
Concept explainers
The
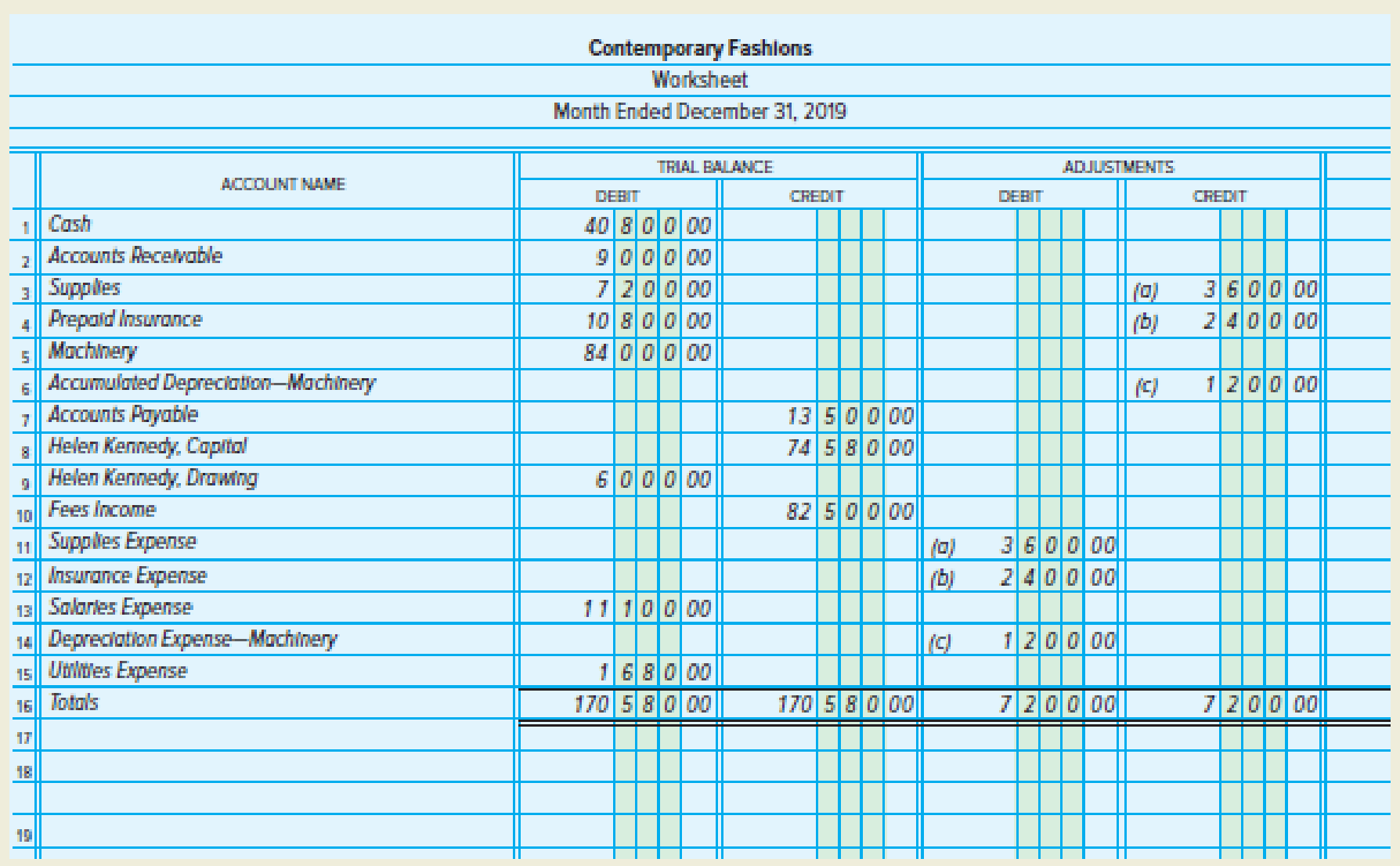
ADJUSTMENTS
- a. Supplies used, $3,600
- b. Expired insurance, $2,400
- c.
Depreciation expense for machinery, $1,200
INSTRUCTIONS
- 1. Complete the worksheet.
- 2. Prepare an income statement.
- 3. Prepare a statement of owner’s equity.
- 4. Prepare a
balance sheet . - 5. Journalize the
adjusting entries in the general journal, page 3. - 6. Journalize the closing entries in the general journal, page 4.
- 7. Prepare a postclosing trial balance.
Analyze: If the adjusting entry for expired insurance had been recorded in error as a credit to Insurance Expense and a debit to Prepaid Insurance for $2,400, what reported net income would have resulted?
1.
Complete the worksheet for C Fashions for the month ended December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Worksheet: Worksheet is an accounting tool that helps accountants to record adjustments and up-date balances required to prepare financial statements. Worksheet is a central place where trial balance, adjustments, adjusted trial balance, income statement, and balance sheet are presented.
Complete the worksheet for C Fashions for the month ended December 31, 2019.
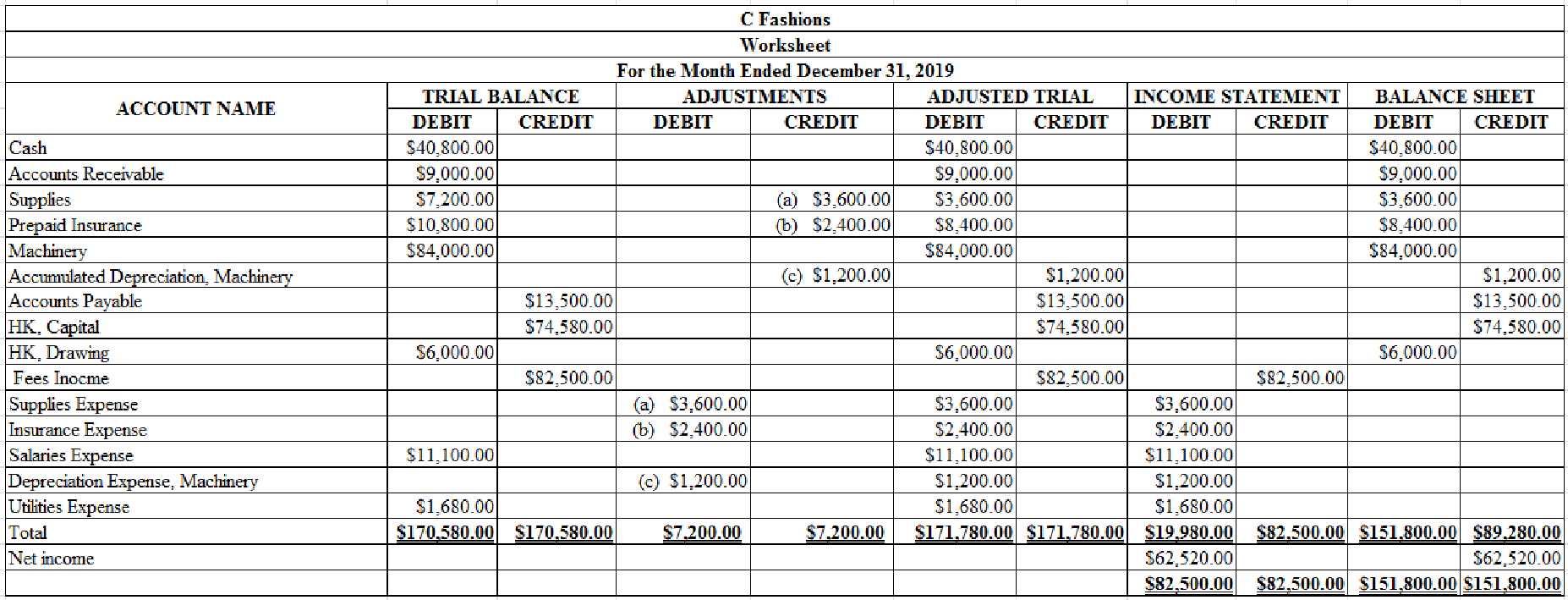
Table (1)
2.
Prepare income statement for C Fashions for the month of December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operation and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare an income statement for C Fashions for the month ended December 31, 2019.
| C Fashions | ||
| Income Statement | ||
| For the Month Ended December 31, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Revenues: | ||
| Fees Income | 82,500 | |
| Expenses: | ||
| Supplies Expense | 3,600 | |
| Insurance Expense | 2,400 | |
| Salaries Expense | 11,100 | |
| Depreciation Expense, Machinery | 1,200 | |
| Utilities Expense | 1,680 | |
| Total expenses | 19,980 | |
| Net income | $62,520 | |
Table (2)
3.
Prepare statement of owners’ equity for C Fashions for the month of December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Statement of owners’ equity: This statement reports the beginning owner’s equity and all the changes which led to ending owners’ equity. Additional capital, net income from income statement is added to, and drawings are deducted from beginning owner’s equity to arrive at the end result, ending owner’s equity.
Prepare a statement of owners’ equity for C Fashions for the month ended December 31, 2019.
| C Fashions | ||
| Statement of Owners’ Equity | ||
| For the Month Ended December 31, 2019 | ||
| Particulars | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| HK, Capital, December 1, 2019 | $74,580 | |
| Net income for December | 62,520 | |
| Less: Withdrawals for December | 6,000 | |
| Increase in capital | 56,520 | |
| HK, Capital, December 31, 2019 | $131,100 | |
Table (3)
4.
Prepare balance sheet for C Fashions for the month of December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Balance sheet: This financial statement reports a company’s resources (assets) and claims of creditors (liabilities) and owners (owners’ equity) over those resources. The resources of the company are assets which include money contributed by owners and creditors. Hence, the main elements of the balance sheet are assets, liabilities, and owners’ equity.
Prepare the balance sheet for C Fashions as at December 31, 2019.
| C Fashions | ||
| Balance Sheet | ||
| December 31, 2019 | ||
| Assets | Amount ($) | Amount ($) |
| Cash | $40,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 9,000 | |
| Supplies | 3,600 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 8,400 | |
| Machinery | $84,000 | |
| Less: Accumulated Depreciation | 1,200 | 82,800 |
| Total Assets | $144,600 | |
| Liabilities and owner’s equity | ||
| Liabilities | ||
| Accounts Payable | 13,500 | |
| Owners’ Equity | ||
| HK, Capital | 131,100 | |
| Total Liabilities and Owners’ Equity | $144,600 | |
Table (4)
5.
Prepare adjusting entry for the given transactions in general ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and balance sheet accounts (assets, liabilities, and owners’ or stockholders’ equity) to maintain the records according to accrual basis principle and matching concept.
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
Prepare adjusting entry for supplies.
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 3 | |||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2019 | Supplies expense | 3,600 | ||
| Supplies | 3,600 | |||
| (To record supplies used) | ||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Supplies Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Supplies are an asset account. Since amount of supplies is used, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare adjusting entry for insurance expense:
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 3 | |||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2019 | Insurance expense | 2,400 | ||
| Prepaid Insurance | 2,400 | |||
| (To record part of prepaid insurance expired) | ||||
Table (6)
Description:
- Insurance Expense is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Prepaid Insurance is an asset account. Since amount of insurance is expired, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
Prepare adjusting entry for depreciation expense-Machinery:
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 3 | |||
| Date | Account Title and Explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| December 31, 2019 | Depreciation expense-Machinery | 1,200 | ||
| Accumulated depreciation-Machinery | 1,200 | |||
| (To record depreciation expense) | ||||
Table (7)
Description:
- Depreciation Expense, Machinery is an expense account. Since expenses decrease equity, equity value is decreased, and a decrease in equity is debited.
- Accumulated Depreciation, Machinery is a contra-asset account, and contra-asset accounts would have a normal credit balance, hence, the account is credited.
6.
Prepare closing entries for the given transactions in general ledger.
Explanation of Solution
Closing entries: The journal entries prepared to close the temporary accounts to capital account are referred to as closing entries. The revenue, expense, and drawing accounts are referred to as temporary accounts because the information and figures in these accounts is held temporarily and consequently transferred to permanent account at the end of accounting year.
Steps in closing procedure:
- 1. Close the revenue accounts to Income Summary account.
- 2. Close the expense accounts to Income Summary account.
- 3. Close the Income Summary account and transfer the net income or net loss balance to the Capital account.
- 4. Close the Drawing account to Capital account.
Close the revenue accounts to Income Summary account.
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 4 | |||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2019 | Fees Income | 82,500 | ||||
| December | 31 | Income Summary | 82,500 | |||
| (Record closing of revenue to Income Summary account) | ||||||
Table (8)
Description:
- Fees income is a revenue account. Revenue account has a normal credit balance. Since revenue is closed to Income Summary account, the account is debited.
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is credited to hold the transferred balance from revenue account.
Close the expense accounts to Income Summary account.
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 4 | |||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2019 | Income Summary | 19,980 | ||||
| December | 31 | Supplies Expense | 3,600 | |||
| Insurance Expense | 2,400 | |||||
| Salaries Expense | 11,100 | |||||
| Depreciation Expense, Machinery | 1,200 | |||||
| Utilities Expense | 1,680 | |||||
| (Record closing of expenses to Income Summary account) | ||||||
Table (9)
Description:
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. The account is debited to hold the transferred balance from expense accounts.
- Supplies Expense, Insurance Expense, Salaries Expense, Depreciation Expense, and Utilities Expense are expense accounts. Expense account has a normal debit balance. Since expenses are closed to Income Summary account, the accounts are credited.
Close the net income to Income Summary account.
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 4 | |||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2019 | Income Summary | 62,520 | ||||
| December | 31 | HK, Capital | 62,520 | |||
| (Record closing of net income to capital account) | ||||||
Table (10)
Description:
- Income Summary is a clearing account which closes revenue, expense, drawings, and net of revenues and expenses to capital accounts. Since net income is closed, the account is reversed; hence, the Income Summary account is debited.
- HK, Capital is a capital account. Since net income is transferred to the account, the value increased, and an increase in capital is credited.
Working Note 1:
Compute net income.
Close the Drawing account to Capital account.
| GENERAL JOURNAL | Page 4 | |||||
| Date | Account Titles and Explanations | Post. Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| 2019 | HK, Capital | 6,000 | ||||
| December | 31 | HK, Drawing | 6,000 | |||
| (Record closing of drawing to capital account) | ||||||
Table (11)
Description:
- HK, Capital is a capital account. Since drawings are transferred to the account, the value decreased, and a decrease in capital is debited.
- HK, Drawing is a capital account. Since drawings are transferred, the account is credited to reverse the previously debited effect.
7.
Prepare a post-closing trial balance for C Fashions at December 31, 2019.
Explanation of Solution
Post-closing trial balance: Post-closing trial balance is a summary of all the assets, liabilities, and capital accounts and their balances, after the closing entries are prepared. So, post-closing trial balance reports the balances of permanent accounts only.
Prepare a post-closing trial balance for C Fashions at December 31, 2019.
|
C Fashions Post- closing Trial Balance December 31, 2019 | ||
| Account Title |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| Cash | 40,800 | |
| Accounts Receivable | 9,000 | |
| Supplies | 3,600 | |
| Prepaid Insurance | 8,400 | |
| Machinery | 84,000 | |
| Accumulated Depreciation | 1,200 | |
| Accounts Payable | 13,500 | |
| HK, Capital | 131,100 | |
| Total | 145,800 | 145,800 |
Table (12)
Analyze: If expired insurance is wrongly adjusted as a credit to insurance expense and a debit to prepaid insurance for $2,400, then the net income would be increased by $4,800. The amount of net income would be reported as $67,320
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
LooseLeaf for College Accounting: A Contemporary Approach
- Ans plzarrow_forwardPROBLEM A Sabio, as her original investment in the firm of Sabio and Mariano, contributed equipment that had been recorded in the books of her own business as costing P900,000, with accumulated depreciation of P620,000. The partners agreed on a valuation of P400,000. They also agreed to accept Sabio's accounts receivable of P360,000, realizable or collectible to the extent of 85%. Required: 1. Prepare the journal entry: a. To adjust Sabio's assets b. To close Sabio's books c. To record Sabio's investment to the partnership PROBLEM B On March 1, 2025, Gogola and Paglinawan formed a partnership. Gogola contributed cash of P1,260,000 and computer equipment that cost P540,000. The fair value of the computer is P360,000. Gogola has notes payable on the computer of P120,000 to be assumed by the partnership. Gogola is to have 60% capital interest in the partnership. Paglinawan contributed cash amounting to P900,000. The partners agreed to share profit and loss equally. Required: 1. Prepare…arrow_forwardYork Manufacturing uses a standard cost system. • • Standard direct labor requirement: 1.8 direct labor hours per unit Standard labor rate: $12 per hour Actual production: 15,000 units during the year Direct labor costs incurred: $322,200 for 28,600 hours Compute the Direct Labor Efficiency Variance.arrow_forward
- Hello tutor solve this question accountingarrow_forwardGeM Industries' common stock is currently selling for $72.15 per share. Last year, the company paid dividends of $1.25 per share. The projected growth rate of dividends for this stock is 4.85%. What rate of return does an investor expect to receive on this stock if it is purchased today?arrow_forwardRight Answerarrow_forward
- What is the company's plantwide overhead ratearrow_forwardI want to correct answer general accounting questionarrow_forwardSwift Manufacturing has the following financial ratios: . Tax Burden Ratio: 0.75 Leverage Ratio: 1.8 . Interest Burden: 0.65 Return on Sales: 12% . Asset Turnover: 2.8 Required: What is the company's Return on Equity (ROE)?arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
 Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781337280570Author:Scott, Cathy J.Publisher:South-Western College Pub  Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage LearningCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage





