
Refer to the shaft shown in Figure 6-4. Determine the missing dimensions in the table using the dimensions given. All dimensions are in inches.
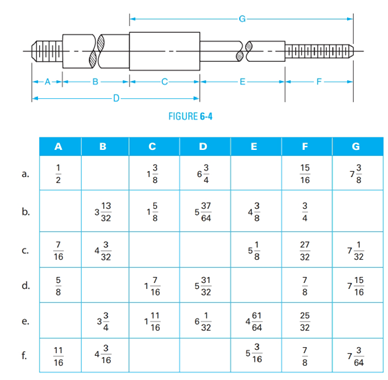
(a)
Evaluate the missing dimension
Answer to Problem 13A
The missing dimension
Explanation of Solution
Given:
All the dimensions are shown below:
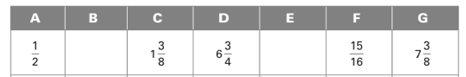
Calculation:
Dimension
Subtract addition of
Dimension
Subtract addition of
Thus, the missing dimension
Conclusion:
The missing dimension
(b)
Evaluate the missing dimension
Answer to Problem 13A
The missing dimension
Explanation of Solution
Given:
All the dimensions are shown below:
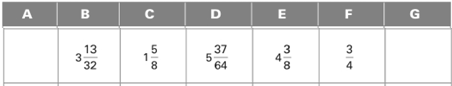
Calculation:
Dimension is calculated as follows:
Subtract addition of
Dimension G is calculated as follows:
Add of C, E and F.
Thus, the missing dimension A and G are
Conclusion:
The missing dimension A and G are
(c)
Evaluate the missing dimension C and D.
Answer to Problem 13A
The missing dimension C and D are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
All the dimensions are shown below:
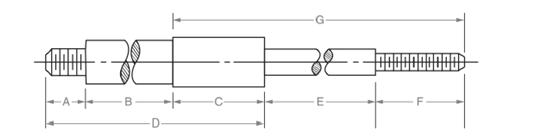
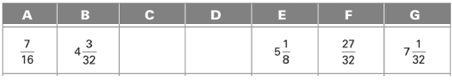
Calculation:
Dimension C is calculated as follows:
Subtract addition of E and F from G.
Dimension D is calculated as follows:
Add of A, B and C.
Thus, the missing dimension C and D are
Conclusion:
The missing dimension C and D are
(d)
Evaluate the missing dimension B and E.
Answer to Problem 13A
The missing dimension B and E are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
All the dimensions are shown below:
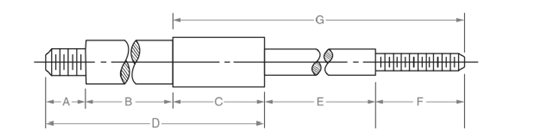
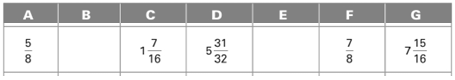
Calculation:
Dimension B is calculated as follows:
Subtract addition of A and C from D.
Dimension E is calculated as follows:
Subtract addition of C and F from G.
Thus, the missing dimension B and E are
Conclusion:
The missing dimension B and E are
(e)
Evaluate the missing dimension A and G.
Answer to Problem 13A
The missing dimension A and G are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
All the dimensions are shown below:
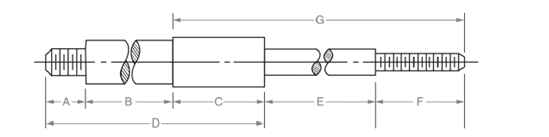
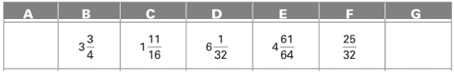
Calculation:
Dimension A is calculated as follows:
Subtract addition of B and C from D.
Dimension G is calculated as follows:
Add C, E and F.
Thus, the missing dimension A and G are
Conclusion:
The missing dimension A and G are
(f)
Evaluate the missing dimension C and D.
Answer to Problem 13A
The missing dimension C and D are
Explanation of Solution
Given:
All the dimensions are shown below:
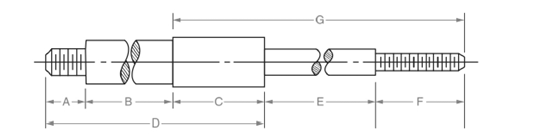
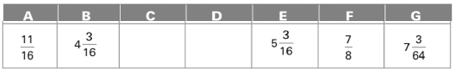
Calculation:
Dimension C is calculated as follows:
Subtract addition of E and F from G.
Dimension D is calculated as follows:
Add of A, B and C.
Thus, the missing dimension C and D are
Conclusion:
The missing dimension C and D are
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK MATHEMATICS FOR MACHINE TECHNOLOGY
- Topic: Group Theory | Abstract Algebra Question: Let G be a finite group of order 45. Prove that G has a normal subgroup of order 5 or order 9, and describe the number of Sylow subgroups for each. Instructions: • Use Sylow's Theorems (existence, conjugacy, and counting). • List divisors of 45 and compute possibilities for n for p = 3 and p = 5. Show that if n = 1, the subgroup is normal. Conclude about group structure using your analysis.arrow_forwardTopic: Group Theory | Abstract Algebra Question: Let G be a finite group of order 45. Prove that G has a normal subgroup of order 5 or order 9, and describe the number of Sylow subgroups for each. Instructions: • Use Sylow's Theorems (existence, conjugacy, and counting). • List divisors of 45 and compute possibilities for n for p = 3 and p = 5. Show that if n = 1, the subgroup is normal. Conclude about group structure using your analysis.arrow_forwardTopic: Group Theory | Abstract Algebra Question: Let G be a finite group of order 45. Prove that G has a normal subgroup of order 5 or order 9, and describe the number of Sylow subgroups for each. Instructions: • Use Sylow's Theorems (existence, conjugacy, and counting). • List divisors of 45 and compute possibilities for n for p = 3 and p = 5. Show that if n = 1, the subgroup is normal. Conclude about group structure using your analysis.arrow_forward
- Complete solution requiredarrow_forwardTopic: Group Theory | Abstract Algebra Question: Let G be a finite group of order 45. Prove that G has a normal subgroup of order 5 or order 9, and describe the number of Sylow subgroups for each. Instructions: • Use Sylow's Theorems (existence, conjugacy, and counting). • List divisors of 45 and compute possibilities for n for p = 3 and p = 5. Show that if n = 1, the subgroup is normal. Conclude about group structure using your analysis.arrow_forwardTopic: Group Theory | Abstract Algebra Question: Let G be a finite group of order 45. Prove that G has a normal subgroup of order 5 or order 9, and describe the number of Sylow subgroups for each. Instructions: • Use Sylow's Theorems (existence, conjugacy, and counting). • List divisors of 45 and compute possibilities for n for p = 3 and p = 5. Show that if n = 1, the subgroup is normal. Conclude about group structure using your analysis.arrow_forward
- Do on pen and paper onlyarrow_forwardProblem 9: The 30-kg pipe is supported at A by a system of five cords. Determine the force in each cord for equilibrium. B 60º A E Harrow_forwardd((x, y), (z, w)) = |xz|+|yw|, show that whether d is a metric on R² or not?. Q3/Let R be a set of real number and d: R² x R² → R such that -> d((x, y), (z, w)) = max{\x - zl, ly - w} show that whether d is a metric on R² or not?. Q4/Let X be a nonempty set and d₁, d₂: XXR are metrics on X let d3,d4, d5: XX → R such that d3(x, y) = 4d2(x, y) d4(x, y) = 3d₁(x, y) +2d2(x, y) d5(x,y) = 2d₁ (x,y))/ 1+ 2d₂(x, y). Show that whether d3, d4 and d5 are metric on X or not?arrow_forward
 Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
 Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning
Elementary Geometry for College StudentsGeometryISBN:9781285195698Author:Daniel C. Alexander, Geralyn M. KoeberleinPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,





