
Concept explainers
1.
General Ledger
General ledger refers to the ledger that records all the transactions of the business related to the company’s assets, liabilities, owners’ equities, revenues, and expenses. Each subsidiary ledger is represented in the general ledger by summarizing the account.
Accounts payable control account and subsidiary ledger
Accounts payable account and subsidiary ledger is the ledger which is used to post the creditors transaction in one particular ledger account. It helps the business to locate the error in the creditor ledger balance. After all transactions of creditor accounts are posted, the balances in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger should be totaled, and compare with the balance in the general ledger of accounts payable. If both the balance does not agree, the error has been located and corrected.
Purchase journal
Purchase journal refers to the journal that is used to record all purchases on account. In the purchase journal, all purchase transactions are recorded only when the business purchased the goods on account. For example, the business purchased cleaning supplies on account.
Cash payments journal
Cash payments journal refers to the journal that is used to record all transaction which involves the cash payments. For example, the business paid cash to employees (salary paid to employees).
To Prepare: A single column revenue journal and cash receipt journal, and post the accounts in the accounts payable subsidiary ledger.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Purchase journal
Purchase journal of Company WTE in the month of October 2016 is as follows:
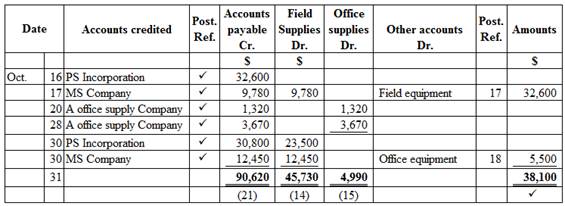
Figure (1)
Cash payment journal
Cash payment journal of Company WTE in the month of October 2016 is as follows:
Cash payment journal
| Date | Check No. | Account debited | Post Ref. | Other accounts Dr. | Accounts payable Dr. | Cash Dr. | |
| Oct. | 16 | 1 | Rent expense | 71 | 7,000 | 7,000 | |
| 18 | 2 | Field supplies | 14 | 4,570 | 4,570 | ||
| Office supplies | 15 | 650 | 650 | ||||
| 24 |
|
✓ | 32,600 | 32,600 | |||
| 26 |
|
✓ | 9,780 | 9,780 | |||
| 28 | Land | 240,000 | 240,000 | ||||
| 30 |
|
✓ | 1,320 | 1,320 | |||
| 31 | Salary expense | 61 | 32,000 | 32,000 | |||
| 31 | 284,220 | 43,700 | 327,920 | ||||
| ✓ | (21) | (11) | |||||
Table (1)
Accounts payable subsidiary ledger
| Name: A Office supply Company | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| Oct. | 20 | P1 | 1,320 | 1,320 | ||
| 28 | P1 | 3,670 | 4,990 | |||
| 30 | CP1 | 1,320 | 3,670 | |||
Table (2)
| Name: MS Company | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| Oct. | 17 | P1 | 9,780 | 9,780 | ||
| 26 | CP1 | 9,780 | - | |||
| 30 | P1 | 12,450 | 12,450 | |||
Table (3)
| Name: PS Incorporation | ||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref | Debit ($) |
Credit ($) | Balance ($) | |
| Oct. | 16 | P1 | 32,600 | 32,600 | ||
| 24 | CP1 | 32,600 | - | |||
| 30 | P1 | 30,800 | 30,800 | |||
Table (4)
2. and 3.
To
2. and 3.
Explanation of Solution
Prepare the general ledger for given accounts as follows:
| Account: Cash Account no. 11 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 31 | CP1 | 327,920 | 327,920 | |||
Table (5)
| Account: Field supplies Account no. 14 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 18 | CP1 | 4,570 | 4,570 | |||
| 31 | P1 | 47,530 | 52,100 | ||||
Table (6)
| Account: Office supplies Account no. 15 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 18 | CP1 | 650 | 650 | |||
| 31 | P1 | 4,990 | 5,460 | ||||
Table (7)
| Account: Prepaid rent Account no. 16 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 31 | J1 | 15,000 | 15,000 | |||
Table (8)
| Account: Field equipment Account no. 17 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 16 | P1 | 32,600 | 32,600 | |||
| 31 | J1 | 15,000 | 17,600 | ||||
Table (9)
| Account: Office equipment Account no. 18 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| 31 | P1 | 5,500 | 5,500 | ||||
Table (10)
| Account: Land Account no. 19 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 23 | CP1 | 240,000 | 240,000 | |||
Table (11)
| Account: Accounts payable Account no. 21 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 31 | P1 | 90,620 | 90,620 | |||
| 31 | CP1 | 43,700 | 46,920 | ||||
Table (12)
| Account: Salary expense Account no. 61 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 31 | CP1 | 32,000 | 32,000 | |||
Table (13)
| Account: Rent expense Account no. 71 | |||||||
| Date | Item | Post. Ref |
Debit ($) | Credit ($) | Balance | ||
| Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||||||
| Oct. | 16 | CP1 | 7,000 | 7,000 | |||
Table (14)
| Journal Page 01 | |||||
| Date | Description | Post. Ref | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | |
| Oct. | 31 | Prepaid rent | 16 | 15,000 | |
| Field equipment | 17 | 15,000 | |||
| (To record leasing of field equipment) | |||||
Table (15)
4.
To prepare: The accounts payable creditor balances.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Accounts payable creditor balance
Accounts payable creditor balance is as follows:
| Company WTE | |
| Accounts payable creditor balances | |
| October 31, 2016 | |
| Amount ($) | |
| A Office supply Company | 3,670 |
| MS Company | 12,450 |
| PS Incorporation | 30,800 |
| Total |
46,920 |
Table (16)
Accounts payable controlling account
Ending balance of accounts payable controlling account is as follows:
| Company WTE | |
| Accounts payable (Controlling account) | |
| October 31, 2016 | |
| Amount ($) | |
| Opening balance | 0 |
| Add: | |
| Total credits (from purchase journal) | 90,620 |
| 90,620 | |
| Less: | |
| Total debits (from cash payment journal) | (43,700) |
| Total accounts payable | 46,920 |
Table (17)
In this case, accounts payable subsidiary ledger is used to identify, and locate the error by way of cross-checking the creditor balance and accounts payable controlling account. From the above calculation, we can understand that both balances of accounts payable is agree, hence there is no error in the recording and posing of transactions.
5.
To discuss: The reason for using subsidiary ledger for the field equipment.
5.
Explanation of Solution
A subsidiary ledger for the field equipment helps the company to track the cost of each piece of equipment, location, useful life, and other necessary data. This information is used for safeguarding the equipment and determining
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Custom Bundle: Accounting, Loose-leaf Version, 26th + Working Papers, Chapters 1-17, 26th Edition
- PLEASE HELParrow_forwardOne company might depreciate a new computer over three years while another company might depreciate the same model computer over five years...and both companies are right. True Falsearrow_forwardno chatgpAccumulated Depreciation will appear as a deduction within the section of the balance sheet labeled as Property, Plant and Equipment. True Falsearrow_forward
- No ai Depreciation Expense is shown on the income statement in order to achieve accounting's matching principle. True Falsearrow_forwardno aiOne company might depreciate a new computer over three years while another company might depreciate the same model computer over five years...and both companies are right. True Falsearrow_forwardno ai An asset's useful life is the same as its physical life? True Falsearrow_forward
- no ai Depreciation Expense reflects an allocation of an asset's original cost rather than an allocation based on the economic value that is being consumed. True Falsearrow_forwardThe purpose of depreciation is to have the balance sheet report the current value of an asset. True Falsearrow_forwardDepreciation Expense shown on a company's income statement must be the same amount as the depreciation expense on the company's income tax return. True Falsearrow_forward
- Century 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning  Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial Accounting: The Impact on Decision Make...AccountingISBN:9781305654174Author:Gary A. Porter, Curtis L. NortonPublisher:Cengage Learning





