
Concept explainers
(a)
To show the difference between the output of the array when it is passed as an array for BUILD-MAX-HEAP and BUILD-MAX-HEAP'.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
Given Information: A heap that has n-elements.
Explanation:
Pseudo code for BUILD-MAX-HEAP is given below:
| BUILD-MAX-HEAP( A ) |
| A.heapsize = A.length |
| for i = A.length/2 downto 1 |
| MAX-HEAPIFY( A,i ) |
Consider an array A= {1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6}. If the above
The for-loop will iterate from 3 to 1.
At i=3 , MAX-HEAPIFY will be called with arguments as array A and i=3 . The following pseudo code for MAX-HEAPIFY is as follows:
| MAX-HEAPIFY( A,i ) |
| l = LEFT( i ) |
| r = RIGHT( i ) |
| ifl <= A.heapsize and A[l]> A[i] |
| largest = l |
| Else |
| largest = i |
| ifr <= A.heapsize and A[r]> A[largest] |
| largest=r |
| iflargest != i |
| exchange A [ i ] with A [ largest ] |
| MAX-HEAPIFY( A,largest ) |
Currently at i=3 , A [3]=3 and have the following tree:
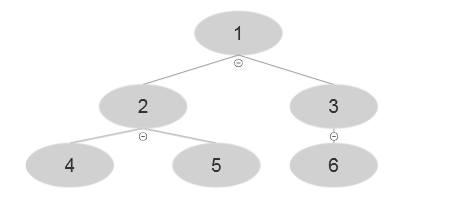
At the end of the iteration:
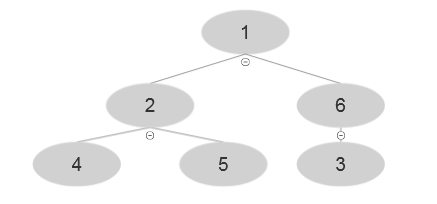
At i=2 , A [2]=2 and after executing the algorithm, the following tree is evolved:
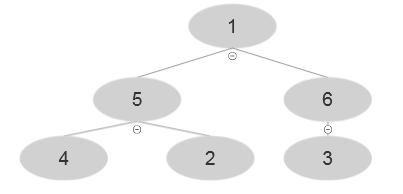
At i=1 , A [1]=1 and after executing the algorithm, the following tree is evolved:
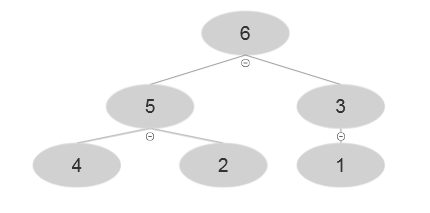
Resultant array after BUILD-MAX-HEAP is A= {6, 5, 3, 4, 2, 1}
However, according to the question, the algorithm for BUILD-MAX-HEAP ', there is an alteration in A.heapsize, which is by default 1. Moreover, the value of i starts from 2 and goes on till A.length that is 6.
At i=2 , A [2]=2. The tree is given below-
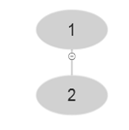
Look at the algorithm of BUILD-MAX-HEAP' . It is using MAX-HEAP-INSERT. So, it becomes-
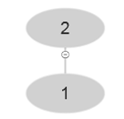
At i=3 , A [3]=3 and after using MAX-HEAP-INSERT
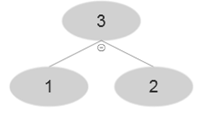
At i=4 , A [4]=4 and after using MAX-HEAP-INSERT
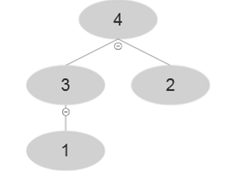
At i=5 , A [5]=5 and after using MAX-HEAP-INSERT
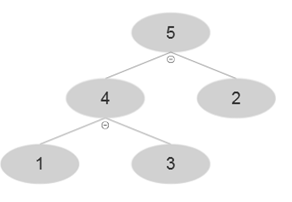
Finally at i=6,A [6]=6 and after using MAX-HEAP-INSERT
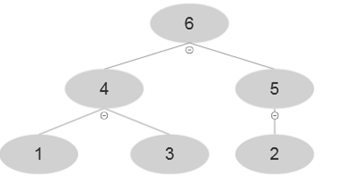
Resultant array after BUILD-MAX-HEAP' is A= {6, 4, 5, 1, 3, 2}
Hence, the resultant array after BUILD-MAX-HEAP and BUILD-MAX-HEAP' is not the same.
(b)
To determine the worst case scenario for BUILD-MAX-HEAP' while entering n-elements.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
The BUILD-MAX-HEAP' has MAX-HEAP-INSERT in it, which has worst case of Θ(log n). The call to this function is done for n-1 times, since it is not considering the parent node here.
The worst case for MAX-HEAP-INSERT happens when an array is sorted in ascending order.
Each insert step takes maximum Θ(log n ) steps, and since it is done for n times, it takes a worst case of Θ(nlog n ). Each iteration in the new block is actually taking more time as the older version as it has more iteration in it. The new block will work in even work in even worse case as it has the usage of other algorithm as well.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Introduction To Algorithms, Third Edition (international Edition)
- Explian this C program code. #include <stdio.h> void binary(unsigned int n) { if (n /2!=0) { binary(n /2); } printf("%d", n %2); } int main() { unsignedint number =33777; unsignedchar character ='X'; printf("Number: %u\n", number); printf("Binary: "); binary(number); printf("\nDecimal: %u\nHexadecimal: 0x%X\n\n", number, number); printf("Character: %c\n", character); printf("ASCII Binary: "); binary(character); printf("\nASCII Decimal: %u\nASCII Hexadecimal: 0x%X\n", character, character); return0; }arrow_forwardDesign a dynamic programming algorithm for the Longest Alternating Subsequence problem described below: Input: A sequence of n integers Output: The length of the longest subsequence where the numbers alternate between being larger and smaller than their predecessor The algorithm must take O(n²) time. You must also write and explain the recurrence. Example 1: Input: [3, 5, 4, 1, 3, 6, 5, 7, 3, 4] Output: 8 ([3, 5, 4, 6, 5, 7, 3, 4]) Example 2: Input: [4,7,2,5,8, 3, 8, 0, 4, 7, 8] Output: 8 ([4, 7, 2, 5, 3, 8, 0,4]) (Take your time with this for the subproblem for this one)arrow_forwardDesign a dynamic programming algorithm for the Coin-change problem described below: Input: An amount of money C and a set of n possible coin values with an unlimited supply of each kind of coin. Output: The smallest number of coins that add up to C exactly, or output that no such set exists. The algorithm must take O(n C) time. You must also write and explain the recurrence. Example 1: Input: C24, Coin values = = [1, 5, 10, 25, 50] Output: 6 (since 24 = 10+ 10+1+1 +1 + 1) Example 2: Input: C = 86, Coin values = [1, 5, 6, 23, 35, 46, 50] Output: 2 (since 86 = 46+35+5)arrow_forward
- Design a dynamic programming algorithm for the Longest Common Subsequence problem de- scribed below Input: Two strings x = x1x2 xm and y = Y1Y2... Yn Output: The length of the longest subsequence that is common to both x and y. . The algorithm must take O(m n) time. You must also write and explain the recurrence. (I want the largest k such that there are 1 ≤ i₁ < ... < ik ≤ m and 1 ≤ j₁ < ... < jk ≤ n such that Xi₁ Xi2 Xik = Yj1Yj2 ··· Yjk) Example 1: Input: x = 'abcdefghijklmnopqrst' and y = 'ygrhnodsh ftw' Output: 6 ('ghnost' is the longest common subsequence to both strings) Example 2: Input: x = 'ahshku' and y = ‘asu' Output: 3 ('asu' is the longest common subsequence to both strings)arrow_forwardDesign a dynamic programming algorithm for the problem described below Input: A list of numbers A = = [a1,..., an]. Output: A contiguous subsequence of numbers with the maximum sum. The algorithm must take O(n) time. You must also write and explain the recurrence. (I am looking for an i ≥ 1 and k ≥ 0 such that a + ai+1 + ···ai+k has the largest possible sum among all possible values for i and k.) Example 1: Input: A[5, 15, -30, 10, -5, 40, 10]. Output: [10, 5, 40, 10] Example 2: Input: A = [7, 5, 7, 4, -20, 6, 9, 3, -4, -8, 4] Output: [6,9,3]arrow_forwardDesign a dynamic programming algorithm for the Longest Increasing Subsequence problem described below: Input: A sequence of n integers Output: The length of the longest increasing subsequence among these integers. The algorithm must take O(n²) time. You must also write and explain the recurrence. Example 1: Input: [5, 3, 6, 8, 4, 6, 2, 7, 9, 5] Output: 5 ([3, 4, 6, 7, 9]) Example 2: Input: [12, 42, 66, 73, 234, 7, 543, 16] Output: 6 ([42, 66, 73, 234, 543])arrow_forward
- Design a dynamic programming algorithm for the Subset Sum problem described below: Input: A set of n integers A and an integer s Output: A subset of A whose numbers add up to s, or that no such set exists. The algorithm must take O(n·s) time. You must also write and explain the recurrence. Example 1: Input: A = {4, 7, 5, 2, 3}, s = 12 Output: {7,2,3} Example 2: Input: A{4, 7, 5,3}, s = 6 Output: 'no such subset'arrow_forwardTECNOLOGIE DEL WEB 2023/2023 (VER 1.1) Prof. Alfonso Pierantonio 1. Project Requirements The project consists in designing and implementing a Web application according to the methodology and the technologies illustrated and developed during the course. This document describe cross-cutting requirements the application must satisfy. The application must be realized with a combination of the following technologies: PHP MySQL HTML/CSS JavaScript, jQuery, etc templating The requirements are 2. Project size The application must have at least 18 SQL tables The number of SQL tables refers to the overall number of tables (including relation normalizations). 3. Methodology The application must be realized by adopting separation of logics, session management, and generic user management (authentication/permissions). Missing one of the above might correspond to a non sufficient score for the project. More in details: 3.1 Separation of Logics The separation of logics has to be realizse by using…arrow_forwardWrite a C program to calculate the function sin(x) or cos(x) using a Taylor series expansion around the point 0. In other words, you will program the sine or cosine function yourself, without using any existing solution. You can enter the angles in degrees or radians. The program must work for any input, e.g. -4500° or +8649°. The function will have two arguments: float sinus(float radians, float epsilon); For your own implementation, use one of the following relations (you only need to program either sine or cosine, you don't need both): Tip 1: Of course, you cannot calculate the sum of an infinite series indefinitely. You can see (if not, look in the program) that the terms keep getting smaller, so there will definitely be a situation where adding another term will not change the result in any way (see problem 1.3 – machine epsilon). However, you can end the calculation even earlier – when the result changes by less than epsilon (a pre-specified, sufficiently small number, e.g.…arrow_forward
- Write a C program that counts the number of ones (set bits) in the binary representation of a given number. Example:Input: 13 (binary 1101)Output: 3 unitsarrow_forwardI need help to resolve or draw the diagrams. thank youarrow_forwardYou were requested to design IP addresses for the following network using the addressblock 166.118.10.0/8, connected to Internet with interface 168.118.40.17 served by the serviceprovider with router 168.118.40.1/20.a) Specify an address and net mask for each network and router interface in the table provided. b) Give the routing table at Router 1.c) How will Router 1 route the packets with destinationi) 168.118.10.5ii) 168.118.10.103iii) 168.119.10.31iii) 168.118.10.153arrow_forward
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr- Programming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
 New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning Operations Research : Applications and AlgorithmsComputer ScienceISBN:9780534380588Author:Wayne L. WinstonPublisher:Brooks Cole
Operations Research : Applications and AlgorithmsComputer ScienceISBN:9780534380588Author:Wayne L. WinstonPublisher:Brooks Cole





