
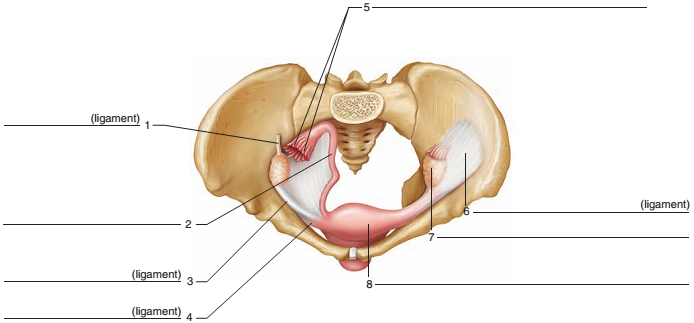
FIGURE 51.1 Label the ligaments and other structures associated with the female internal reproductive organs.
To label:
The ligaments and other structures related with the female reproductive organs.
Introduction:
The female reproductive system is comprised of the external and internal sex organs which play a role in the reproduction of new offspring. This system in human females is immature at birth but develops during the maturity at the age of puberty. It helps in the production of gametes and carries a fetus.
Explanation of Solution
The ligaments and other structures related with the female reproductive organs are given below:
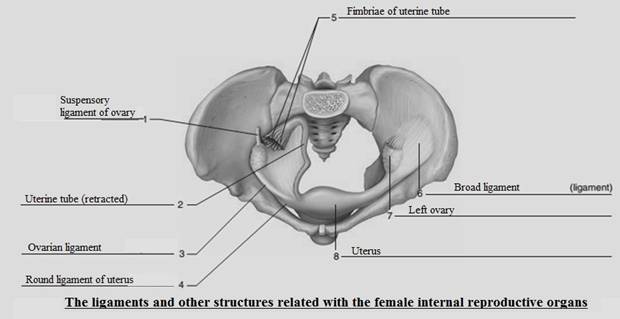
Ovary:
It is a female reproductive organ. In this organ eggs or ova are produced. These are present in pair in humans and other vertebrates.
Uterus:
It is an organ located in the lower body of a female mammal or woman. In this region the offspring is conceived. It is known as a womb in which the fetus is gestate before birth.
Uterine tubes:
These are small and coiled tubes located near the ovaries. They travel a small distance to meet the uterine horns. These are also known as the fallopian tubes or oviducts.
The ovarian ligament:
It is also known as the utero-ovarian ligament. It is a fibrous ligament which joins the ovary to the side surface of the uterus. This ligament expands from the ovary in the different direction.
The broad ligament:
It is also known as the peritoneal fold. It connects the ovaries, fallopian tubes, and uterus to the pelvis. It is a double-layered piece of the mesothelial cells. It runs from the borders of the uterus medially to the pelvic sidewalls laterally as well as the pelvic floor inferiorly. Thus, it is the largest of the ovarian attachments.
The female reproductive system is comprised of the external and internal sex organs which play a role in the reproduction of new offspring.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 51 Solutions
Laboratory Manual for Holes Human Anatomy & Physiology Fetal Pig Version
- If a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade one small protein molecule into 8 molecules of pyruvic acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume there is no other carbon source. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in molecules of ATP.arrow_forwardIf a bacterium using aerobic respiration was to degrade a 30 mM solution of citric acid, how many ATP would that cell make? Assume no other carbon source is available. Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forwardHow much ATP will be produced during the following metabolic scenario: Aerobic respiration of a 5mM lipid solution that is made up of one glycerol and an 8-carbon fatty acid and 12-carbon fatty acid. Recall that when glycerol breaks down to Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate it costs one ATP but your get an extra FADH2. Every two carbons of a fatty acid break down to one acetyl-CoA. (pathways will be provided on the exam) Units cannot be entered in this style of question but the units of your answer should be in mM of ATP.arrow_forward
- When beta-lactamase was isolated from Staphylcoccus aureus and treated with a phosphorylating agent, only the active site, serine was phosphorylated. Additionally, the serine was found to constitute 0.35% (by weight) of this beta-lactamase enzyme. Using this, calculate the molecular weight of this enzyme and estimate the number of amino acids present in the polypeptide.arrow_forwardBased on your results from the Mannitol Salt Agar (MSA) media, which of your bacteria were mannitol fermenters and which were not mannitol fermenters?arrow_forwardhelp tutor pleasearrow_forward
- Q8. A researcher wants to study the effectiveness of a pill intended to reduce stomach heartburn in pregnant women. The researcher chooses randomly 400 women to participate in this experiment for 9 months of their pregnancy period. They all need to have the same diet. The researcher designs two groups of 200 participants: One group take the real medication intended to reduce heartburn, while the other group take placebo medication. In this study what are: Independent variable: Dependent variable: Control variable: Experimental group: " Control group: If the participants do not know who is consuming the real pills and who is consuming the sugar pills. This study is It happens that 40% of the participants do not find the treatment helpful and drop out after 6 months. The researcher throws out the data from subjects that drop out. What type of bias is there in this study? If the company who makes the medication funds this research, what type of bias might exist in this research work?arrow_forwardHow do I determine the inhertiance pattern from the pedigree diagram?arrow_forwardits an open book assignemntarrow_forward
- Describe two different gene regulation mechanisms involving methylationarrow_forwardWhat is behavioral adaptarrow_forward22. Which of the following mutant proteins is expected to have a dominant negative effect when over- expressed in normal cells? a. mutant PI3-kinase that lacks the SH2 domain but retains the kinase function b. mutant Grb2 protein that cannot bind to RTK c. mutant RTK that lacks the extracellular domain d. mutant PDK that has the PH domain but lost the kinase function e. all of the abovearrow_forward
 Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781305112100Author:Cecie Starr, Beverly McMillanPublisher:Cengage Learning Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





