
(Modeling) Mach Number An airplane flying faster than the speed of sound sends out sound waves that form a cone, as shown in the figure. The cone intersects the ground to form a hyperbola. As this hyperbola passes over a particular point on the ground, a sonic boom is heard at that point. If θ is the
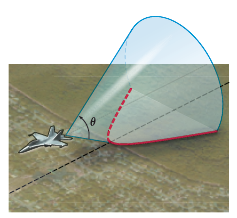
where m is the Mach number for the speed of the plane. (We assume m> 1.) The Mach number is the ratio of the speed of the plane to the speed of sound. Thus, a speed of Mach 1.4 means that the plane is flying at 1.4 times the speed of sound.
In each of the following exercises, θ or m is given. Find the other value (θ to the nearest degree and m to the nearest tenth as applicable).
61. θ = 60°
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 5 Solutions
Trigonometry plus MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Access Card Package (11th Edition)
- Question 10 (5 points) (07.04 MC) Vectors u and v are shown in the graph. -12-11 -10 -9 -8 -7 -6 -5 What is proju? a -6.5i - 4.55j b -5.2i+2.6j с -4.7631 3.334j d -3.81i+1.905j < + 10 6 5 4 3 2 -3 -2 -10 1 -1 -2 -3 u -4 -5 -6 -7arrow_forwardFind the lengths of PR and OR in terms of the angles α and β. Find the angles ∠ONQ and ∠NPQ. Find the lengths of ON and PN in terms of the angle β. Find the length of PQ. Find the length of QR. Find the length of OM. Find the length of RM. What formula can you write down by noting that PR = QR + PQ? What formula can you write down by noting that OR = OM - RM?arrow_forward5) Solve the triangle. 2 95° 4 B с A) c=3.63, A=59.5°, B = 25.5° C) c = 4.63, A = 59.5°, B = 25.5° A B) c 4.63, A 25.5°, B = 59.5° = = D) c 5.63, A = 25.5°, B = 59.5°arrow_forward
- Find zw. Leave your answer in polar form. = လ 3π 2 z = 6 cos 6 cos 37 3π + i sin 2 57 W = 12 cos + i sin 6 6 ༠།ལྦ་arrow_forward10 Write the expression (1 – i) i)in the standard form a + bi.arrow_forward11) The letters r and 0 represent polar coordinates. Write the equation r sine = 10 using rectangular coordinates (x, y). A) x = 10y B) y = 10 C) x = 10 D) y = 10xarrow_forward
- 18) Find all the complex cube roots of - 8i. Leave your answers in polar form with the argument in degrees.arrow_forwardWrite the complex number √3 - i in polar form.arrow_forward2 10) The letters x and y represent rectangular coordinates. Write the equation x² + 4y = 4 using polar coordinates (r, e). A) 4 cos² 0 + sin² 0 = 4r C) r²(4 cos² 0 + sin² 0) = 4 B) cos² 0 + 4 sin² 0 = 4r D) r² (cos20 + 4 sin² 0) = 4arrow_forward
- 2) A radio transmission tower is 130 feet tall. How long should a guy wire be if it is to be attached 6 feet from the top and is to make an angle of 20° with the ground? Give your answer to the nearest tenth of a foot.arrow_forward4) Two sides and an angle are given. Determine whether the given information results in one triangle, two triangles, or no triangle at all. Solve any triangle(s) that results. b=6, c=7, B = 80° A) one triangle B=40°, A = 60°, a = 13 C) one triangle C 39°, A 61°, a = 15 = B) one triangle C=41°, A = 59°, a = 17 D) no trianglearrow_forward7) A painter needs to cover a triangular region 63 meters by 67 meters by 74 meters. A can of paint covers 70 square meters. How many cans will be needed?arrow_forward
- Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning


