
Concept explainers
Time-Driven Activity-Based Costing LO5—6
Saratoga Company manufactures jobs to customer specifications. The company is conducting a time-driven activity-based costing study in its Purchasing Department to better understand how Purchasing Department labor costs are consumed by individual jobs. To aid the study, the company provided the following data regarding its Purchasing Department and three of its many jobs:
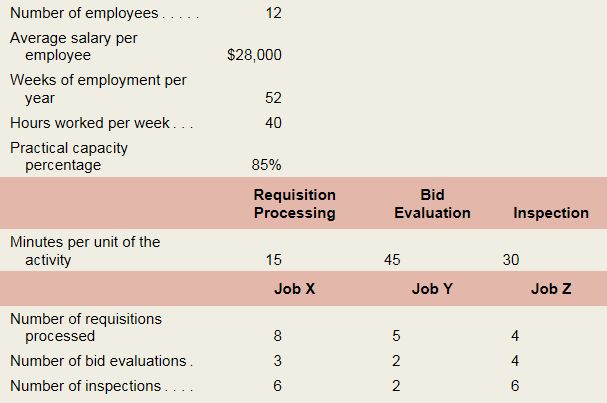
Required:
Calculate the cost per minute of the resource supplied in the Purchasing Department.
1.
Concept introduction:
Activity-based costing (ABC):
Activity-based costing refers to the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This costing method identifies the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. After establishing the relationship, the indirect cost is allocated to the products.
The cost per minute of the resource supplied.
Answer to Problem 5A.1E
The cost per minute of the resource supplied is 0.40.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the cost per minute of the resource supplied:
Thus, the cost per minute of the resource supplied is 0.40.
Working note 1:
Calculate the total cost of resources supplied:
Working note 2:
Calculate the capacity per employee:
Working note 3:
Calculate the practical capacity of resources supplied:
2.
Concept introduction:
Activity-based costing (ABC):
Activity-based costing refers to the method of costing where the overhead cost is assigned to various products. This costing method identifies the relationship between the manufacturing overhead costs and the activities. After establishing the relationship, the indirect cost is allocated to the products.
To Calculate: The time-driven activity rate for the given activities.
Answer to Problem 5A.1E
The time-driven activity rate is $6, $18 and $12 for requisition processing,bid evaluation, and inspection.
Explanation of Solution
Calculate the time-driven activity rate for the given activities:
| Particulars | Requisition Processing | Bid Evaluation | Inspection |
| Minutes per unit of the activity (a) | 15 | 45 | 30 |
| Cost per minute of the resource supplied (b) | $0.40 | $0.40 | $0.40 |
| Time-driven activity rate (a × b) | $6.00 | $18.00 | $12.00 |
Table: (1)
Thus, the time-driven activity rate is $6, $18, and $12 for requisition processing,bid evaluation, and inspection.
3.
Concept introduction:
Cost allocation:
Costallocation refers to the process where the common cost of the production and service rendered to the various departments of the business are distributed. It is used to calculate the actual cost attributed to a specific department.
The purchasing labor cost for Job X, Job Y, and Job Z.
Answer to Problem 5A.1E
The total cost of Job X, Job Y, and Job Z is $102, $162 and $168 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Determine the purchasing labor cost for Job X, Job Y, and Job Z:
| Particulars | Job X | Job Y | Job Z |
| Requisition processing costs | $48 | $30 | $24 |
| Bid evaluation costs | $54 | $36 | $72 |
| Inspection costs | $72 | $24 | $72 |
| Total costs | $174 | $90 | $168 |
Table: (2)
Thus, the total cost of Job X, Job Y, and Job Z is $102, $162 and $168 respectively.
Working note 1:
Calculate the requisition processing costs:
| Particulars | Time-driven activity rate(a) | Number of requisitions processed(b) | Requisition processing costs(c = a × b) |
| Job X | $6.00 | 8 | $48.00 |
| Job Y | $6.00 | 5 | $30.00 |
| Job Z | $6.00 | 4 | $24.00 |
Table: (3)
Calculate the bid evaluation costs:
| Particulars | Time-driven activity rate(a) | Number of bid evaluations(b) | Bid evaluation costs(c = a × b) |
| Job X | $18.00 | 3 | $54.00 |
| Job Y | $18.00 | 2 | $36.00 |
| Job Z | $18.00 | 4 | $72.00 |
Table: (4)
Calculate the bid inspection costs:
| Particulars | Time-driven activity rate(a) | Number of inspections(b) | Inspection costs(c = a × b) |
| Job X | $12.00 | 6 | $72.00 |
| Job Y | $12.00 | 2 | $24.00 |
| Job Z | $12.00 | 6 | $72.00 |
Table: (5)
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5A Solutions
MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING F/MGRS.
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem with appropriate steps and explanations?arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forward
- Can you solve this general accounting problem using appropriate accounting principles?arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardI need assistance with this general accounting question using appropriate principles.arrow_forward
- I need help solving this general accounting question with the proper methodology.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardCan you solve this general accounting problem using accurate calculation methods?arrow_forward
- Please provide the answer to this general accounting question using the right approach.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this general accounting question with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardI need help with this general accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forward
 Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Cost AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305087408Author:Edward J. Vanderbeck, Maria R. MitchellPublisher:Cengage Learning Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Cornerstones of Cost Management (Cornerstones Ser...AccountingISBN:9781305970663Author:Don R. Hansen, Maryanne M. MowenPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College


