
To find: the indicated probability for a randomly selected x-value from the distribution using the standard normal table.
Given information:
The probability to be found is:
It is given that the distribution is normal and has mean
Concept Used:
Standard
The standard normal distribution is the normal distribution with mean 0 and standard deviation1. The formula below can be used to transform x-values from a normal distribution with mean
The z-value for a particular x-value is called the z-score for the x-value and is the number of standard deviations the x-value lies above or below the mean
Standard Normal Table
If z is a randomly selected value from a standard normal distribution, the table below can be used to find the probability that z is less than or equal to some given value.
| Standard Normal Table | ||||||||||
| z | .0 | .1 | .2 | .3 | .4 | .5 | .6 | .7 | .8 | .9 |
| -3 | .0013 | .0010 | .0007 | .0005 | .0003 | .0002 | .0002 | .0001 | .0001 | .0000+ |
| -2 | .0228 | .0179 | .0139 | .0107 | .0082 | .0062 | .0047 | .0035 | .0026 | .0019 |
| -1 | .1587 | .1357 | .1151 | .0968 | .0808 | .0668 | .0548 | .0446 | .0359 | .0287 |
| -0 | .5000 | .4602 | .4207 | .3821 | .3446 | .3085 | .2743 | .2420 | .2119 | .1841 |
| 0 | .5000 | .5398 | .5793 | .6179 | .6554 | .6915 | .7257 | .7580 | .7881 | .8159 |
| 1 | .8413 | .8643 | .8849 | .9032 | .9192 | .9332 | .9452 | .9554 | .9641 | .9713 |
| 2 | .9772 | .9821 | .9861 | .9893 | .9918 | .9938 | .9953 | .9965 | .9974 | .9981 |
| 3 | .9987 | .9990 | .9993 | .9995 | .9997 | .9998 | .9998 | .9999 | .9999 | 1.0000- |
Explanation:
The objective is to find
First step is to find the z-score corresponding to the x-value of 89.
So,
Now, to find this value, find the intersection point where row -0 and column .9 intersects.
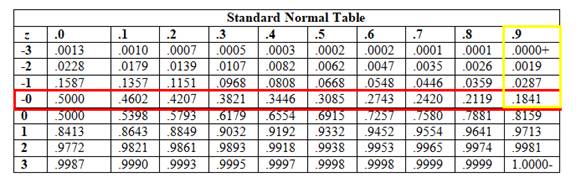
The table shows that:
This means that:
Chapter 6 Solutions
EBK ALGEBRA 2
- Safari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help Ο Ω OV O mA 0 mW ర Fri Apr 4 1 222 tv A F9 F10 DII 4 F6 F7 F8 7 29 8 00 W E R T Y U S D பட 9 O G H J K E F11 + 11 F12 O P } [arrow_forwardSo confused. Step by step instructions pleasearrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forward
- In simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forward
- Write each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





