
Suppose that your
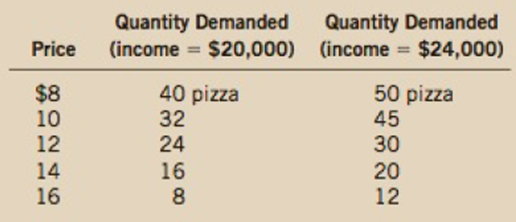
a. Use the midpoint method to calculate your
b. Calculate your income elasticity of demand as your income increases from $20,000 to $24,000 if (i) the price is $12 and (ii) the price is $16.
Subpart (a):
Price elasticity of demand.
Explanation of Solution
- (i) If the income is $20,000, then the price of pizza rises from $8 to $10, and the quantity demanded decreases from 40 to 32. By midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand is calculated as follows:
The price elasticity of demand for pizza is -1.
- (ii) If the income is $24,000, then the price of pizza rises from $8 to $10, and the quantity demanded decreases from 50 to 45. By midpoint method, the price elasticity of demand is calculated as follows:
The price elasticity of demand for pizza is -0.5.
Concept Introduction:
Price elasticity of demand: Price elasticity of demand refers to the percentage change in the demand for goods and services due to change occurred in the price level.
Subpart (b):
Income elasticity of demand.
Explanation of Solution
- (i) If the price is $12 and an income increases from $20,000 to $24,000, then the quantity demanded increases from 24 to 30. By midpoint method, the income elasticity of demand is calculated as follows:
The income elasticity of demand for pizza is 1.22.
- (ii) If the price is $12 and an income increases from $20,000 to $24,000, then the quantity demanded increases from 24 to 30. By midpoint method, the income elasticity of demand is calculated as follows:
The income elasticity of demand for pizza is 2.22.
Concept Introduction:
Income elasticity of demand: It measures how much quantity demanded of a good responds to the change in consumers’ income.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK ESSENTIALS OF ECONOMICS
- Can you show me how to do part d?arrow_forwardProblem Set#8 Part I You are the manager of a firm producing a good in a particular market environment. The following table details the price charged (P) and the total cost (TC) incurred by your firm at various production levels (Q). Price (P) $125 Quantity (Q) Total Cost (TC) 0 150 125 1 175 125 2 210 125 3 255 125 4 310 125 5 375 125 6 450 125 7 535 125 8 630 125 9 735 125 10 850 125 11 975 125 12 1,110 125 13 1,255 125 14 1,410 125 15 1,575 1. Based on the information provided in the table above, identify the type of market structure in which the firm operates. Explain your reasoning! 2. Add seven columns to the table above, one for each of the following variables: AFC, ATC, VC, AVC, MC, TR, and MRarrow_forwardThe table below presents the demand schedule and marginal costs facing a monopolist producer. a. Fill in the total revenue and marginal revenue columns. Instructions: Enter your answers as a whole number. If you are entering any negative numbers be sure to include a negative sign (-) in front of those numbers. Leave no cells blank. Enter 0 if appropriate. Q 0 P ($) 8 TR ($) 0 MR ($) MC ($) 1 7 2 6 3 5 1 2 3 4 4 4 5 5 3 6 6 2 7 1 8 0 b. What is the profit-maximizing level of output? units c. What price will the monopolist charge to maximize profits? $ 7 8arrow_forward
- not use ai pleasearrow_forward1. Lisa has $48 per week set aside for coffees (x) and lunches (z). The price of coffee is $4 and lunches are $6. What is Lisa's budget line equation (with z on the left-hand side)? Graph the budget line, and show how it changes when the price of lunches rise to $8 (including intercepts). What is the new budget line equation? 2. Suppose utility for a consumer of movies (x) and golf (z) is U = 20x0.420.5. The consumer has set aside $1000 to consumer movies and golf for a year. a. If the price of movies is $20 and the price of golf is $40, what is the utility-maximizing consumption of movies and golf? b. Show the optimal consumption bundle on a graph, showing a budget line (with intercepts), a tangent indifference curve, and the optimal choice. 3. Sam has set aside $480 for entertainment this month, which is golf (x) and/or bowling (z). A round of golf is $40 and a night of bowling is $30. His utility function is U = 3x + 2z. a. What is his MRS? b. Solve for the optimal choice of golf…arrow_forwardQuestion Seven There are specific applications of the hidden-action or moral hazard model. Consider employment contracts signed between a firm's owners and a manager who runs the firm on behalf of the owners. The manager is offered an employment contract which they can accept and decide how much effort, e ≥ 0, to exert. Suppose that an increase in effort, e, increases the firm's gross profit, not including payments to the manager, but is personally costly to the manager and the firm's gross profit, Пg, takes the following form: Пg = e +ε, ε~N(0,2). Let s denote the salary, which may depend on effort and/or gross profit, depending on what the owner can observe, offered as part of the contract between the owner and manager. Suppose that the manager is risk averse and has a utility function with respect to salary of the form: Aσ² U(W)=μ- 2 a) Derive the optimal result of the owner's expected net profit where there is full information and state what it implies. b) Suppose now that the…arrow_forward
- 1. The IS/MP model assumes that the Fed sets the real interest rate at a given level Rt. Suppose the Fed adopts a monetary policy rule that instructs it how to change the real interest rate in response to short-run output. Let's call this a monetary policy rule (MPR): The parameter x is positive. Rt=+xY a) Redraw the IS/MP diagram replacing the MP curve with the MPR curve. Show how an aggregate demand shock affects output and interest rates in the short run. Use the IS and MPR equations to solve for the changes in output and the real interest rate. b) How does the change in a affect investment in the IS/MPR model? Explain how a tax cut affects short-run output and investment in this version of the short-run model. The effect on investment is called crowding out. c) Add the Phillips curve to complete the short-run model. Illustrate how the Fed's choice of large it makes reveals its trade off between inflation and output in the short run.arrow_forwardnot use ai pleasearrow_forwardFems A and B are duopolist producers of widgets. The cost function for producing widgets C(Q)-Q² The market demand function for widgets i Q-192P Qmeasures thousands of widgets per year, Competition in the widget market is described by the Coumot model Instructions: Round your answers to 2 decimal places a What are the firms' Nanh equbrium output? b. What is the resulting price? c. What do they each emp How does the price compare to marginal cost? Price is ck to marginal cost How do the price and the two fems' joint profit compare to the monopoly price and prof Compared to the monopoly price, the Cournot price is to sed. Compared to the monopoly profit, the joint profit of the two fems to selectarrow_forward
- Suppose the marginal social cost of television sets is $100. This is constant and equal to the average cost of television sets. The annual demand for television sets is given by the following equation: Q = 200,000-500P, where Qis the quantity sold per year and P is the price of television sets. a) If television sets are sold in a perfectly competitive market, calculate the annual number sold. Under what circumstances will the market equilibrium be efficient? b) Show the losses in well-being each year that would result from a law limiting sales of television sets to 100,000 per year. Show the effect on the price, marginal social benefit, and marginal social cost of television sets. Show the net loss in well-being that will result from a complete ban on the sales of television sets. (show with graphs.)arrow_forwardrefer to exhibit 8.12 and identify each curve in the grapharrow_forwardQ1. (Chap 1: Game Theory.) In the simultaneous games below player 1 is choosing between Top and Bottom, while player 2 is choosing between Left and Right. In each cell the first number is the payoff to player 1 and the second is the payoff to player 2. Part A: Player 1 Top Bottom Player 2 Left 25, 22 Right 27,23 26,21 28, 22 (A1) Does player 1 have a dominant strategy? (Yes/No) If your answer is yes, which one is it? (Top/Bottom) (A2) Does player 2 have a dominant strategy? (Yes/No.) If your answer is yes, which one is it? (Left/Right.) (A3) Can you solve this game by using the dominant strategy method? (Yes/No) If your answer is yes, what is the solution?arrow_forward
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
 Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning
Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337617383Author:Roger A. ArnoldPublisher:Cengage Learning







