(t) = y(t) y' (t) y" (t) (b) Use your solution to the system to find the solution to the original equation (verify!).arrow_forward
 Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Discrete Mathematics and Its Applications ( 8th I...MathISBN:9781259676512Author:Kenneth H RosenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
Mathematics for Elementary Teachers with Activiti...MathISBN:9780134392790Author:Beckmann, SybillaPublisher:PEARSON
 Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Thinking Mathematically (7th Edition)MathISBN:9780134683713Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Discrete Mathematics With ApplicationsMathISBN:9781337694193Author:EPP, Susanna S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Pathways To Math Literacy (looseleaf)MathISBN:9781259985607Author:David Sobecki Professor, Brian A. MercerPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





