
To calculate: The size of settlements, and if Person X is a plaintiff, what will be his choice on the interest rate.
Introduction:
The series of payments that are made at equal intervals is an
Answer to Problem 58QP
Solution:
The size of the settlement or the award is $527,202.72.
Explanation of Solution
Given information:
Person X serves on a jury. A plaintiff sues the city for the injuries that are continued after the accident of a sweeper in the street. In the trial, the doctors stated that it will be 5 years earlier the plaintiff would be able to return back to work. The decision made by the jury was in favor of the plaintiff. Person X is the foreperson of the jury. The jury proposes that the plaintiff will be provided an award that is as follows:
- a) The
present value of the 2 years back pay. The annual salary of the plaintiff for the last 2 years would have been $43,000 and $46,000. - b) The present value of the 5 years’ salary in future is assumed to be $49,000 for a year.
- c) The sum that has to be paid for the pain and suffering is $200,000.
- d) The amount of the court costs is $25,000.
It has to be assumed that the payment of the salary is made at the end of the month in equal amounts. The rate of interest is 7% at an effective annual rate.
Time line of the cash flow:
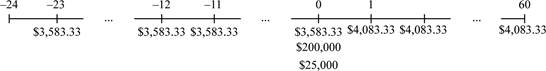
Note: The cash flows here would have happened in the past and will also occur in the future. It is essential to find the present cash flows. Before computing the present value of the cash flow, it is essential to adjust the rate of interest and thus, the effective monthly interest rate can be found. Finding the annual percentage rate with compounding monthly and dividing it by twelve, it will provide the effective monthly rate. The annual percentage rate with the monthly compounding is calculated as follows:
Compute the annual percentage rate with the effective annual rate:
Hence, the annual percentage rate is 0.0678 or 6.78%.
To determine the today’s value of the back pay from 2 years ago, it is essential to find the
Formula to calculate the future value of an annuity:
Note: C denotes the payments, r denotes the rate of exchange, and t denotes the period.
Compute the future value annuity:
Hence, the future value of an annuity is $44,362.73.
Formula to compute the future value:
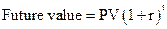
Note: C denotes the annual cash flow or an annuity payment, r represents the rate of interest, and t denotes the number of payments.
Compute the future value:
Hence, the future value is $47,468.12
Note: The future value of the annuity is determined by the effective monthly rate and the future value of the lump sum is determined by the effective annual rate. The other alternate way to determine the future value of the lump sum with the effective annual rate as long it is utilized for 12 periods. The solution would be the same in either way.
Now the today’s value of the last year’s back pay is calculated as follows:
Compute the future value annuity:
Hence, the future value of the annuity is $47,457.81.
Next, it is essential to determine today’s value of the 5 year’s future salary.
Formulae to calculate the present value annuity:
Note: C denotes the payments, r denotes the rate of exchange, and t denotes the period.
Compute the present value annuity for without fee:
Hence, the present value of the annuity is $207,276.79.
The today’s value of the jury award is calculated by adding the sum of salaries, the court costs, and the compensation for the pain and sufferings. The award amount is calculated as follows:
Hence, the award amount or the size of the settlement is $527,202.72.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Essentials of Corporate Finance (Mcgraw-hill/Irwin Series in Finance, Insurance, and Real Estate)
- High Hand Nursery has total assests of $900,000, current liabilities of $202,000, and long-term liabilities of $104,000. There is $90,000 in preferred stock outstanding. Twenty thousand shares of common stock have been issued. a. Compute book value (net worth) per share. b. If there is $40,000 in earnings available to common stockholders for dividends, and the firm's stock has a P/E of 22 times earnings per share, what is the current price of the stock? c. What is the ratio of market value per share to book value per share?arrow_forwardNeed the WACC % WACC and Optimal Capital Structure F. Pierce Products Inc. is considering changing its capital structure. F. Pierce currently has no debt and no preferred stock, but it would like to add some debt to take advantage of the tax shield. Its investment banker has indicated that the pre-tax cost of debt under various possible capital structures would be as follows: Market Debt-to-Value Ratio (wd) Market Equity-to-Value Ratio (ws) Market Debt-toEquity Ratio (D/S) Before-Tax Cost ofDebt (rd) 0.0 1.0 0.00 6.0 % 0.10 0.90 0.1111 6.4 0.20 0.80 0.2500 7.0 0.30 0.70 0.4286 8.2 0.40 0.60 0.6667 10.0 F. Pierce uses the CAPM to estimate its cost of common equity, rs, and at the time of the analaysis the risk-free rate is 5%, the market risk premium is 7%, and the company's tax rate is 25%. F. Pierce estimates that its beta now (which is "unlevered" because it currently has no debt) is 1.4. Based on this information, what…arrow_forwardNed's Co. has an average collection period of 45 days and an operating cycle of 130 days. It has a policy of keeping at least $10 on hand as a minimum cash balance, and has a beginning cash balance for the first quarter of $20. Beginning receivables for the quarter amount to $35. Sales for the first and second quarters are expected to be $110 and $125, respectively, while purchases amount to 80% of the next quarter's forecast sales. The accounts payable period is 90 days. What are the cash disbursements for the first quarter? Question 4 options: $92 $88 $76 $100 $110arrow_forward
- Liberal credit terms for customers is associated with a restrictive short-term financial policy. Question 3 options: True Falsearrow_forwardAn accounts payable period decrease would increase the length of a firm's cash cycle. Consider each in isolation. Question 6 options: True Falsearrow_forwardWhich of the following is the best definition of cash budget? Question 10 options: Costs that rise with increases in the level of investment in current assets. A forecast of cash receipts and disbursements for the next planning period. A secured short-term loan that involves either the assignment or factoring of the receivable. The time between sale of inventory and collection of the receivable. The time between receipt of inventory and payment for it.arrow_forward
- Short-term financial decisions are typically defined to include cash inflows and outflows that occur within __ year(s) or less. Question 9 options: Four Two Three Five Onearrow_forwardA national firm has sales of $575,000 and cost of goods sold of $368,000. At the beginning of the year, the inventory was $42,000. At the end of the year, the inventory balance was $45,000. What is the inventory turnover rate? Question 8 options: 8.46 times 13.22 times 43.14 times 12.78 times 28.56 timesarrow_forwardThe formula (Cash cycle + accounts payable period) correctly defines the operating cycle. Question 7 options: False Truearrow_forward
- An accounts payable period decrease would increase the length of a firm's cash cycle. Consider each in isolation. Question 6 options: True Falsearrow_forwardWhich of the following issues is/are NOT considered a part of short-term finance? Question 5 options: The amount of credit that should be extended to customers The firm determining whether to issue commercial paper or obtain a bank loan The amount of the firms current income that should be paid out as dividends The amount the firm should borrow short-term A reasonable level of cash for the firm to maintainarrow_forwardLiberal credit terms for customers is associated with a restrictive short-term financial policy. Question 3 options: True Falsearrow_forward
