
Interpretation:
An energy diagram for the molecular orbitals of period 2 diatomic molecules should be drawn and the difference in ordering for B2, C2 and N2 should be compared to O2, F2 and Ne2.
Concept introduction:
MOT is more accurate theory than
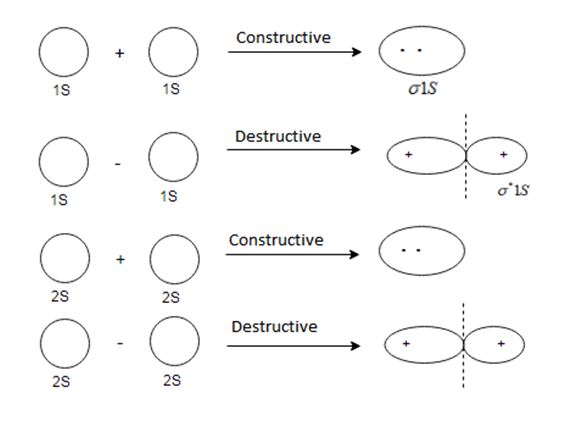
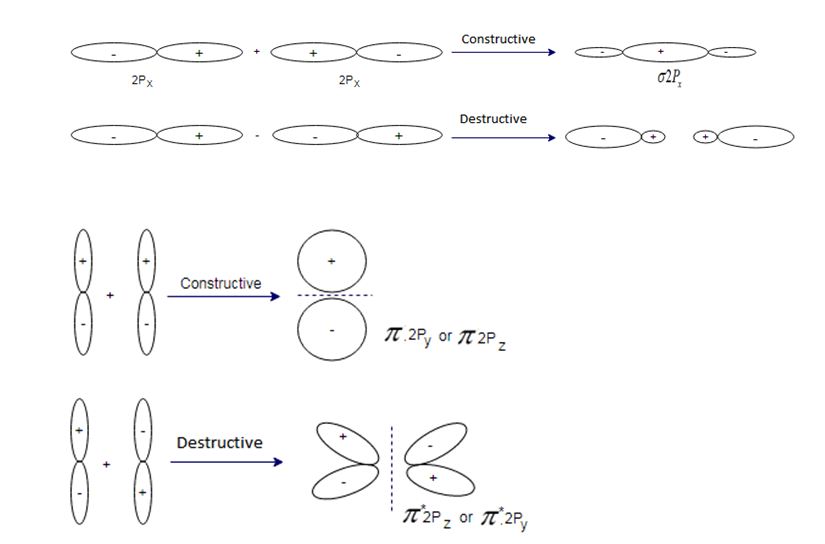
(i) The molecular orbitals are formed by the linear combination of atomic orbitals. There are two type of combination (a) constructive (b) destructive interference
(ii)Molecular orbitals formed by constructive interference is known as bonding molecular orbital, and its energy is less than atomic orbital
(iii) Molecular orbital formed by destructive interference is known as anti bonding molecular orbital and its energy is greater than atomic orbital.
(iv) Electrons in molecular orbitals are filled according to Aufbau’s rule, Pauli’s Exclusion Principle, and Hund’s rule.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 6 Solutions
Mastering Chemistry with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
- When two solutions, one of 0.1 M KCl (I) and the other of 0.1 M MCl (II), are brought into contact by a membrane. The cation M cannot cross the membrane. At equilibrium, x moles of K+ will have passed from solution (I) to (II). To maintain the neutrality of the two solutions, x moles of Cl- will also have to pass from I to II. Explain this equality: (0.1 - x)/x = (0.1 + x)/(0.1 - x)arrow_forwardCalculate the variation in the potential of the Pt/MnO4-, Mn2+ pair with pH, indicating the value of the standard potential. Data: E0 = 1.12.arrow_forwardGiven the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt. Calculate the emf of the cell as a function of pH.arrow_forward
- The decimolar calomel electrode has a potential of 0.3335 V at 25°C compared to the standard hydrogen electrode. If the standard reduction potential of Hg22+ is 0.7973 V and the solubility product of Hg2Cl2 is 1.2x 10-18, find the activity of the chlorine ion at this electrode.Data: R = 8.314 J K-1 mol-1, F = 96485 C mol-1, T = 298.15 K.arrow_forward2. Add the following group of numbers using the correct number of significant figures for the answer. Show work to earn full credit such as rounding off the answer to the correct number of significant figures. Replace the question marks with the calculated answers or write the calculated answers near the question marks. 10916.345 37.40832 5.4043 3.94 + 0.0426 ? (7 significant figures)arrow_forwardThe emf at 25°C of the cell: Pt l H2(g) l dis X:KCl (sat) l Hg2Cl2(s) l Hg l Pt was 612 mV. When solution X was replaced by normal phosphate buffer solution with a pH of 6.86, the emf was 741 mV. Calculate the pH of solution X.arrow_forward
- Indicate how to calculate the potential E of the reaction Hg2Cl2(s) + 2e ⇄ 2Hg + 2Cl- as a function of the concentration of Cl- ions. Data: the solubility product of Hg2Cl2.arrow_forwardHow can Beer’s Law be used to determine the concentration in a selected food sample. Provide an in-depth discussion and examples of this.arrow_forwardb) H3C- H3C Me CH 3 I HN Me H+arrow_forward
- Using Luther's rule, determine the reference potentials of the electrodes corresponding to the low stability systems Co³+/Co and Cr²+/Cr from the data in the table. Electrodo ΕΝ Co²+/Co Co3+/Co²+ -0,28 +1,808 Cr³+ / Cr -0,508 Cr3+ / Cr²+ -0,41arrow_forwardThe molecule PYRIDINE, 6tt electrons and is there pore aromuntre and is Assigned the Following structure contenus Since aromatk moleculey undergo electrophilic allomatic substitution, Pyridine should undergo The Following reaction + HNO3 12504 a. write all of the possible Mononitration Products that could Result From this roaction Based upon the reaction the reaction mechanism determine which of these producty would be the major Product of the hegetionarrow_forwardUsing Benzene as starting materia Show how each of the Following molecules could Ve synthesked 9. CHI d. 10450 b 0 -50311 ८ City -5034 1-0-650 e NO2arrow_forward
 Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax
Chemistry by OpenStax (2015-05-04)ChemistryISBN:9781938168390Author:Klaus Theopold, Richard H Langley, Paul Flowers, William R. Robinson, Mark BlaserPublisher:OpenStax General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning





