
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
Answer to Problem 23AR
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
The angle
The given figure is as shown below.
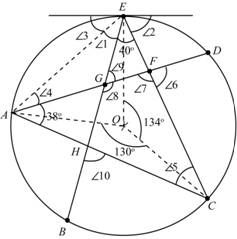
Figure -(1)
Write the expression for angle
Write the expression for the angle
Write the expression for angle
Write the expression for angle
Write the expression for the angle sum property of a triangle
Here, the first angle of the triangle is
Write the expression for angle
Write the expression for angle
Write the expression for angle
Write the expression for angle
Write the expression for angle
Write the expression for the angle sum property of a line.
Here, the respective angles on the lines are
Calculation:
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Conclusion:
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
The measure of angle
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 58 Solutions
Mathematics For Machine Technology
- Let f:R->R be defined by f(x)=x^(3)+5.(a) Determine if f is injective. why?(b) Determine if f is surjective. why?(c) Based upon (a) and (b), is f bijective? why?arrow_forwardLet f:R->R be defined by f(x)=x^(3)+5.(a) Determine if f is injective.(b) Determine if f is surjective. (c) Based upon (a) and (b), is f bijective?arrow_forward1 S 0 sin(lnx) x² - 1 Inx dxarrow_forward
- 2 6. Modelling. Suppose that we have two tanks (A and B) between which a mixture of brine flows. Tank A contains 200 liters of water in which 50 kilograms of salt has been dissolved and Tank B contains 100 liters of pure water. Water containing 1kg of salt per liter is pumped into Tank A at the rate of 5 liters per minute. Brine mixture is pumped into Tank A from Tank B at the rate of 3 liters per minute and brine mixture is pumped from Tank A into Tank B at the rate of 8 liters per minute. Brine is drained from Tank B at a rate of 5 liters per minute. (a) Draw and carefully label a picture of the situation, including both tanks and the flow of brine between them. JankA 1ks of Salt Slits Pump EL Brine mit tark A from tank 13 Tank 13 k 3L zooliters of Ico liters of water with pure water. Saky salt → 777 disslore inside Brine mix is pumped from tank A to B of 82 Brine drainen min by Gf salt (b) Assume all brine mixtures are well-stirred. If we let t be the time in minutes, let x(t) 1ks…arrow_forwardNo chatgpt plsarrow_forwardRemix 4. Direction Fields/Phase Portraits. Use the given direction fields to plot solution curves to each of the given initial value problems. (a) x = x+2y 1111 y = -3x+y with x(0) = 1, y(0) = -1 (b) Consider the initial value problem corresponding to the given phase portrait. x = y y' = 3x + 2y Draw two "straight line solutions" passing through (0,0) (c) Make guesses for the equations of the straight line solutions: y = ax.arrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781305652224Author:Charles P. McKeague, Mark D. TurnerPublisher:Cengage Learning Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,
Elementary Geometry For College Students, 7eGeometryISBN:9781337614085Author:Alexander, Daniel C.; Koeberlein, Geralyn M.Publisher:Cengage,




