
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
12th Edition
ISBN: 9780321909107
Author: Paul G. Hewitt
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Textbook Question
Chapter 5, Problem 67RCQ
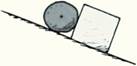
The stone is at rest, interacting with both the surface of the incline and the block, (a) Identify all the forces that act on the stone, and draw appropriate force vectors, (b) Show that the net force on the stone is zero. (Hint 1: There are two normal forces on the stone. Hint2: Be sure the vectors you draw are for forces that act on the stone, not by the stone on the surfaces.)
Expert Solution & Answer
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Students have asked these similar questions
3
Set
ба
||Axl
49.32
6b
71
Ay
22
Magnitude of A
Angle of A
24.04
Angle of -A
22
54
155.96
° (pos Ax) 204.04
° (neg Ax) 335.96
°
(pos Ax)
° (neg Ax)
115.77
° (pos Ax) 295.77
° (pos Ax)
-39
81
208.78
° (neg Ax) 28.78
°
(neg Ax)
3AA . not sure what i am getting wrong
Chapter 5 Solutions
Conceptual Physics (12th Edition)
Ch. 5 - When you push against a wall with your fingers,...Ch. 5 - A boxer can hit a heavy bag with great force. Why...Ch. 5 - How many forces are required for an interaction?Ch. 5 - Prob. 4RCQCh. 5 - Consider hitting a baseball with a bat. If we call...Ch. 5 - Prob. 6RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 7RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 8RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 9RCQCh. 5 - Earth pulls down on you with a gravitational force...
Ch. 5 - Prob. 11RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 12RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 13RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 14RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 15RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 16RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 17RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 18RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 19RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 20RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 21RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 22RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 23RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 24RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 25RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 26RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 27RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 28RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 29RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 30RCQCh. 5 - 31. A van exerts a force on trailers of different...Ch. 5 - a. The accelerations of the boxes
b. The...Ch. 5 - 33. Three identical pucks, A, B, and C, are...Ch. 5 - Prob. 34RCQCh. 5 - 35. The photo shows Steve Hewitt and daughter...Ch. 5 - Prob. 36RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 37RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 38RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 39RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 40RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 41RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 42RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 43RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 44RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 45RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 46RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 47RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 48RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 49RCQCh. 5 - Suppose that two carts, one twice as massive as...Ch. 5 - Prob. 51RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 52RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 53RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 54RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 55RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 56RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 57RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 58RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 59RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 60RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 61RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 62RCQCh. 5 - The same stone is being accelerated vertically...Ch. 5 - Prob. 64RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 65RCQCh. 5 - Here the stone is sliding down a friction-free...Ch. 5 - The stone is at rest, interacting with both the...Ch. 5 - Prob. 68RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 69RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 70RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 71RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 72RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 73RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 74RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 75RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 76RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 77RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 78RCQCh. 5 - Prob. 79RCQCh. 5 - The strong man can withstand the tension force...
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill
Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...PhysicsISBN:9780078807213Author:Paul W. ZitzewitzPublisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781285737027Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Physics: Principles and Problems, Student...
Physics
ISBN:9780078807213
Author:Paul W. Zitzewitz
Publisher:Glencoe/McGraw-Hill

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781285737027
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning
Newton's First Law of Motion: Mass and Inertia; Author: Professor Dave explains;https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=1XSyyjcEHo0;License: Standard YouTube License, CC-BY