
(a)
To determine : The inequality relating to the average cost per calendar to the desired cost per calendar.
The required inequality is
Given information :
A school is publishing a wildlife calendar to raise money for a local charity. The total cost of using the photos in the calendar is
Explanation :
Let the number of calendars to be printed be
The total cost of printing
The average cost of printing
The school wants the average cost per calendar to be below
(b)
To graph : The inequality to find the number of calendars needed to be printed to bring the average cost per calendar below $10.
Given information :
A school is publishing a wildlife calendar to raise money for a local charity. The total cost of using the photos in the calendar is
Graph :
The inequality is
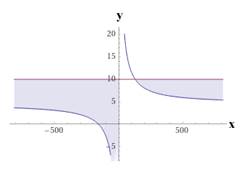
Interpretation :
The number of calendars needed to be printed to bring the average cost per calendar below $10 is more than
(c)
To calculate : The number of calendars to be printed to have the average cost per calendar below
The number of calendars to be printed to have the average cost per calendar below
Given information :
A school is publishing a wildlife calendar to raise money for a local charity. The total cost of using the photos in the calendar is
Explanation :
Let the number of calendars to be printed be
The total cost of printing
The average cost of printing
The school wants the average cost per calendar to be below
Solve the inequality.
Therefore, the number of calendars to be printed to have the average cost per calendar below
Chapter 5 Solutions
Algebra 2: New York Edition (holt Mcdougal Larson Algebra 2)
- Safari File Edit View History Bookmarks Window Help Ο Ω OV O mA 0 mW ర Fri Apr 4 1 222 tv A F9 F10 DII 4 F6 F7 F8 7 29 8 00 W E R T Y U S D பட 9 O G H J K E F11 + 11 F12 O P } [arrow_forwardSo confused. Step by step instructions pleasearrow_forwardIn simplest terms, Sketch the graph of the parabola. Then, determine its equation. opens downward, vertex is (- 4, 7), passes through point (0, - 39)arrow_forward
- In simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forward
- Write each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





