
Concept explainers
Given the following
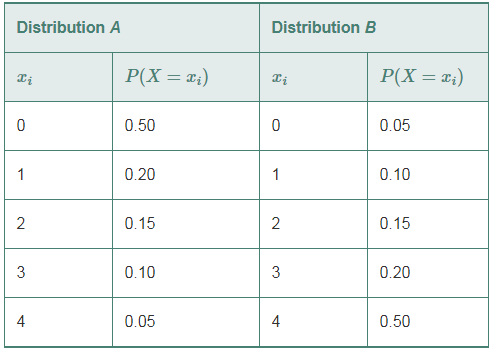
- Compute the expected value for each distribution.
- Compute the standard deviation for each distribution.
- Compare the results of distributions A and B.
(a)
To find: The expected values for both the distributions.
Answer to Problem 5.1LB
The expected values are 1 and 3 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The probability distributions are:
| Distribution A | Distribution B | ||
| 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.05 |
| 1 | 0.2 | 1 | 0.1 |
| 2 | 0.15 | 2 | 0.15 |
| 3 | 0.1 | 3 | 0.2 |
| 4 | 0.05 | 4 | 0.5 |
Formula used:
The formula to compute the expected mean is:
Here,
The formula to compute the standard deviation is:
Calculation:
The expected values for both the distributions can be calculated as:
Distribution A:
Distribution B:
Thus, the required expected values are 1 and 3 respectively.
(b)
To find: The standard deviation for each distribution.
Answer to Problem 5.1LB
The standard deviations are 1.225 and 1.225 respectively.
Explanation of Solution
The standard deviation for each distribution can be computed as:
Distribution A:
Distribution B:
Thus, the required standard deviations are 1.225 and 1.225 respectively.
(c)
To compare: The provided distributions.
Explanation of Solution
From the above two parts, it is clear that the mean of distribution B is greater than the mean of distribution B but there is no difference in the standard deviation of two distributions.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK BUSINESS STATISTICS
Additional Math Textbook Solutions
Elementary Statistics ( 3rd International Edition ) Isbn:9781260092561
A First Course in Probability (10th Edition)
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)
Elementary & Intermediate Algebra
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th Edition)
Precalculus: Mathematics for Calculus (Standalone Book)
- 2011 listing by carmax of the ages and prices of various corollas in a ceratin regionarrow_forwardس 11/ أ . اذا كانت 1 + x) = 2 x 3 + 2 x 2 + x) هي متعددة حدود محسوبة باستخدام طريقة الفروقات المنتهية (finite differences) من جدول البيانات التالي للدالة (f(x . احسب قيمة . ( 2 درجة ) xi k=0 k=1 k=2 k=3 0 3 1 2 2 2 3 αarrow_forward1. Differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables, providing examples for each type. 2. Consider a discrete random variable representing the number of patients visiting a clinic each day. The probabilities for the number of visits are as follows: 0 visits: P(0) = 0.2 1 visit: P(1) = 0.3 2 visits: P(2) = 0.5 Using this information, calculate the expected value (mean) of the number of patient visits per day. Show all your workings clearly. Rubric to follow Definition of Random variables ( clearly and accurately differentiate between discrete and continuous random variables with appropriate examples for each) Identification of discrete random variable (correctly identifies "number of patient visits" as a discrete random variable and explains reasoning clearly.) Calculation of probabilities (uses the probabilities correctly in the calculation, showing all steps clearly and logically) Expected value calculation (calculate the expected value (mean)…arrow_forward
- if the b coloumn of a z table disappeared what would be used to determine b column probabilitiesarrow_forwardConstruct a model of population flow between metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas of a given country, given that their respective populations in 2015 were 263 million and 45 million. The probabilities are given by the following matrix. (from) (to) metro nonmetro 0.99 0.02 metro 0.01 0.98 nonmetro Predict the population distributions of metropolitan and nonmetropolitan areas for the years 2016 through 2020 (in millions, to four decimal places). (Let x, through x5 represent the years 2016 through 2020, respectively.) x₁ = x2 X3 261.27 46.73 11 259.59 48.41 11 257.96 50.04 11 256.39 51.61 11 tarrow_forwardIf the average price of a new one family home is $246,300 with a standard deviation of $15,000 find the minimum and maximum prices of the houses that a contractor will build to satisfy 88% of the market valuearrow_forward
- 21. ANALYSIS OF LAST DIGITS Heights of statistics students were obtained by the author as part of an experiment conducted for class. The last digits of those heights are listed below. Construct a frequency distribution with 10 classes. Based on the distribution, do the heights appear to be reported or actually measured? Does there appear to be a gap in the frequencies and, if so, how might that gap be explained? What do you know about the accuracy of the results? 3 4 555 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 23 3 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 5 6 6 8 8 8 9arrow_forwardA side view of a recycling bin lid is diagramed below where two panels come together at a right angle. 45 in 24 in Width? — Given this information, how wide is the recycling bin in inches?arrow_forward1 No. 2 3 4 Binomial Prob. X n P Answer 5 6 4 7 8 9 10 12345678 8 3 4 2 2552 10 0.7 0.233 0.3 0.132 7 0.6 0.290 20 0.02 0.053 150 1000 0.15 0.035 8 7 10 0.7 0.383 11 9 3 5 0.3 0.132 12 10 4 7 0.6 0.290 13 Poisson Probability 14 X lambda Answer 18 4 19 20 21 22 23 9 15 16 17 3 1234567829 3 2 0.180 2 1.5 0.251 12 10 0.095 5 3 0.101 7 4 0.060 3 2 0.180 2 1.5 0.251 24 10 12 10 0.095arrow_forward
- step by step on Microssoft on how to put this in excel and the answers please Find binomial probability if: x = 8, n = 10, p = 0.7 x= 3, n=5, p = 0.3 x = 4, n=7, p = 0.6 Quality Control: A factory produces light bulbs with a 2% defect rate. If a random sample of 20 bulbs is tested, what is the probability that exactly 2 bulbs are defective? (hint: p=2% or 0.02; x =2, n=20; use the same logic for the following problems) Marketing Campaign: A marketing company sends out 1,000 promotional emails. The probability of any email being opened is 0.15. What is the probability that exactly 150 emails will be opened? (hint: total emails or n=1000, x =150) Customer Satisfaction: A survey shows that 70% of customers are satisfied with a new product. Out of 10 randomly selected customers, what is the probability that at least 8 are satisfied? (hint: One of the keyword in this question is “at least 8”, it is not “exactly 8”, the correct formula for this should be = 1- (binom.dist(7, 10, 0.7,…arrow_forwardKate, Luke, Mary and Nancy are sharing a cake. The cake had previously been divided into four slices (s1, s2, s3 and s4). What is an example of fair division of the cake S1 S2 S3 S4 Kate $4.00 $6.00 $6.00 $4.00 Luke $5.30 $5.00 $5.25 $5.45 Mary $4.25 $4.50 $3.50 $3.75 Nancy $6.00 $4.00 $4.00 $6.00arrow_forwardFaye cuts the sandwich in two fair shares to her. What is the first half s1arrow_forward
 Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt
Big Ideas Math A Bridge To Success Algebra 1: Stu...AlgebraISBN:9781680331141Author:HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURTPublisher:Houghton Mifflin Harcourt


