
Draw the major control devices of a programmable controller.
Answer to Problem 1SQ
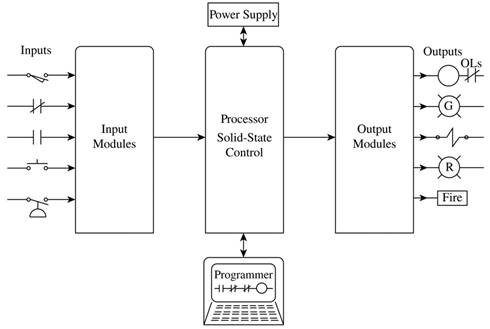
The major control devices of a programmable controller are as follows:
Explanation of Solution
Discussion:
A solid-state, electronic microprocessor-based control system is known as a programmable controller.
A programmable controller contains the following components.
- Power supply.
- Input modules.
- Processor.
- Output modules.
- Programmer.
The input devices such as push buttons, limit switches, and condition sensors are connected to input modules. The input module is monitored by the system to detect changes occurred in the input devices. Depending upon the status of input signals, the controller system reacts using user- programmed internal logic. The response obtained by the controller device is used to drive the output loads such as motor starter, control relays, contactors, and alarms.
The major control devices of a programmable controller are shown in Figure 1.
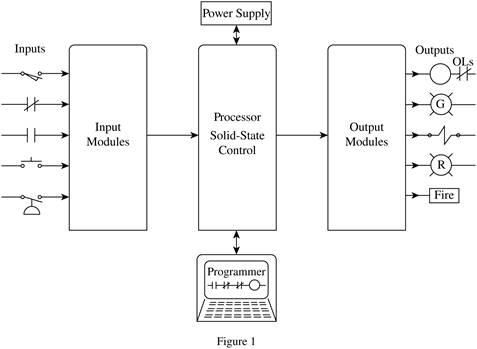
Conclusion:
Thus, major control devices of a programmable controller are shown in Figure 1.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 58 Solutions
Electric Motor Control
- 10.8 In the network of Fig. P10.8, Za = Zb = Zc = (25+ j5) W.Determine the line currents.arrow_forwardUsing D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter. The counter counts in the sequence 1,3,5,7, 1,7,5,3,1,3,5,7,.... when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter count 0. Present state Next state x=0 Next state x=1 Output SO 52 S1 1 S1 54 53 3 52 53 S2 56 51 0 $5 5 54 S4 53 0 55 58 57 7 56 56 55 0 57 S10 59 1 58 58 S7 0 59 S12 S11 7 $10 $10 59 0 $11 $14 $13 5 $12 S12 $11 0 513 $15 SO 3 S14 $14 S13 0 $15 515 SO 0 Explain how to get the table step by step with drawing the state diagram and finding the Karnaugh map.arrow_forwardFor the oscillator resonance circuit shown in Fig. (5), derive the oscillation frequency Feedback and open-loop gains. L₁ 5 mH (a) ell +10 V R₁ ww R3 S C2 HH 1 με 1000 pF 100 pF R₂ 1 με RA H (b) +9 V R4 CA 470 pF C₁ R3 HH 1 με R₁ ww L₁ 000 1.5 mH R₂ ww Hi 1 μF L2 m 10 mHarrow_forward
- Expert handwritten solution onlyarrow_forwardB. For the oscillator circuit shown in frequency, feedback and open-loop gains. +10 V name the circuit, derive and find the oscillation P.Av +9 V -000 4₁ 5 mH w R₁ C₂ HH 1 με w 100 pF R₂ T R CA www. 470 pF w ww www 1000 pF HH 1μF C₁ HH 1μF Ra ww HI 4₁ 000 1.5 mH H 4 AF 000 10 mHarrow_forwardI want to check if the current that I have from using the mesh analysis is correct? I1 = 0.214mA I2 = -0.429mAarrow_forward
- I want to find the current by using mesh analysis pleasearrow_forwardI want to find the current by using mesh analysis pleasearrow_forwardR₁ W +10 V R3 +9 V C₂ R₁ CA C₁ 470 pF HH 1000 pF HH 1 με C4 1 μF 1 uF C₁ R₂ R4 100 pF Find Open-loop Jain L₁ 5 mH (a) Av=S,B={" H R₁₂ ✓ ww (b) R₁ L₁ 000 1.5 mH R₂ H 1 uF 12 10 mHarrow_forward
- A) Calculate the efficiency of the test transformer at the resistive loads (X-25%, 50%, 75%, 100%, 125% full load). B) From part (A) draw the plot (efficiency Vs power output) of the transformer. C) Discuss the plot of part (B).arrow_forwarda- Determine fH; and Ho b- Find fg and fr. c- Sketch the frequency response for the high-frequency region using a Bode plot and determine the cutoff frequency. Ans: 277.89 KHz; 2.73 MHz; 895.56 KHz; 107.47 MHz. 14V Cw=5pF Cwo-8pF Coc-12 pF 5.6kQ Ch. 40. pF C-8pF 68kQ 0.47µF Vo 0.82 kQ V₁ B=120 0.47µF www 3.3kQ 10kQ 1.2kQ =20µF Narrow_forwardUsing D flip-flops, design a synchronous counter. The counter counts in the sequence 1,3,5,7, 1,7,5,3,1,3,5,7,.... when its enable input x is equal to 1; otherwise, the counter. This counter is for individual settings only need the state diagram and need the state table to use 16 states from So to S15.arrow_forward

 Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337399128Author:Russell E. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning
Electricity for Refrigeration, Heating, and Air C...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337399128Author:Russell E. SmithPublisher:Cengage Learning

