
Concept explainers
The Number of Ending Inventory Units.
Explanation of Solution
The ending Inventory units is a difference between units of goods available for sale and units sold and has been computed as under:
| Ending Inventory Units: | |
| | UNITS |
| Units available for sale | 820 |
| Less: Units sold | |
| Mar-9 Sales | 420 |
| Mar-29 Sales | 160 |
| Ending Inventory Units: | 240 |
Requirement 3-a:
First in First Out:
The first in first out method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that are entered first in the store room shall be issued first for sale and hence the cost shall be recorded at its initial prices of goods entered in store room. The perpetual Inventory system means the records are maintained on a continuous basis.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under FIFO.
Explanation of Solution
The FIFO method of perpetual inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of oldest material lies in the store on that particular date.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERPETUAL FIFO METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| 1-Mar | | | | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| 5-Mar | 400 | 55 | 22000 | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| | | | | | | | 400 | 55 | 22000 |
| 9-Mar | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 | | | |
| | | | | 320 | 55 | 17600 | 80 | 55 | 4400 |
| 18-Mar | 120 | 60 | 7200 | | | | 80 | 55 | 4400 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| 25-Mar | 200 | 62 | 12400 | | | | 80 | 55 | 4400 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| | | | | | | | 200 | 62 | 12400 |
| 29-Mar | | | | 80 | 55 | 4400 | 40 | 60 | 2400 |
| | | | | 80 | 60 | 4800 | 200 | 62 | 12400 |
| TOTAL | 720 | | 41600 | 580 | | 31800 | 240 | | 14800 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 240 units of $14800.
Requirement 3-b:
Last in First Out:
The Last in first out method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that are entered recently in the store room shall be issued first for sale and hence the cost shall be recorded at its recent prices of goods entered in store room. The perpetual Inventory system means the records are maintained on a continuous basis.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under LIFO.
Explanation of Solution
The LIFO method of perpetual inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of newest material lies in the store on that particular date.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERPETUAL LIFO METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| 1-Mar | | | | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| 5-Mar | 400 | 55 | 22000 | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| | | | | | | | 400 | 55 | 22000 |
| 9-Mar | | | | 400 | 55 | 22000 | | | |
| | | | | 20 | 50 | 1000 | 80 | 50 | 4000 |
| 18-Mar | 120 | 60 | 7200 | | | | 80 | 50 | 4000 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| 25-Mar | 200 | 62 | 12400 | | | | 80 | 50 | 4000 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| | | | | | | | 200 | 62 | 12400 |
| 29-Mar | | | | 160 | 62 | 9920 | 80 | 50 | 4000 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| | | | | | | | 40 | 62 | 2480 |
| TOTAL | 720 | | 41600 | 580 | | 32920 | 240 | | 13680 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 240 units of $13680.
Requirement 3-c:
Weighted Average:
The Weighted Average method of issuing inventory is based on principle that the goods shall be issued at a average of prices of goods which are lying in the store room at the time of issuing for sale. The perpetual Inventory system means the records are maintained on a continuous basis.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under Weighted average.
Explanation of Solution
The Weighted Average method of perpetual inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of average cost of material lies in the store on that particular date.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERPETUAL WEIGHTED AVERAGE METHOD | |||||||||
| RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | |||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| 1-Mar | | | | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| 5-Mar | 400 | 55 | 22000 | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| | | | | | | | 400 | 55 | 22000 |
| Average | | | | | | | 500 | 54 | 27000 |
| 9-Mar | | | | 420 | 54 | 22680 | 80 | 54 | 4320 |
| 18-Mar | 120 | 60 | 7200 | | | | 80 | 54 | 4320 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| 25-Mar | 200 | 62 | 12400 | | | | 80 | 54 | 4320 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| | | | | | | | 200 | 62 | 12400 |
| Average | | | | | | | 400 | 59.8 | 23920 |
| 29-Mar | | | | 160 | 59.8 | 9568 | 240 | 59.8 | 14352 |
| TOTAL | 720 | | 41600 | 580 | | 32248 | 240 | 59.8 | 14352 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 240 units of $14,352.
Requirement 3-d:
Specific Identification:
Specific Identification method of assigning the cost to goods sold is based on the principle that the goods that have been issued for sale has been specifically identified to be issued from the particular lot of material. Therefore, the cost of that particular lot shall be assigned on the same. The perpetual Inventory system means the records are maintained on a continuous basis.
The Cost assigned to ending Inventory under Specific Identification.
Explanation of Solution
The Specific Identification method of perpetual inventory suggests that the goods issued for sale on a particular date shall be assigned cost on the basis of cost of material specifically identified as issued from the store on that particular date.
The Ending Inventory shall be computed as under:
| STATEMENT SHOWING INVENTORY RECORD UNDER PERPETUAL SPECIFIC IDENTIFICATION METHOD | |||||||||
| | RECIEPTS | COST OF GOODS SOLD | BALANCE | ||||||
| DATE | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ | UNITS | RATE | AMOUNT $ |
| 1-Mar | | | | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| 5-Mar | 400 | 55 | 22000 | | | | 100 | 50 | 5000 |
| | | | | | | | 400 | 55 | 22000 |
| 9-Mar | | | | 80 | 50 | 4000 | 20 | 50 | 1000 |
| | | | | 340 | 55 | 18700 | 60 | 55 | 3300 |
| 18-Mar | 120 | 60 | 7200 | | | | 20 | 50 | 1000 |
| | | | | | | | 60 | 55 | 3300 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| 25-Mar | 200 | 62 | 12400 | | | | 20 | 50 | 1000 |
| | | | | | | | 60 | 55 | 3300 |
| | | | | | | | 120 | 60 | 7200 |
| | | | | | | | 200 | 62 | 12400 |
| 29-Mar | | | | 40 | 60 | 2400 | 20 | 50 | 1000 |
| | | | | 120 | 62 | 7440 | 60 | 55 | 3300 |
| | | | | | | | 80 | 60 | 4800 |
| | | | | | | | 80 | 62 | 4960 |
| TOTAL | 720 | | 41600 | 580 | | 32540 | 240 | | 14060 |
Therefore, Ending Inventory is 240 units of $14060.
Requirement 4:
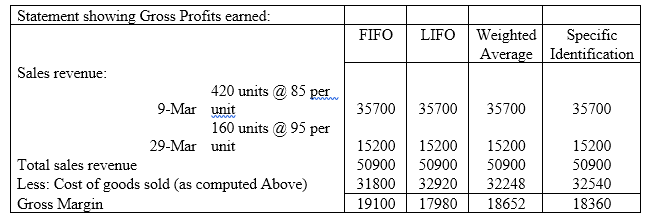
Gross Profits:
Gross Profits means excess of sales revenue over the cost of goods sold.
Gross profits earned by the company under various methods.
Explanation of Solution
The Gross profits is computed as a difference between the sales revenue and cost of goods sold as assigned under various methods and has been computed as under:
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamental Accounting Principles
- What is the return on assets (ROA)? Accounting questionarrow_forwardCan you help me find the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem using valid principles?arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this financial accounting question with accurate financial calculations.arrow_forward
- Please provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forwardI need the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using the standard accounting approach.arrow_forwardwhat is the after-tax income from this increase in sales? accounting questionarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





