
Concept explainers
1.
Journalize
1.
Explanation of Solution
Adjusting entries: Adjusting entries are those entries which are recorded at the end of the year, to update the income statement accounts (revenue and expenses) and
Record the adjusting entries of Company N.
| Date | Accounts title and explanation | Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| a. | Store supplies expense (1) | 4,050 | ||
| Store supplies | 4,050 | |||
| (To record store supplies expense) | ||||
| b. | Insurance expenses | 1,400 | ||
| Prepaid expenses | 1,400 | |||
| (To record prepaid selling expenses) | ||||
| c. | 1,525 | |||
| 1,525 | ||||
| (To record depreciation expenses) | ||||
| d. | Cost of goods sold | 1,600 | ||
| Merchandise inventory (2) | 1,600 | |||
| (To record the inventory shrinkage) |
Table (1)
a. To record store supplies expense:
- Store supplies expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, debit office supplies expense with $4,050.
- Store supplies are an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit office supplies with $4,050.
b. To record prepaid insurance expenses:
- Insurance expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $1,400.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $1,400.
c. To record depreciation expenses:
- Depreciation expense is an expense account and it is increased. Therefore, it is debited with $1,525.
- Prepaid expense is an asset account and it is decreased. Therefore, credit prepaid selling expense with $1,525.
d. To record the shrinkage of inventory:
- Cost of goods sold is an expense and they are increased. Thus, it is debited with $1,600.
- Inventory is an asset account, and they are increased. Hence, debit the inventory returns estimated account by $1,600.
Working Note:
Compute the Store supplies expense.
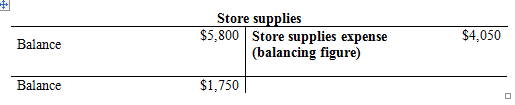 (1)
(1)
Compute the shrinkage of inventory.
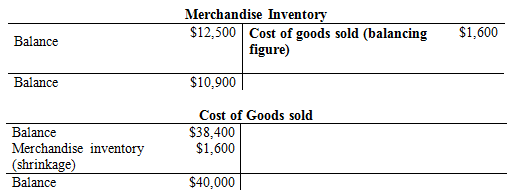 (2)
(2)
2.
Prepare the multi-step income statement of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Multi-step income statement: The income statement represented in multi-steps with several subtotals, to report the income from principal operations, and separate the other expenses and revenues which affect net income, is referred to as multi-step income statement.
Prepare the income statement of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015.
| Company N | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended January 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Sales | $111,950 | |
| Less: Sales discounts | $2,000 | |
| Sales returns and allowances | $2,200 | ($4,200) |
| Net sales | $107,750 | |
| Less: Cost of goods sold (2) | ($40,000) | |
| Gross profit | $67,750 | |
| Expenses | ||
| Selling expenses | ||
| Depreciation expense—Store equipment | $1,525 | |
| Sales salaries expense | $17,500 | |
| Rent expense—Selling space | $7,500 | |
| Store supplies expense (1) | $4,050 | |
| Advertising expense | $9,800 | |
| Total selling expenses | $40,375 | |
| General and administrative expenses | ||
| Insurance expense | $1,400 | |
| Office salaries expense | $17,500 | |
| Rent expense—Office space | $7,500 | |
| Total general and administrative expenses | $26,400 | |
| Total expenses | ($66,775) | |
| Net income | $975 | |
Table (2)
Thus, the net income of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015 is $975.
3.
Prepare the single-step income statement of Company N for the year ended December 31, 2015.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Single-step income statement: This statement displays the total revenues as one line item from which the total expenses including cost of goods sold is subtracted to arrive at the net profit /net loss for the period.
Prepare the income statement of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015.
| Company N | ||
| Statement of Income | ||
| For the year ended January 31, 2015 | ||
| Particulars | Amount | Amount |
| Net sales | $107,750 | |
| Less: Expenses | ||
| Cost of goods sold (2) | $40,000 | |
| Selling expenses (Refer Table (2)) | $40,375 | |
| General and administrative expense (Refer Table (2)) | $26,400 | |
| Total expenses | ($106,775) | |
| Net income | $975 | |
Table (3)
Thus, the net income of Company N for the year ended January 31, 2015 is $975.
4.
Compute
4.
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the
Acid test ratio: It is a ratio used to determine a company’s ability to pay back its current liabilities by liquid assets that are current assets except inventory and prepaid expenses.
Gross margin ratio: The percentage of gross profit generated by every dollar of net sales is referred to as gross margin ratio. This ratio measures the profitability of a company by quantifying the amount of income earned from sales revenue generated after cost of goods sold are paid. The higher the ratio, the more ability to cover operating expenses.
Formula:
Compute current ratio, acid test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company N.
| Computation of ratios | |
| Particulars | Amount |
| Cash | $1,000 |
| Merchandise inventory (2) | $10,900 |
| Store supplies (1) | $1,750 |
| Prepaid insurance | $1,000 |
| Total current assets (A) | $14,650 |
| Current liabilities (B) | $10,000 |
| Current ratio | 1.47 |
| Quick assets (Cash) (C) | $1,000 |
| Current liabilities (D) | $10,000 |
| Acid-test ratio | 0.10 |
| Net Sales (E) | $107,750 |
| Less: Cost of Goods Sold (2) | ($40,000) |
| Gross margin (F) | $67,750 |
| Gross margin ratio | 0.63 or 63% |
Table (4)
The current ratio, acid- test ratio and gross margin ratio of Company N is 1.47, 0.10 and 0.63 or 63% respectively.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Financial Accounting.
- Summit Outdoors began the year with an accounts receivable balance of $150,000 and ended the year with a balance of $175,000. The company's credit sales for the year totaled $700,000, generating a gross profit of $280,000. Calculate the receivables turnover ratio for the year.arrow_forwardPlease provide problem with accounting questionarrow_forwardPlease provide solution this accounting questionarrow_forward
- DC Corporation's accounting records reflect the following inventories: Inventory Type Dec. 31, 2023 Dec. 31, 2022 Raw materials inventory $350,000 Work in process inventory $280,000 Finished goods inventory $210,000 $290,000 $170,000 $180,000 If DC Corporation's cost of goods manufactured for 2023 amounted to $1,520,000, its cost of goods sold for the year is ____. Answer: $1,490,000arrow_forwardAccounting problemsarrow_forwardWhat is the firm's return on equity?? Accountingarrow_forward
- BlueSky Corp. has $1.5 million in current assets and $700,000 in fixed assets, less $250,000 in accumulated depreciation. The firm's current liabilities total $350,000, and long-term liabilities total $450,000. What is the firm's equity? a) $1,150,000 b) $1,450,000 c) $1,250,000 d) $1,050,000arrow_forwardHello tutor answer the accounting question not use ai please don'tarrow_forwardGeneral accounting questionarrow_forward
- Sarah bought 150 shares of stock at $28 per share. During the year, she received $270 in dividends. She later sold the stock for $42 per share. What was Sarah's return on the stock? a) $2,250 b) $2,370 c) $2,520 d) $2,700arrow_forwardplease post this question in Account tutors feedarrow_forwardNeed help with this question solution general accountingarrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





