
Concept explainers
1.
Journalize
1.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and
Record the adjusting entries of Company FP.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Store supplies expense (1) | 6,000 | ||
| Store supplies | 6,000 | |||
| (To record store supplies expense) | ||||
| b. | Insurance expenses | 2,800 | ||
| Prepaid expenses | 2,800 | |||
| (To record prepaid selling expenses) | ||||
| c. | 3,000 | |||
| 3,000 | ||||
| (To record depreciation expenses) | ||||
| d. | Cost of goods sold | 2,700 | ||
| Merchandise inventory (2) | 2,700 | |||
| (To record the inventory shrinkage) |
Table (1)
a. To record store supplies expense:
- Store supplies expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit office supplies expense with $6,000.
- Store supplies are an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office supplies with $6,000.
b. To record prepaid insurance expenses:
- Insurance expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $2,800.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $2,800.
c. To record depreciation expenses:
- Depreciation expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $3,000.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $3,000.
d. To record the shrinkage of inventory:
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and they are increased. Thus, it is debited with $2,700.
- Inventory is an asset account, and they are increased. Hence, debit the inventory returns estimated account by $2,700.
Working Note:
Compute the Store supplies expense.
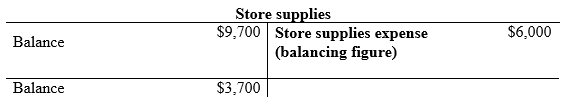 (1)
(1)
Compute the shrinkage of inventory.
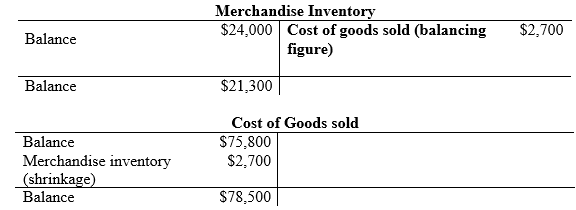 (2)
(2)
2.
Prepare the multi- step income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare the income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015.
| Company FP | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended October 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Sales | $227,100 | |
| Less: Sales discounts | $1,000 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | $5,000 | ($6,000) |
| Net sales | $221,100 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold (2) | ($78,500) | |
| Gross profit | $142,600 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Selling expenses | ||
| Depreciation expense—Store equipment | $3,000 | |
| Sales salaries expense | $31,500 | |
| Rent expense—Selling space | $13,000 | |
| Store supplies expense (1) | $6,000 | |
| Advertising expense | $17,800 | |
| Total selling expenses | $71,300 | |
| General and administrative expenses | ||
| Insurance expense | $2,800 | |
| Office salaries expense | $31,500 | |
| Rent expense—Office space | $13,000 | |
| Total general and administrative expenses | $47,300 | |
| Total expenses | ($118,600) | |
| Net income | $24,000 | |
Table (2)
Thus, the net income of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015 is $24,000.
3.
Prepare the single-step income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Single-step income statement: This statement displays the total revenues as one line item from which the total expenses including cost of goods sold is subtracted to arrive at the net profit /net loss for the period.
Prepare the income statement of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015.
| Company FP | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended October 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Net sales | $221,100 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold (2) | $78,500 | |
| Selling expenses (Refer Table (2)) | $71,300 | |
| General and administrative expense (Refer Table (2)) | $47,300 | |
| Total expenses | ($197,100) | |
| Net income | $24,000 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the net income of Company FP for the year ended October 31, 2015 is $24,000.
4.
Compute
4.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the
Acid test ratio: It is a ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay back its current liabilities by liquid assets that are current assets except inventory and prepaid expenses.
Gross margin ratio: The percentage of gross profit generated by every dollar of net sales is referred to as gross margin ratio. This ratio measures the profitability of a company by quantifying the amount of income earned from sales revenue generated after cost of goods sold are paid. The higher the ratio, the more ability to cover operating expenses.
Formula:
Compute current ratio, acid test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company FP.
| Computation of ratios | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Cash | $7,400 |
| Merchandise inventory (2) | $21,300 |
| Store supplies (1) | $3,700 |
| Prepaid insurance | $3,800 |
| Total current assets (A) | $36,200 |
| Current liabilities (B) | $18,000 |
| Current ratio | 2.01 |
| Quick assets (Cash) (C) | $7,400 |
| Current liabilities (D) | $18,000 |
| Acid-test ratio | 0.41 |
| Net Sales (E) | $221,100 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (2) | ($78,500) |
| Gross margin (F) | $142,600 |
| Gross margin ratio | 0.64 or 64% |
Table (4)
The current ratio, acid- test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company FP is 2.01, 0.41 and 0.64 or 64% respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting, Chapters 1-17 - With Access (Looseleaf)
- Can you help me solve this general accounting question using the correct accounting procedures?arrow_forwardHorngren's Financial & Managerial Accounting: The Managerial Chapters, 8th Edition. E-M:9-14 Describing the balanced scorecard and identifying key performance indicators for each perspectiveConsider the following key performance indicators and classify each indicator according to the balanced scorecard perspective it addresses. Choose from the financial perspective, customer perspective, internal business perspective, and the learning and growth perspective. a.Number of customer complaintsb.Number of information system upgrades completedc.Residual incomed.New product development timee.Employee turnover ratef.Percentage of products with online help manualsg.Customer retentionh.Percentage of compensation based on performancei.Percentage of orders filled each weekj.Gross margin growthk.Number of new patentsl.Employee satisfaction ratingsm.Manufacturing cycle time (average length of production process)n.Earnings growtho.Average machine setup timep.Number of new customersq.Employee…arrow_forwardDo fast answer of this general accounting questionarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





