
The tension in each segment of the cable and the vertical distance between points
Answer to Problem 5.1P
The tension in segment
The tension in segment
The tension in segment
The vertical distance between points
Explanation of Solution
Concept Used:
Write the expression for the net moment about end
Here
Calculations:
The free body diagram for the system is shown below.
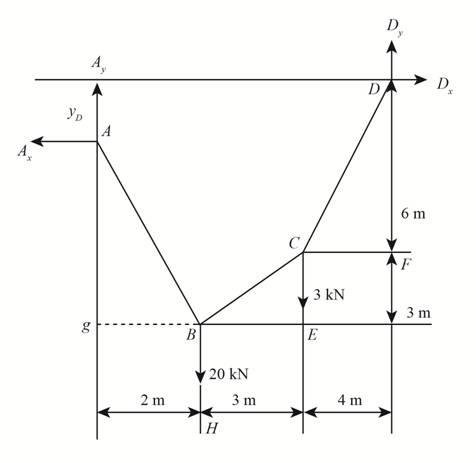
Figure-(1)
Here, the unknown vertical reactions are
The slope of cable
Write the moment about
Consider
Given
Given that
Therefore
Consider
Apply Pythagoras theorem in
Here, the distance between points
Substitute
Take square root on both sides.
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
The free body diagram at point C is shown below.
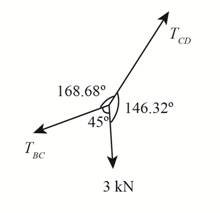
Figure-(2)
Apply Sine Law at point
Here, the tension in cable
Determine
Thus the tension in segment
Thus the tension in segment
Analyze point
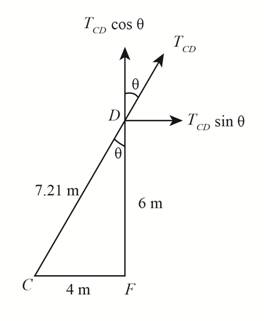
Figure-(3)
Apply Angle Sum Property in
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Consider
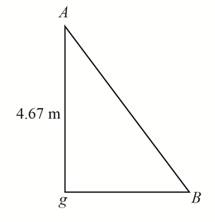
Figure-(4)
Calculate the length
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Analyze point
The free body diagram for point
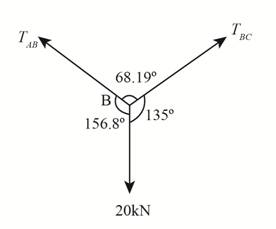
Figure-(5)
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Calculate
Substitute
Apply Sine Law at point
Here, the tension in cable
Determine
Thus the tension in segment
Conclusion:
The tension in segment
The tension in segment
The tension in segment
The vertical distance between points
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Structural Analysis, Student Value Edition Plus Mastering Engineering With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (10th Edition)
- Convert the Followingarrow_forwardSolve for the following right triangle for missing parts: - Angle A - Angle B - Side a - Areaarrow_forwardYOUR TOP STADIA CROSSHAIR IN YOUR LEVEL YEILDS A Roo READING of 7.32 FT. YOUR BOTTOM STADIA CROSSHAIR READS 6.23 FT. How FAR AWAY FROM YOUR INSTRUMENT (LEVEL) IS YOUR STATION WHERE YOUR PHilly Roo IS LOCATED:arrow_forward
- SITUATION. A uniform live load of 16 kN/m and a single concentrated live force of 34 kN are placed on the top beams. If the beams also support a uniform dead load of 3 kN/m, determinearrow_forwardComplete the profile leveling notes in Table 1. Show the arithmetic check and sample calculations of your work. Draw a neat sideview sketch showing the location of all stations and indicate on the sketch all of the numbers in your completed table.arrow_forward3. A level loop was run starting at BM 20 and going clockwise around the loop shown below in Figure 2. The given known elevation of BM 20 is 1418.013 ft. When closing the level loop, BM 20 was found to have an elevation of 1417.890 ft. (a) Adjust the elevation of each station to correct for error. Show sample calculations of your work. (b) What is the accuracy ratio of the survey? BM 20 Elev. 1418.013 2.3 mi BM 20A Observed Elev. 1234.567 2.7 mi 1.6 mil 0.9 mi BM 20B Observed Elev. 1357.913 BM 20C Observed Elev. 1396.963arrow_forward
- A W14 x 82 with 20 ft length column is part of a braced frame. The load and moments computed from service loads, and bending is about the x axis are (axial compressive dead load of 63 k; axial compressive live load of 76 k; upper dead moment of 32 ft-k; upper live moment of 56 ft-k; lower dead moment of 65 ft-k; lower live moment of 95 ft-k; the moments cause the member to bend in double curvature). Determine the lateral-torsional buckling modification factor C₁. ial live load ofarrow_forwardPROBLEM 1 Find the reaction at A and F. Compute for the force in members AB, BD, and DF. Use Method of Joints OR Method of Sections OR both. 3m B D C E 3m 100KN 3m 4marrow_forwardI need detailed help solving this exercise from homework of Engineering Mathematics II.I do not really understand how to do, please do it step by step, not that long but clear. Thank you!P.S.: Please do not use AI, thanks!arrow_forward

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning





