
Concept explainers
The classification of soil based on United States department of agriculture textural classification chart.
Answer to Problem 5.1P
The classification of soil A as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil B as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil C as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil D as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil E as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil F as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil G as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil H as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil I as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
The classification of soil J as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
Consider soil A:
Refer Figure (5.1) “U.S. Department of agriculture textural classification (USDA)”
in the text book.
Mark the percentage of sand for soil A as 20 %, percentage of silt as 20 %, and percentage of clay as 60 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil A as in Figure (1).
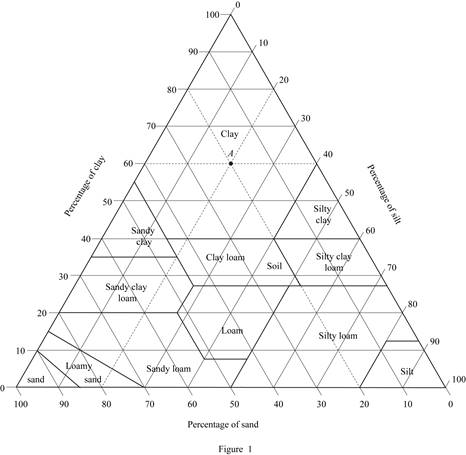
Refer Figure (1).
Hence, the classification of soil A as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil B:
Mark the percentage of sand for soil B as 55 %, percentage of silt as 5 %, and percentage of clay as 40 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil B as in Figure (2).
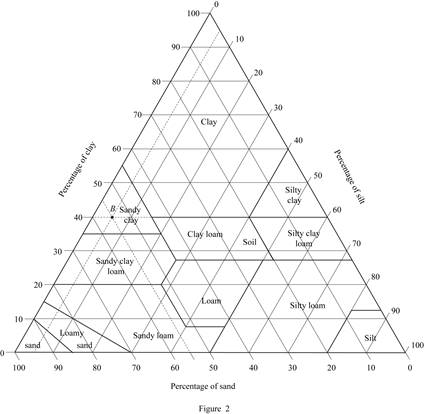
Refer Figure (2).
Thus, classification of soil B as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil C:
Mark the percentage of sand for soil C as 45 %, percentage of silt as 35 %, and percentage of clay as 20 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil C as in Figure (3).
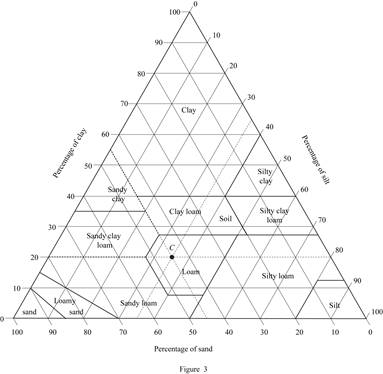
Refer Figure (3).
The classification of soil C as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil D:
Mark the percentage of sand for soil D as 50 %, percentage of silt as 15 %, and percentage of clay as 35 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil D as in Figure (4).
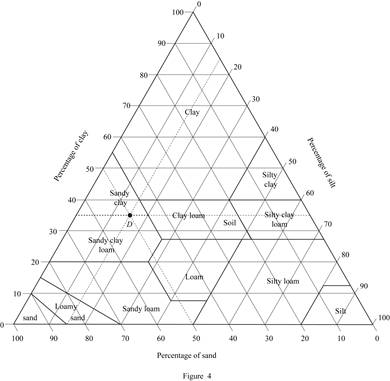
Refer Figure (4).
The classification of soil D as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil E:
Mark the percentage of sand for soil E as 70 %, percentage of silt as 15 %, and percentage of clay as 15 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil E as in Figure (5).
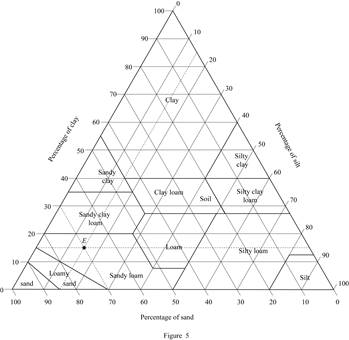
Refer Figure (5).
The classification of soil E as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil F:
Refer Figure (5.1) “U.S. Department of agriculture textural classification (USDA)”
in the text book.
Mark the percentage of sand for soil F as 30 %, percentage of silt as 58 %, and percentage of clay as 12 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil F as in Figure (6).
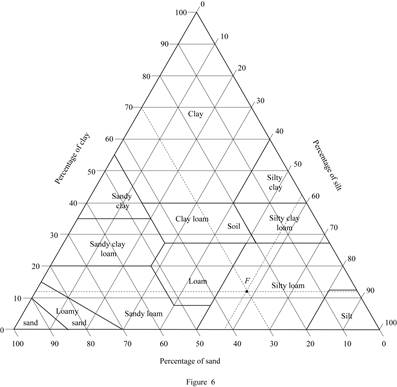
Refer Figure (6).
Hence, the classification of soil F as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil G:
Mark the percentage of sand for soil G as 40 %, percentage of silt as 25 %, and percentage of clay as 35 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil G as in Figure (7).
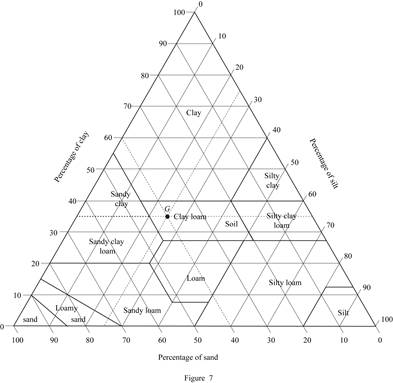
Refer Figure (7).
Thus, classification of soil G as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil H:
Mark the percentage of sand for soil H as 30 %, percentage of silt as 25 %, and percentage of clay as 45 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil H as in Figure (8).
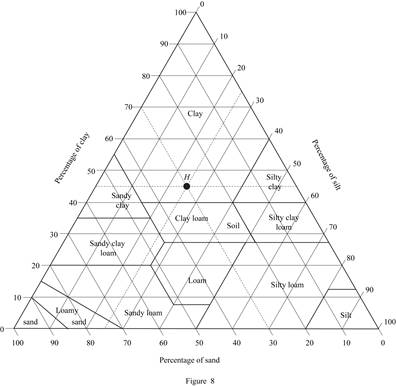
Refer Figure (8).
The classification of soil H as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil I:
Mark the percentage of sand for soil I as 5 %, percentage of silt as 45 %, and percentage of clay as 50 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil I as in Figure (9).
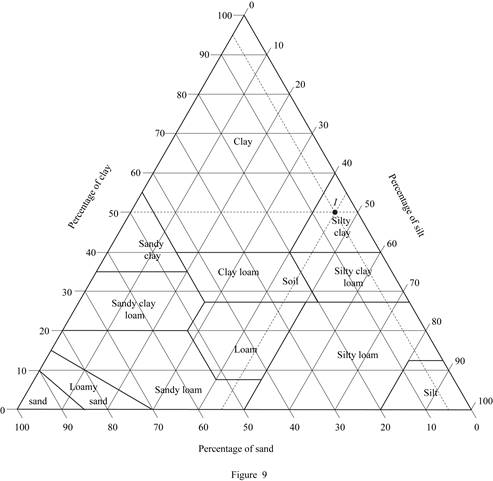
Refer Figure (9).
The classification of soil I as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Consider soil J:
Mark the percentage of sand for soil J as 45 %, percentage of silt as 45 %, and percentage of clay as 10 % in Figure (5.1) and mark the point of intersection of three lines.
Show the percentage of sand, silt, and clay of soil J as in Figure (10).
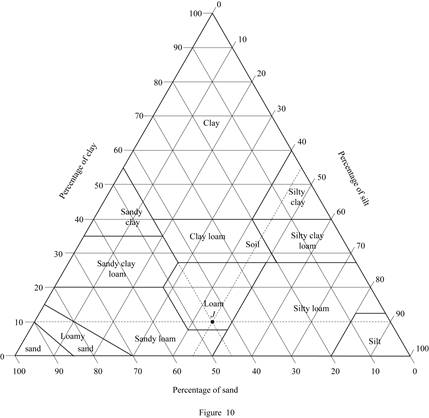
Refer Figure (10).
The classification of soil J as per the United States department of agriculture textural classification chart is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap Course List)
- Problem 2 (A is fixed and C is a pin) Find the reactions and A and C. 10 k- 6 ft 6 ft B A 2 k/ft 15 ftarrow_forward6. A lake with no outlet is fed by a river with a constant flow of 1200 ft3/s. Water evaporates from the surface at a constant rate of 13 ft3/s per square mile of surface area. The surface area varies with the depth h (in feet) as A (square miles) = 4.5 + 5.5h. What is the equilibrium depth of the lake? Below what river discharge (volume flow rate) will the lake dry up?arrow_forwardProblem 5 (A, B, C and D are fixed). Find the reactions at A and D 8 k B 15 ft A -20 ft C 10 ft Darrow_forward
- Problem 4 (A, B, E, D and F are all pin connected and C is fixed) Find the reactions at A, D and F 8 m B 6m E 12 kN D F 4 marrow_forwardProblem 1 (A, C and D are pins) Find the reactions and A, C and D. D 6 m B 12 kN/m 8 m A C 6 marrow_forwardUniform Grade of Pipe Station of Point A is 9+50.00. Elevation Point A = 250.75.Station of Point B is 13+75.00. Elevation Point B = 244.10 1) Calculate flowline of pipe elevations at every 50 ft. interval (Half Station). 2) Tabulate station and elevation for each station like shown on example 3) Draw Sketcharrow_forward
- quantity surveyingarrow_forwardNote: Please accurately answer it!. I'll give it a thumbs up or down based on the answer quality and precision. Question: What is the group name of Sample B in problem 3 from the image?. By also using the ASTM flow chart!. This unit is soil mechanics btwarrow_forwardPick the rural location of a project site in Victoria, and its catchment area-not bigger than 25 sqkm, and given the below information, determine the rainfall intensity for ARI = 5, 50, 100 year storm event. Show all the details of the procedure. Each student must propose different length of streams and elevations. Use fig below as a sample only. Pt. E-ht. 95.0 200m 600m PLD-M. 91.0 300m Pt. C-93.0 300m PL.B-ht. 92.0 PL.F-ht. 96.0 500m Pt. A-M. 91.00 To be deemed satisfactory the solution must include: Q.F1.1.Choice of catchment location Q.F1.2. A sketch displaying length of stream and elevation Q.F1.3. Catchment's IFD obtained from the Buro of Metheorology for specified ARI Q.F1.4.Calculation of the time of concentration-this must include a detailed determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.5.Use must be made of the Bransby-Williams method for the determination of the equivalent slope. Q.F1.6.The graphical display of the estimation of intensities for ARI 5,50, 100 must be shown.arrow_forward
 Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning
Construction Materials, Methods and Techniques (M...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305086272Author:William P. Spence, Eva KultermannPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage,
Fundamentals Of Construction EstimatingCivil EngineeringISBN:9781337399395Author:Pratt, David J.Publisher:Cengage, Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning





