
Concept explainers
In a single-flash geothermal power plant, geothermal water enters the flash chamber (a throttling valve) at 230°C as a saturated liquid at a rate of 50 kg/s. The steam resulting from the flashing process enters a turbine and leaves at 20 kPa with a moisture content of 5 percent. Determine the temperature of the steam after the flashing process and the power output from the turbine if the pressure of the steam at the exit of the flash chamber is (a) 1 MPa, (b) 500 kPa, (c) 100 kPa, (d) 50 kPa.
FIGURE P5–186
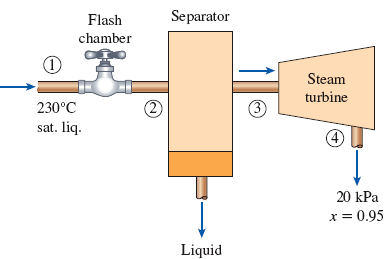
(a)
The temperature of the steam after the flashing process and the power output from the turbine if the pressure of the steam at the exit of flash chamber is
Answer to Problem 186RP
The exit temperature of flash chamber is
The power output turbine is
Explanation of Solution
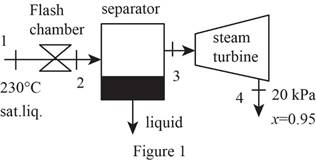
Draw schematic diagram of single flash geothermal power plant as shown in Figure 1.
Write the general energy rate balance equation.
Here, the rate of total energy in is
Consider the system operates at steady state. Hence, the rate of change in net energy of the system becomes zero.
The Equation (I) is reduced as follows.
Refer Figure 1.
The flash chamber is nothing but the expansion valve. At expansion valve, the enthalpy kept constant.
Express the energy balance equation for the flash chamber.
Express the energy balance equation for the separator.
Express the energy balance equation for the turbine.
At state 1:
The geothermal water is extracted at the state of saturated liquid at the temperature of
The enthalpy at state 1 is as follows.
Refer Table A-4, “Saturated water-Temperature table”
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-1, “Molar mass, gas constant, and critical-point properties”.
At state 2:
The exit pressure of the flash chamber is
The geothermal steam is flashed at constant enthalpy. The exit steam of the flash chamber is at the quality of
Here, the fluid enthalpy is
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following corresponding to the pressure of
At state 3:
There is no pressure drop in the separator. The separator separates vapor and liquid form the flashed steam, and the separated vapor alone sent to the turbine.
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
At state 4:
The steam is at the state of saturated mixture at the pressure of
The quality at state 4 is as follows.
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following corresponding to the pressure of
Write the formula for mass flow rate of vapor at entering the turbine.
Conclusion:
The temperature of the steam after flashing process is equal to the saturation temperature at the exit pressure of flash chamber i.e.
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The temperature
Thus, the exit temperature of flash chamber is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (V).
Substitute
Equation (III).
Thus, the power output turbine is
(b)
The temperature of the steam after the flashing process and the power output from the turbine if the pressure of the steam at the exit of flash chamber is
Answer to Problem 186RP
The exit temperature of flash chamber is
The power output turbine is
Explanation of Solution
At state 2:
The exit pressure of the flash chamber is
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following corresponding to the pressure of
At state 3:
There is no pressure drop in the separator. The separator separates vapor and liquid form the flashed steam, and the separated vapor alone sent to the turbine.
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
Conclusion:
The temperature of the steam after flashing process is equal to the saturation temperature at the exit pressure of flash chamber i.e.
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The temperature
Thus, the exit temperature of flash chamber is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (III).
Thus, the power output turbine is
(c)
The temperature of the steam after the flashing process and the power output from the turbine if the pressure of the steam at the exit of flash chamber is
Answer to Problem 186RP
The exit temperature of flash chamber is
The power output turbine is
Explanation of Solution
At state 2:
The exit pressure of the flash chamber is
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following corresponding to the pressure of
At state 3:
There is no pressure drop in the separator. The separator separates vapor and liquid form the flashed steam, and the separated vapor alone sent to the turbine.
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
Conclusion:
The temperature of the steam after flashing process is equal to the saturation temperature at the exit pressure of flash chamber i.e.
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The temperature
Thus, the exit temperature of flash chamber is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (III).
Thus, the power output turbine is
(d)
The temperature of the steam after the flashing process and the power output from the turbine if the pressure of the steam at the exit of flash chamber is
Answer to Problem 186RP
The exit temperature of flash chamber is
The power output turbine is
Explanation of Solution
At state 2:
The exit pressure of the flash chamber is
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
Obtain the following corresponding to the pressure of
At state 3:
There is no pressure drop in the separator. The separator separates vapor and liquid form the flashed steam, and the separated vapor alone sent to the turbine.
The enthalpy
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The enthalpy
Conclusion:
The temperature of the steam after flashing process is equal to the saturation temperature at the exit pressure of flash chamber i.e.
Refer Table A-5, “Saturated water-Pressure table”.
The temperature
Thus, the exit temperature of flash chamber is
Substitute
Substitute
Substitute
Equation (III).
Thus, the power output turbine is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
THERMODYNAMICS: ENG APPROACH LOOSELEAF
- The gears shown in the figure have a diametral pitch of 2 teeth per inch and a 20° pressure angle. The pinion rotates at 1800 rev/min clockwise and transmits 200 hp through the idler pair to gear 5 on shaft c. What forces do gears 3 and 4 transmit to the idler shaft? TS I y 18T 32T This a 12 x 18T C 48T 5arrow_forwardQuestion 1. Draw 3 teeth for the following pinion and gear respectively. The teeth should be drawn near the pressure line so that the teeth from the pinion should mesh those of the gear. Drawing scale (1:1). Either a precise hand drawing or CAD drawing is acceptable. Draw all the trajectories of the involute lines and the circles. Specification: 18tooth pinion and 30tooth gear. Diameter pitch=P=6 teeth /inch. Pressure angle:20°, 1/P for addendum (a) and 1.25/P for dedendum (b). For fillet, c=b-a.arrow_forward5. The figure shows a gear train. There is no friction at the bearings except for the gear tooth forces. The material of the milled gears is steel having a Brinell hardness of 170. The input shaft speed (n2) is 800 rpm. The face width and the contact angle for all gears are 1 in and 20° respectively. In this gear set, the endurance limit (Se) is 15 kpsi and nd (design factor) is 2. (a) Find the revolution speed of gear 5. (b) Determine whether each gear satisfies the design factor of 2.0 for bending fatigue. (c) Determine whether each gear satisfies the design factor of 2.0 for surface fatigue (contact stress). (d) According to the computation results of the questions (b) and (c), explain the possible failure mechanisms for each gear. N4=28 800rpm N₁=43 N5=34 N₂=14 P(diameteral pitch)=8 for all gears Coupled to 2.5hp motorarrow_forward
- 1. The rotating steel shaft is simply supported by bearings at points of B and C, and is driven by a spur gear at D, which has a 6-in pitch diameter. The force F from the drive gear acts at a pressure angle of 20°. The shaft transmits a torque to point A of TA =3000 lbĘ in. The shaft is machined from steel with Sy=60kpsi and Sut=80 kpsi. (1) Draw a shear force diagram and a bending moment diagram by F. According to your analysis, where is the point of interest to evaluate the safety factor among A, B, C, and D? Describe the reason. (Hint: To find F, the torque Tд is generated by the tangential force of F (i.e. Ftangential-Fcos20°) When n=2.5, K=1.8, and K₁ =1.3, determine the diameter of the shaft based on (2) static analysis using DE theory (note that fatigue stress concentration factors need to be used for this question because the loading condition is fatigue) and (3) a fatigue analysis using modified Goodman. Note) A standard diameter is not required for the questions. 10 in Darrow_forward3 N2=28 P(diametral pitch)=8 for all gears Coupled to 25 hp motor N3=34 Full depth spur gears with pressure angle=20° N₂=2000 rpm (1) Compute the circular pitch, the center-to-center distance, and base circle radii. (2) Draw the free body diagram of gear 3 and show all the forces and the torque. (3) In mounting gears, the center-to-center distance was reduced by 0.1 inch. Calculate the new values of center-to-center distance, pressure angle, base circle radii, and pitch circle diameters. (4)What is the new tangential and radial forces for gear 3? (5) Under the new center to center distance, is the contact ratio (mc) increasing or decreasing?arrow_forward2. A flat belt drive consists of two 4-ft diameter cast-iron pulleys spaced 16 ft apart. A power of 60 hp is transmitted by a pulley whose speed is 380 rev/min. Use a service factor (Ks) pf 1.1 and a design factor 1.0. The width of the polyamide A-3 belt is 6 in. Use CD=1. Answer the following questions. (1) What is the total length of the belt according to the given geometry? (2) Find the centrifugal force (Fc) applied to the belt. (3) What is the transmitted torque through the pulley system given 60hp? (4) Using the allowable tension, find the force (F₁) on the tight side. What is the tension at the loose side (F2) and the initial tension (F.)? (5) Using the forces, estimate the developed friction coefficient (f) (6) Based on the forces and the given rotational speed, rate the pulley set. In other words, what is the horse power that can be transmitted by the pulley system? (7) To reduce the applied tension on the tight side, the friction coefficient is increased to 0.75. Find out the…arrow_forward
- The tooth numbers for the gear train illustrated are N₂ = 24, N3 = 18, №4 = 30, №6 = 36, and N₁ = 54. Gear 7 is fixed. If shaft b is turned through 5 revolutions, how many turns will shaft a make? a 5 [6] barrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forwardCE-112 please solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answerarrow_forward
- CE-112 solve this problem step by step and give me the correct answer pleasearrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forwardPlease do not use any AI tools to solve this question. I need a fully manual, step-by-step solution with clear explanations, as if it were done by a human tutor. No AI-generated responses, please.arrow_forward
 Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Technology (Mi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305578296Author:John Tomczyk, Eugene Silberstein, Bill Whitman, Bill JohnsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Heat Transfer (Activate Learning wi...Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781305387102Author:Kreith, Frank; Manglik, Raj M.Publisher:Cengage Learning

