
Concept explainers
a.
Find the
a.
Answer to Problem 34E
The
Explanation of Solution
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the
- Choose Normal under Theoretical Distributions.
- In Normal Distribution, click Edit Parameters.
- Enter mean as 0 and standard deviation as 1 and click Ok.
- Click Two-Tail.
- Click on the 0.950. In custom proportion, enter 0.800.
- Click Ok.
Output obtained using StatKey is as follows:
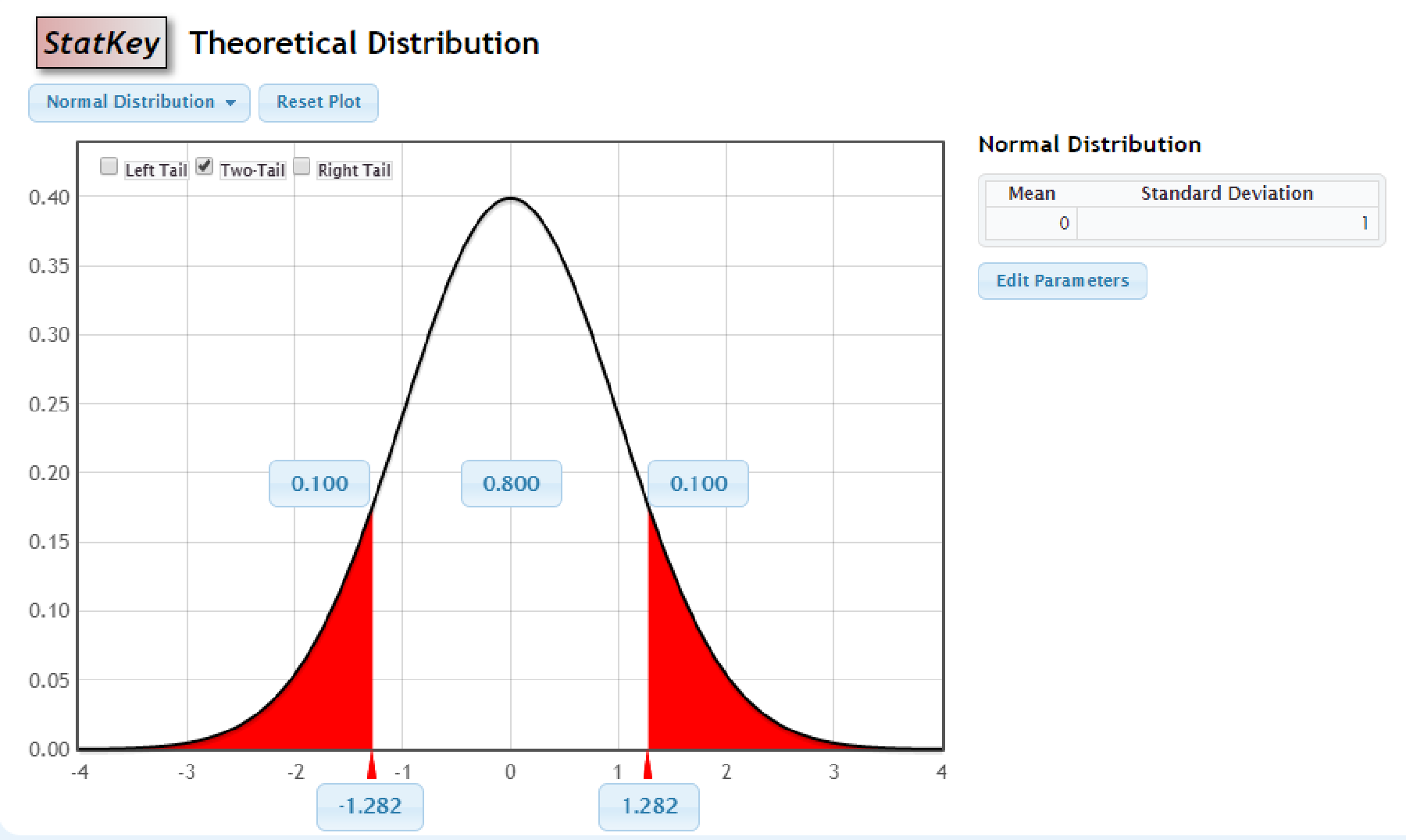
Thus, the
b.
Find the
b.
Answer to Problem 34E
The
Explanation of Solution
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the
- Choose Normal under Theoretical Distributions.
- In Normal Distribution, click Edit Parameters.
- Enter mean as 0 and standard deviation as 1 and click Ok.
- Click Two-Tail.
- Click on the 0.950. In custom proportion, enter 0.840.
- Click Ok.
Output obtained using StatKey is as follows:
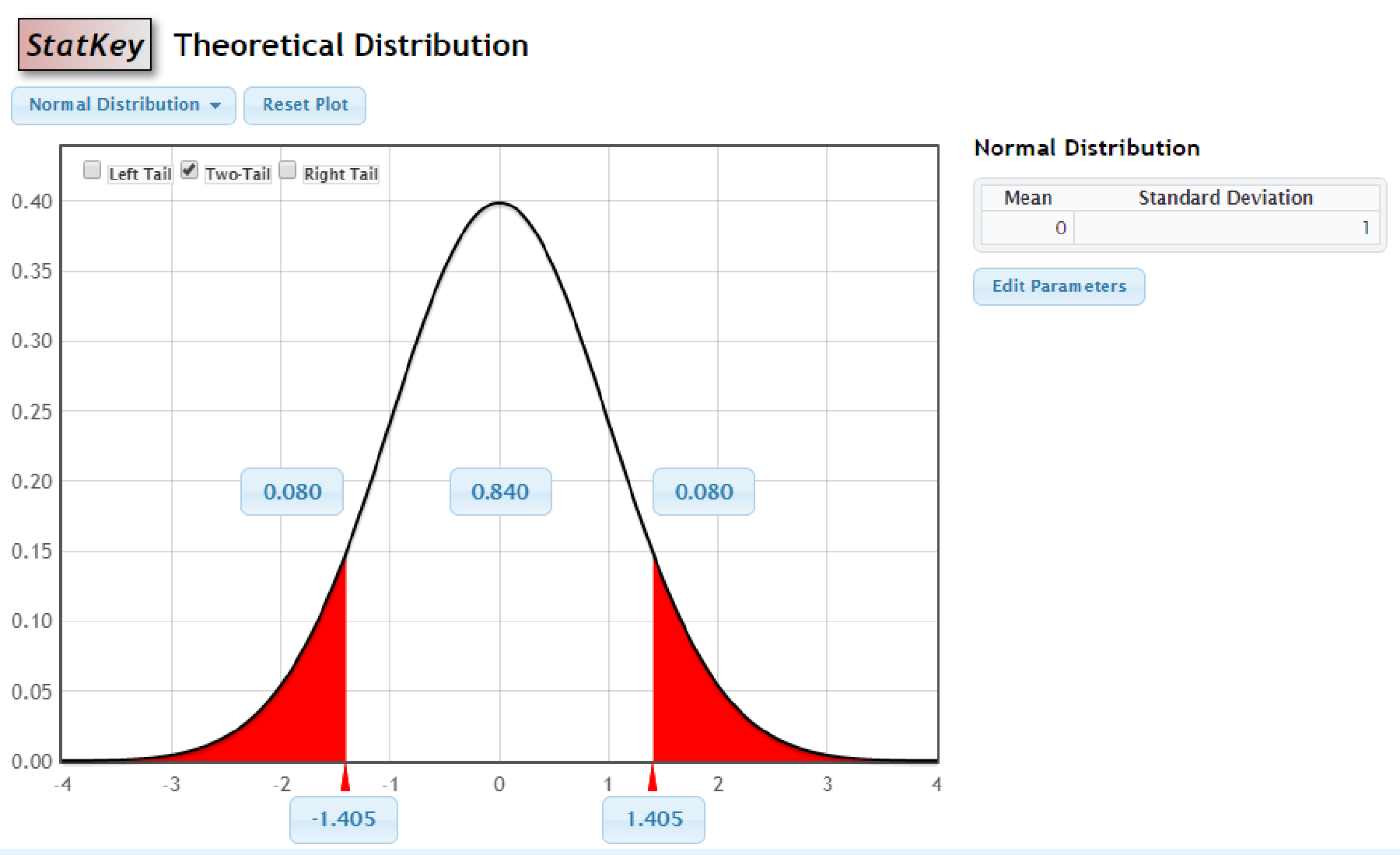
Thus, the
c.
Find the
c.
Answer to Problem 34E
The
Explanation of Solution
Step-by-step procedure to obtain the
- Choose Normal under Theoretical Distributions.
- In Normal Distribution, click Edit Parameters.
- Enter mean as 0 and standard deviation as 1 and click Ok.
- Click Two-Tail.
- Click on the 0.950. In custom proportion, enter 0.920.
- Click Ok.
Output obtained using StatKey is as follows:
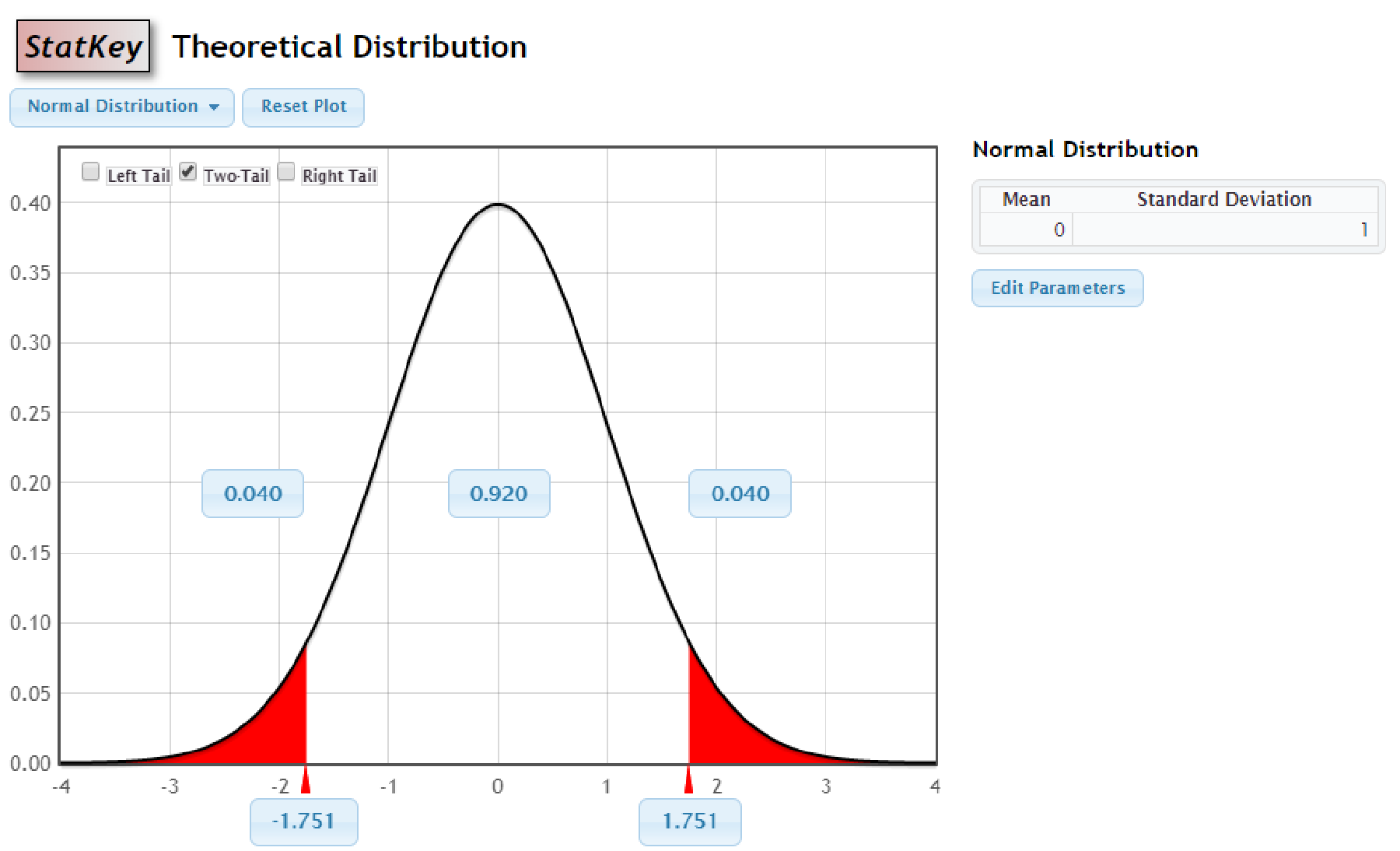
Thus, the
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
STATISTICS-WILEYPLUS ACCESS
- A company found that the daily sales revenue of its flagship product follows a normal distribution with a mean of $4500 and a standard deviation of $450. The company defines a "high-sales day" that is, any day with sales exceeding $4800. please provide a step by step on how to get the answers in excel Q: What percentage of days can the company expect to have "high-sales days" or sales greater than $4800? Q: What is the sales revenue threshold for the bottom 10% of days? (please note that 10% refers to the probability/area under bell curve towards the lower tail of bell curve) Provide answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forwardFind the critical value for a left-tailed test using the F distribution with a 0.025, degrees of freedom in the numerator=12, and degrees of freedom in the denominator = 50. A portion of the table of critical values of the F-distribution is provided. Click the icon to view the partial table of critical values of the F-distribution. What is the critical value? (Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardA retail store manager claims that the average daily sales of the store are $1,500. You aim to test whether the actual average daily sales differ significantly from this claimed value. You can provide your answer by inserting a text box and the answer must include: Null hypothesis, Alternative hypothesis, Show answer (output table/summary table), and Conclusion based on the P value. Showing the calculation is a must. If calculation is missing,so please provide a step by step on the answers Numerical answers in the yellow cellsarrow_forward
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman





