
Concept explainers
Missing Data; Basic CVP Concepts L06−1, L06−9
Fill in the missing amounts in each of the eight case situations below. Each case is independent of the others. (Hint: One way to find the missing amounts would be to prepare a contribution format income statement for each case, enter the known data, and then compute the missing items.)
a. Assume that only one product is being sold in each of the four following case situations: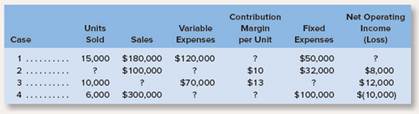
b. Assume that more than one product is being sold in each of the four following case situations: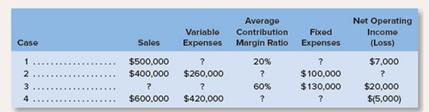
Cost volume profit analysis: Cost volume profit analysis measures the effect on income of a company with the alteration of cost and volume of sales.
The missing amount in the table.
Answer to Problem 11E
Solution:
a) Assuming that only one product is being sold in each of the following case situations:
| Case | Units Sold | Sales | Variable
Expenses | Contribution
Margin per Unit | Fixed Expenses | Net Operating Income(loss) |
| 1 | 15,000 | $180,000 | $120,000 | $4 | $50,000 | $10,000 |
| 2 | 4,000 | $100,000 | $60,000 | $10 | $32,000 | $8,000 |
| 3 | 10,000 | $200,000 | $70,000 | $13 | $118,000 | $12,000 |
| 4 | 6,000 | $300,000 | $210,000 | $15 | $100,000 | ($10,000) |
Case 1
| Contribution format income statement | ||
| Total | Per Unit | |
| Sales (15,000 units) | $180,000 | $12.00 |
| Variable expenses | $120,000 | $8.00 |
| Contribution Margin | $60,000 | $4.00 |
| Fixed expenses | $50,000 | |
| Net operating income | $10,000 | |
Case 2
| Contribution format income statement | ||
| Total | Per Unit | |
| Sales (4,000 units) | $100,000 | $25.00 |
| Variable expenses | $60,000 | $15.00 |
| Contribution Margin | $40,000 | $10.00 |
| Fixed expenses | $32,000 | |
| Net operating income | $8,000 | |
Case 3
| Contribution format income statement | ||
| Total | Per Unit | |
| Sales (10,000 units) | $200,000 | $20.00 |
| Variable expenses | $70,000 | $7.00 |
| Contribution Margin | $130,000 | $13.00 |
| Fixed expenses | $118,000 | |
| Net operating income | $12,000 | |
Case 4
| Contribution format income statement | ||
| Total | Per Unit | |
| Sales (6,000 units) | $300,000 | $50.00 |
| Variable expenses | $210,000 | $35.00 |
| Contribution Margin | $90,000 | $15.00 |
| Fixed expenses | $100,000 | |
| Net operating income | ($10,000) | |
b) Assuming that more than one product is being sold in each of the four case situations:
| Case | Sales | Variable Expenses | Average
Contribution Margin Ratio | Fixed
Expenses | Net Operating
Income (loss) |
| 1 | $500,000 | $400,000 | 20% | $93,000 | $7,000 |
| 2 | $400,000 | $260,000 | 35% | $100,000 | $40,000 |
| 3 | $250,000 | $100,000 | 60% | $130,000 | $20,000 |
| 4 | $600,000 | $420,000 | 30% | $185,000 | ($5,000) |
Case 1
| Contribution format income statement | |
| Amounts | |
| Sales | $500,000 |
| Variable expenses | $400,000 |
| Contribution Margin | $100,000 |
| Fixed expenses | $93,000 |
| Net operating income | $7,000 |
| Contribution format income statement | |
| Amounts | |
| Sales | $400,000 |
| Variable expenses | $260,000 |
| Contribution Margin | $140,000 |
| Fixed expenses | $100,000 |
| Net operating income | $40,000 |
Case 3
| Contribution format income statement | |
| Amounts | |
| Sales | $250,000 |
| Variable expenses | $100,000 |
| Contribution Margin | $150,000 |
| Fixed expenses | $130,000 |
| Net operating income | $20,000 |
Case 4
| Contribution format income statement | |
| Amounts | |
| Sales | $600,000 |
| Variable expenses | $420,000 |
| Contribution Margin | $180,000 |
| Fixed expenses | $185,000 |
| Net operating income | ($5,000) |
Explanation of Solution
A contribution margin is calculated by deducting the variable expenses from the sales revenue. So, if the variable expense is missing, the contribution margin is deducted from the sales revenue and goes same in case of units. The net operating income is calculated by deducting the fixed expenses from the contribution margin. So, if the fixed expenses are missing, the operating income is deducted from the contribution margin. The contribution margin ratio is calculated by dividing the contribution margin by sales revenue. So, if the sales revenue is missing, it can be ascertained by dividing the contribution margin by the contribution margin ratio and if the contribution margin is missing, it is calculated by multiplying the contribution margin with the contribution margin ratio.
Given: a) Assume that only one product is being sold in each of the following case situations:
| Case | Units Sold | Sales | Variable
Expenses | Contribution
Margin per Unit | Fixed Expenses | Net Operating Income(loss) |
| 1 | 15,000 | $180,000 | $120,000 | ? | $50,000 | ? |
| 2 | ? | $100,000 | ? | $10 | $32,000 | $8,000 |
| 3 | 10,000 | ? | $70,000 | $13 | ? | $12,000 |
| 4 | 6,000 | $300,000 | ? | ? | $100,000 | ($10,000) |
b) Assume that more than one product is being sold in each of the four case situations:
| Case | Sales | Variable Expenses | Average
Contribution Margin Ratio | Fixed
Expenses | Net Operating
Income (loss) |
| 1 | $500,000 | ? | 20% | ? | $7,000 |
| 2 | $400,000 | $260,000 | ? | $100,000 | ? |
| 3 | ? | ? | 60% | $130,000 | $20,000 |
| 4 | $600,000 | $420,000 | ? | ? | ($5,000) |
The cost volume profit analysis aims determining an outcome of changes in the various variables of operations. A cost is the expenses incurred on the products which are being sold and the volume is the quantity of the products which is going to be sold. The profit is the difference between the cost incurred and sales revenue of a company. An analysis of cost volume profit helps in predicting or forecasting the various consequences of various decisions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 6 Solutions
INTRO.TO MGRL.ACCT.(LL)W/CONNECT>IP<
Additional Business Textbook Solutions
Gitman: Principl Manageri Finance_15 (15th Edition) (What's New in Finance)
Operations Management: Processes and Supply Chains (12th Edition) (What's New in Operations Management)
Financial Accounting, Student Value Edition (5th Edition)
Essentials of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
Fundamentals of Management (10th Edition)
Principles of Operations Management: Sustainability and Supply Chain Management (10th Edition)
- Can you solve this general accounting question with accurate accounting calculations?arrow_forwardPlease help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct financial process.arrow_forwardPlease provide the correct answer to this general accounting problem using valid calculations.arrow_forward
- Please help me solve this general accounting question using the right accounting principles.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forward
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
- I need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forwardI need help solving this general accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





