
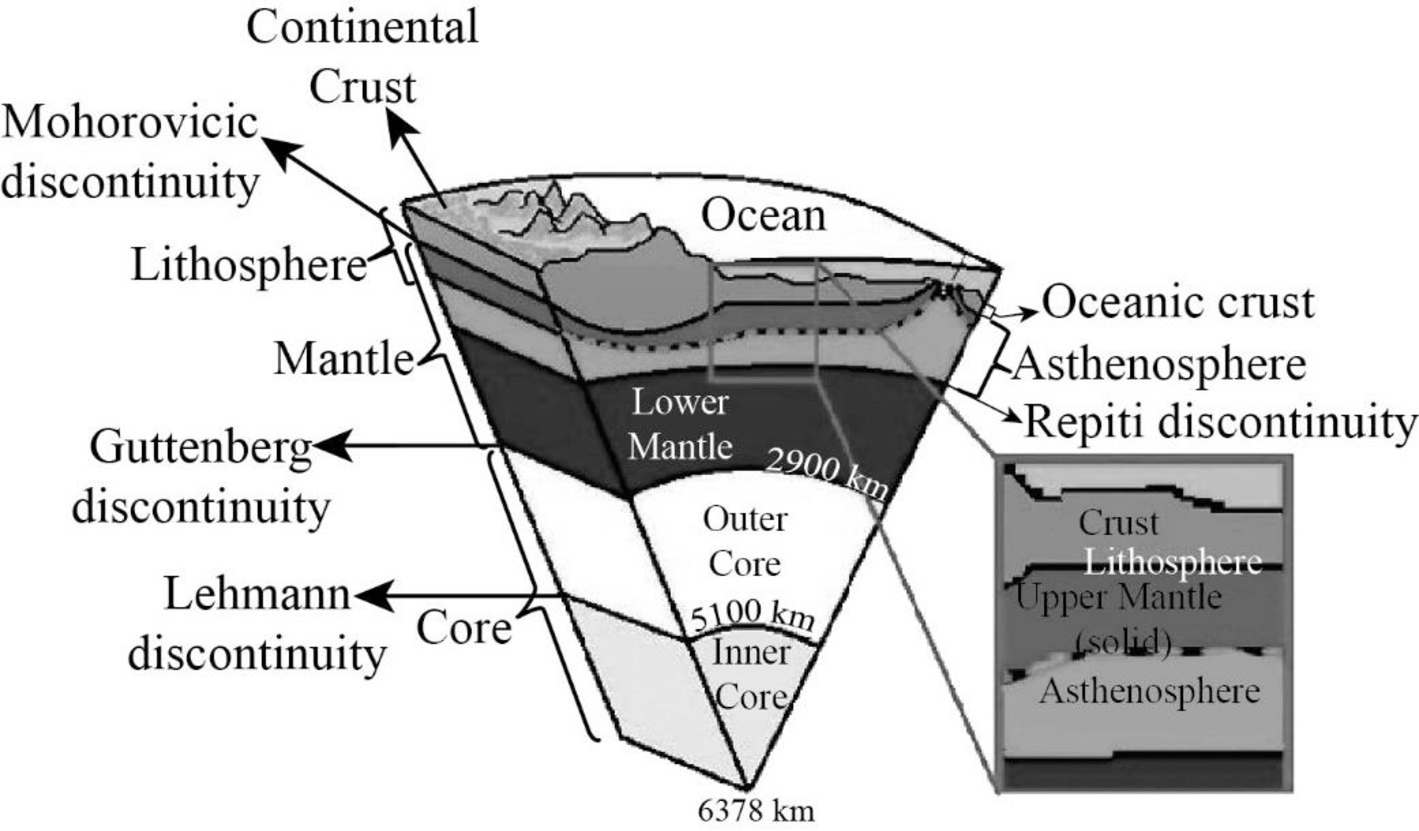
The sketch of the major layers of Earth.
Answer to Problem 1BYL
The Earth incorporates three layers which are the crust, the mantle, and the core where each layer has a distinct chemical composition.
Explanation of Solution
The crust, which is the outermost layer of the Earth,encompasses two main divisions, the younger and denser oceanic crust and the older and less dense continental crust. The oceanic crust that is nearly 7 kilometers thick exhibits almost analogous composition of mostly basaltic rocks while the continental crust whose thickness varied from 35 to 70 kilometers pertaining to surface areas or mountains constitutes granitic rocks called granodiorite. The crust can be also divided into upper crust and lower crust and the discontinuity between them is known as Conrad discontinuity.
The mantle is the second layer of Earth. Peridotite and minerals with good amounts of magnesium and iron occur in the mantle which lies below the lower crust extending upto 2900 kilometers from the base of lower crust, possessing the Earth’s volume by 82 percent. The discontinuity surface located between the crust and mantle is known as Mohorovicic discontinuity.
The mantle is generally divided into upper mantle and lower mantle. The discontinuity lying between them is the Repiti discontinuity. Major part of the upper mantle is made up of the green mineral olivine. The crust together with the uppermost mantle is known as the lithosphere which forms a rigid layer. The portion of the uppermost mantle which is within the lithosphere is called the lithospheric mantle.
The lower mantle also holds a similar composition like the upper mantle. However, it has minerals formed at extremely high pressures. Almost the entire mantle is solid, rather than molten. The greater temperatures at depths caused some portions to be partially molten, while other portions flowedsince they are weak solids.
The mantle which lies directly below the lithosphere is commonly solid. However, it is hotter compared to the rock above and it flows under pressure. This part of the mantle, termed as the asthenosphere, acts as a soft and weak zone, on top of which, the lithosphere moves.
The core forms the third layer of Earth. The discontinuity present between the lower mantle and core is the Guttenberg discontinuity. The core, which is the Earth’s inner most layer has two layers, the liquid outer core (2250 kilometers thick) and the solid inner core (1221 kilometers thick).
An alloy of iron and nickel is present in the core with traces of elements such as oxygen, silicon, and sulfur that are capable of forming compounds with iron. There is a discontinuity surface between the inner and outer core, which is known as the Lehmann discontinuity.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Exploring Earth Science
- SOUTH Judith River Eagle Warm Mowry Shak Kooter Thermope Jurassic Ellis Seyenite Porphry Metamorphic Rocks Gravity-Slide Faults Bearpaw Shale 3 Mississippian Mission Canyph Devonian Jefferson Limestone an Platheadbandstor Bakken/3 Forks Shale NORTH Ordovician Bighorn Dolomite Little Rocky Mountains No Scale - Drawing is approximate length of Reservation Hogeland Basin Creating a cross-section requires some subjective decisions on your part, but it needs to be geologically reasonable. For example, the thickness and dip of a planar layer should remain relatively constant unless the map data requires otherwise. Planar layers should also be laterally continuous unless there is evidence otherwise. Similarly, keep the structure as simple as you can. Steps to producing a cross section: I. Choose the location and direction of the profile on the geological map (usually a straight line) II. Draw or plot the topography of the profile on the cross-section III. Add the geological features from the…arrow_forwardsecond question plssarrow_forwardH D Figure 13.14 4 v C ax. G Figure 13.15 JV T R K 5 ७ हाकालयकाळात Oldest Younges! Oldest 10arrow_forward
- Pretty much all the solidified lava you see near Kilauea and Mauna Loa is basalt. Using just the satellite imagery, how would you know that these lavas are basaltic (as opposed to andesitic or rhyolitic)?arrow_forwardCompare a passive solar heating system with an active solar heating system.arrow_forwardDescribe what the wind power as an energy source is. Describe 5 advantages of wind power as an energy source. Describe 5 disadvantages of wind power as an energy source. Discuss the future potential wind power as an energy source in the United States. Describe how you would convince the residents of the State of Connecticut to utilize more wind power as an energy sourcearrow_forward
- How is the biofuel ethanol produced?arrow_forwardDistinguish between reserves and resoircesarrow_forwardDescribe what kind of energy source oil ia. Describe 5 advantages of oil as an energy source. Describe 5 disadvantages of oil as energy source. Discuss the future potential of oil as energy source in the United States. Describe how you would convince the residents of the State of Connecticut to utilize more oil as an energy source.arrow_forward
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,





