
Concept explainers
a.
To identify: The interest on Treasury securities, and yield curve.
Yield:
Yield is the percentage of securities at which the return is provided by the company to its investors. Yield can be there in the form of dividend and interest.
Yield Curve:
The graphical representation of the expected return, provided by the company to its investors during the years is known as the yield curve.
a.
Answer to Problem 18P
The items required for the calculation of interest rate are the real risk-free rate, inflation rate, and maturity risk premium.
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The risk free rate is 2% or 0.02.
Inflation rate for the first year is 7% or 0.07.
The inflation rate of second year is 5% or 0.05.
The inflation rate after two years is 3% or 0.03.
The maturity risk premium for the first year is 0.2% or 0.002 and it will increase by 0.2% every year till 1%.
Formula to calculate the interest rate,
Where,
- r is the corporate bond yield.
- r* is the risk free rate.
- IP is the inflation premium.
- MRP is the maturity risk premium.
Statement to show the calculation of interest rate
| Maturity |
Real Risk-Free Rate (%) (r*) |
Inflation Rate (%) (IP) |
Maturity Risk Premium (MRP) |
Interest Rate on Treasury Bond
|
| 1 | 2 | 7 | 0.2 | 9.20 |
| 2 | 2 | 5 | 0.4 | 7.40 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 0.6 | 5.60 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 0.8 | 5.80 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 |
| 10 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 |
| 20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 |
Table (1)
The yield curve of the given data
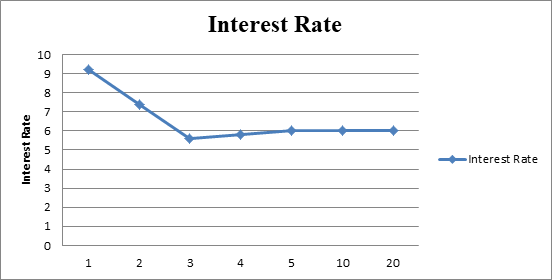
Fig 1
- The x-axis represents the maturity.
- The y-axis represents the interest rate.
- The interest rates with their respective time period can be shown from the graph.
Hence, the interest of 1-year treasury securities is 9.20%, at 2-year treasury securities is 7.60%, 3-year treasury securities is 5.60%, 4-year treasury securities is 5.80% and thereafter is 6%.
b.
To identify: The interest rate on AAA rated securities, and the yield curve.
b.
Answer to Problem 18P
The items required for the calculation of interest rate are real risk-free rate, inflation rate, and maturity risk premium.
Explanation of Solution
Explanation:
Given,
The risk free rate is 2% or 0.02.
Inflation rate for the first year is 7% or 0.07.
The inflation rate of second year is 5% or 0.05.
The inflation rate after two years is 3% or 0.03.
The maturity risk premium for the first year is 0.2% or 0.002 and it will increase by 0.2% every year till 1%.
The default risk premium is 1% which increases
Formula to calculate the interest rate,
Where,
- r is the corporate bond yield.
- r* is the risk free rate.
- IP is the inflation premium.
- MRP is the maturity risk premium.
- DRP is the default risk premium.
Statement to show the calculation of interest rate
| Maturity |
Real Risk-Free Rate (%) (r*) |
Inflation Rate on Treasury Bond (%) (IP) |
Maturity Risk Premium (%) (MRP) |
Interest Rate on Treasury Bond
|
Default Risk Premium (%) (DRP) |
Interest Rate on AAA rated Bonds
|
| 1 | 2 | 7 | 0.2 | 9.20 | 1 | 10.20 |
| 2 | 2 | 5 | 0.4 | 7.40 | 2 | 9.40 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 0.6 | 5.60 | 2 | 7.60 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 0.8 | 5.80 | 3 | 8.80 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 4 | 10 |
| 10 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 11 |
| 20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 5 | 11 |
Table (2)
The yield curve of the given data
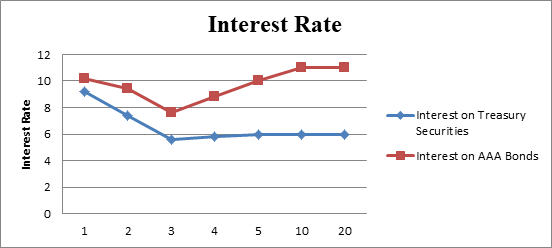
Fig 2
- The x-axis represents the maturity.
- The y-axis represents the interest rate.
- The interest rates of treasury securities and AAA bonds with their respective time period can be shown from the graph.
Hence, the interest of 1-year AAA bond is 10.20%, at 2-year AAA bond is 9.40%, 3-year AAA bond is 7.60%, 4-year AAA bond is 8.80% 5-year AAA bond is 10% and thereafter it is 11%.
c.
To identify: The interest rate on lower rated bonds, and the yield curve.
c.
Answer to Problem 18P
The items required for the calculation of interest rate are the inflation rate, real risk-free rate, and maturity risk premium.
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The risk free rate is 2% or 0.02.
Inflation rate for the first year is 7% or 0.07.
The inflation rate of second year is 5% or 0.05.
The inflation rate after two years is 3% or 0.03.
The maturity risk premium for the first year is 0.2% or 0.002 and it will increase by 0.2% every year till 1%.
The default risk premium is 1% which increases
Formula to calculate the interest rate,
Where,
- r is the corporate bond yield.
- r* is the risk free rate.
- IP is the inflation premium.
- MRP is the maturity risk premium.
- DRP is the default risk premium.
Statement to show the calculation of interest rate on AAA rated bonds
| Maturity |
Real Risk-Free Rate (%) (r*) |
Inflation Rate on Treasury Bond (%) (IP) |
Maturity Risk Premium (%) (MRP) |
Default Risk Premium (%) (DRP) |
Interest Rate
|
| 1 | 2 | 7 | 0.2 | 1 | 10.20 |
| 2 | 2 | 5 | 0.4 | 2 | 9.40 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 0.6 | 2 | 7.60 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 0.8 | 3 | 8.80 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 10 |
| 10 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 11 |
| 20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 11 |
Table (3)
Statement to show the calculation of interest rate on lower rated bonds
| Maturity |
Real Risk-Free Rate (%) (r*) |
Inflation Rate on Treasury Bond (%) (IP) |
Maturity Risk Premium (%) (MRP) |
Default Risk Premium on Lower rated Bonds (%) (DRP) |
Interest Rate (%)
|
| 1 | 2 | 7 | 0.2 | 2 | 11.2 |
| 2 | 2 | 5 | 0.4 | 3 | 10.40 |
| 3 | 2 | 3 | 0.6 | 4 | 9.60 |
| 4 | 2 | 3 | 0.8 | 5 | 10.80 |
| 5 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 5 | 11 |
| 10 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 6 | 12 |
| 20 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 7 | 13 |
Table (4)
The yield curve of the given data
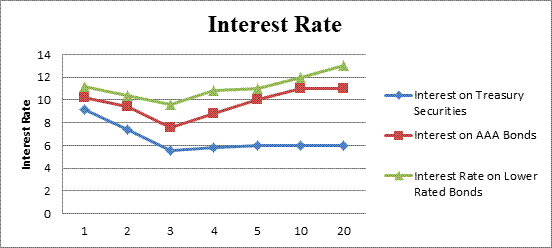
Fig 2
- The x-axis represents the maturity.
- The y-axis represents the interest rate.
- The interest rates of Treasury securities, AAA bonds and lower rated bonds with their respective time period can be shown from the graph.
Hence, the interest of 1-year lower rated bond is 11.20%, at 2-year lower rated bond is 10.40%, 3-year lower rated bond is 9.60%, 4-year lower rated bond is 10.80% 5-year lower rated bond is 11%, 10-year lower rated bond is 12% and thereafter is 13%.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
Fundamentals of Financial Management, Concise Edition (MindTap Course List)
- The decisions relating to the use of profits or income of an entity or organization are known a.Any of these b.Dividend decisions c.Finance decisions d.Investment Decisionarrow_forwardWhat are the three interrelated areas of finance? (a) Financial markets, option and forwards (b) Banking, financial institutions and swap currency (c) Investment, Financial management and Financial market & Financial institution (d) All of abovearrow_forwardThe method that converts the amount of present cash into an amount of cash of equivalent value in future is: a.Budgeting b.Both a and b c.Discounting method d.Compounding methodarrow_forward
- The government finance which includes the principles and practices relating to the Procurement and management of funds for Central Government, and Local bodies is known as: a.Public Finance b.All of these c.Private Finance d.Business Financearrow_forwardwhat is financial ratios?arrow_forwardWhich of the following is the activity which finance people are involved? (a) Investing decisions (b) Marketing decisions (c) Promotion decisions (d) Non of Abovearrow_forward
- You plan to invest $3,500 per year for 39 years into an IRA. What will the value of the IRA be after 39 years if the interest rate is 9% per year? Your answer may vary due to rounding.arrow_forwardIn finance, we refer to the market where new securities are bought and sold for the first time? (a) Money market (b) Capital market (c) Primary market (d) Secondary marketarrow_forward1: ________ is shown on a multiple-step but not on a single-step income statement. A. Credited to Inventory B. A customer utilizes a prompt payment incentive. C. Debited to the Inventory account D. Gross profitarrow_forward
- what is corporate finance? explain it.arrow_forwardA lorenz curve graphs the _________________ received by everyone up to a certain quintile. A. Unequal distribution over time B. Normative shares of income C. Cumulative shares of income D. Total share of incomearrow_forwardNeedhdjxjx ususs shsharrow_forward
 EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT
EBK CONTEMPORARY FINANCIAL MANAGEMENTFinanceISBN:9781337514835Author:MOYERPublisher:CENGAGE LEARNING - CONSIGNMENT Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Financial Management (MindTap Course...FinanceISBN:9781337395083Author:Eugene F. Brigham, Phillip R. DavesPublisher:Cengage Learning

