
Concept explainers
Accounting for Cash Receipts, Purchases, and Cash Payments and Reconciling Items
Nicole’s Getaway Spa (NGS) continues to grow and develop. Nicole is now evaluating a computerized accounting system and needs your help in understanding how source documents inform accounting processes. She also needs some help reconciling NGS’s bank account.
Required:
- 1. For each source document shown below, prepare the appropriate
journal entry or indicate that no journal entry is required.- a. Purchase order dated October 13 for massage chairs costing $765 and oil supplies costing $240.

- b. Remittance advice from customer for $93, received October 17.

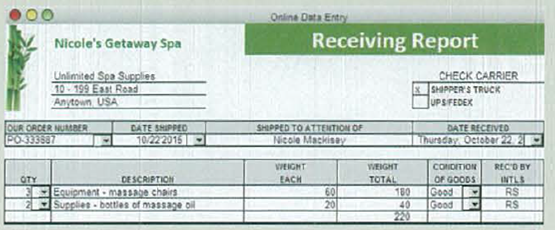
- c. Receiving report indicating October 22 receipt of October 13 order. Also received supplier invoice totaling $1,005.
- d. NGS check for payment in full of October 13 order.

- 2. Nicole has asked you to prepare a bank reconciliation for NGS. According to her records. NGS’s cash balance is $6,000 at December 31, but the bank reports a balance of $5.500.
- a. The bank deducted $250 for an NSF check from a customer deposited on December 22.
- b. NGS has written checks totaling $3,500 that have not yet cleared the bank.
- c. The bank added $10 cash to the account for interest earned in December.
- d. NGS made a $3,480 deposit on December 31, which will be recorded by the bank in January.
- e. The bank deducted $10 for service charges.
- f. NGS wrote a check to a supplier on account for $300 but mistakenly recorded it as $30.
- 3. Prepare journal entries for items (a)–(f) from the bank reconciliation, if applicable. If a journal entry is not required for one or more of the reconciling items, indicate “no journal entry required.”
- 4. If NGS also has $120 of petty cash and $1,000 invested in government Treasury bills purchased in August, what is the amount of Cash and Cash Equivalents on NGS’s December 31 balance sheet?
(1)
To prepare: Journal entries in the books of NG Spa
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
(a)
Prepare journal entry to record event recorded inpurchase order.
Purchase order is a document which indicates the details of the supplier, location of the delivery, and the cost of the supplies. Since there is no economic transaction involved, journal entry is not required.
(b)
Prepare journal entry to record event recorded in remittance advice.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| October | 17 | Cash | 93 | |||
| Accounts Receivable | 93 | |||||
| (To record cash received for services performed on account) | ||||||
Table (1)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is received, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Accounts Receivable is an asset account. Since amount to be received has decreased, asset account decreased, and a decrease in asset is credited.
(c)
Prepare journal entry to record event recorded in receiving report.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| October | 22 | Equipment | 765 | |||
| Supplies | 240 | |||||
| Accounts Payable | 1,005 | |||||
| (To record purchase of equipment and supplies on account) | ||||||
Table (2)
Description:
- Equipment is an asset account. Since equipment is bought, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Supplies is an asset account. Since supplies are bought, asset account increased, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Accounts Payable is a liability account. Since the amount to be paid increased, liability increased, and an increase in liability is credited.
(d)
Prepare journal entry to record for check payment.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| October | 30 | Accounts Payable | 1,005 | |||
| Cash | 1,005 | |||||
| (To record cash paid for purchases on account) | ||||||
Table (3)
Description:
- Accounts Payable is a liability account. Since amount to be paid has decreased, liability account decreased, and a decrease in liability is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. Since cash is paid, asset account decreased, and adecrease in asset is credited.
(2)
To prepare: Bank reconciliation of NG Spa, as atDecember 31
Explanation of Solution
Bank reconciliation: Bank statement is prepared by bank. The company maintains its own records from its perspective. This is why the cash balance per bank and cash balance per books seldom agree. Bank reconciliation is the statement prepared by company to remove the differences and disagreement between cash balance per bank and cash balance per books.
Prepare bank reconciliation of NG Spa, as at December 31.
| NG Spa | ||||
| Bank Reconciliation | ||||
| December 31 | ||||
| Updates to Bank Statement | Updates to Company’s Books | |||
| Ending cash balance per bank statement | $5,500 | Ending cash balance per books | $6,000 | |
| Additions: | Additions: | |||
| Deposits in transit | 3,480 | Interest received | 10 | |
| 8,980 | 6,010 | |||
| Deductions: | Deductions: | |||
| Outstanding checks | 3,500 | NSF check | 250 | |
| Up-to-date ending cash balance | $5,480 | Error in recording check | 270 | |
| Bank service charge | 10 | 530 | ||
| Up-to-date ending cash balance | $5,480 | |||
Table (4)
Working Notes:
Calculate book error amount.
Description:
- The deposits which are not recorded by the bank are referred to as deposits in transit. Since the deposits in transit are not reflected on the bank statement, the company should add deposits in transit to cash balance per bank, while preparation of bank reconciliation statement.
- Outstanding checks are the checks that are issued by the company, but not yet paid by the bank. When the check is issued for payment, the company deducts the cash balance immediately. But the bank deducts only when the cash is paid for the issued check. So, company deducts the cash balance per bank to remove the differences.
- Interest received is credited by bank to the bank account of which the company is not aware of. So, while preparing bank reconciliation statement, company should add the amount to the cash balance per books.
- While bank reconciliation, the NSF check should be deducted from the cash balance per book. This is because the bank could not collect funds from the customer’s bank due to lack of funds. But being recorded as Accounts Receivable previously, the balance should be deducted from books, to increase the Accounts Receivable account.
- The incorrectly written check would increase the cash balance per books. So, company deducts the amount of $270 from balance per book while bank reconciliation preparation.
- Banks deduct the service charge for the services rendered like lock box rental, or printed checks. But the company is not aware of such deductions. So, company deducts the cash balance per books while bank reconciliation preparation.
(3)
To prepare: Adjusting journal entries that arise due to bank reconciliation
Explanation of Solution
Journal entry: Journal entry is a set of economic events which can be measured in monetary terms. These are recorded chronologically and systematically.
Debit and credit rules:
- Debit an increase in asset account, increase in expense account, decrease in liability account, and decrease in stockholders’ equity accounts.
- Credit decrease in asset account, increase in revenue account, increase in liability account, and increase in stockholders’ equity accounts.
(a)
Prepare journal entry to record NSF check.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| December | 31 | Accounts Receivable | 270 | |||
| Cash | 270 | |||||
| (To record NSF check) | ||||||
Table (5)
Description:
- Accounts Receivable is an asset account. The bank has not collected the amount from the customer due to insufficient funds, which was earlier recorded as a receipt. As the collection could not be made, amount to be received increased. Therefore, increase in asset would be debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because bank could not collect amount due to insufficient funds in customer’s account, and a decrease in asset is credited.
(b)
Prepare journal entry for the checks written but not cleared by bank.
These are the outstanding checks, which are recorded by the company. So, company does not record it again, but this is an adjustment for bank balance. Hence, no journal entry is required.
(c)
Prepare journal entry to record interest received.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| December | 31 | Cash | 10 | |||
| Interest Revenue | 10 | |||||
| (To record interest earned) | ||||||
Table (6)
Description:
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is increased because credited the interest earned on checking account, and an increase in asset is debited.
- Interest Revenue is a revenue account. Revenuesincrease Equity account and an increase in Equity is credited.
(d)
Prepare journal entry for the deposits recorded by company.
These are the checks deposited by company but not recorded by bank, which are recorded by the company. So, company does not record it again, but this is an adjustment for bank balance. Hence, no journal entry is required.
(e)
Prepare journal entry to record bank service charge.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| December | 31 | Office Expense | 10 | |||
| Cash | 10 | |||||
| (To record bank service charge) | ||||||
Table (7)
Description:
- Office Expenses is an expense account and the amount is increased because bank has charged service charges. Expenses decrease Equity account and decrease in Equity is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because bank service charge is paid, and a decrease in asset is credited.
(f)
Prepare journal entry to record EFT payment made by bank.
| Date | Account Titles and Explanation | Ref. | Debit ($) | Credit ($) | ||
| December | 31 | Accounts Payable | 270 | |||
| Cash | 270 | |||||
| (To record payment made by bank) | ||||||
Table (8)
Description:
- Accounts Payable is a liability account. The amount has decreased because the amount to be paid is decreased, and a decrease in liabilities is debited.
- Cash is an asset account. The amount is decreased because cash is paid, and a decrease in asset is credited.
(4)
To mention: The amount to be reported as cash and cash equivalents on the balance sheet of NG Spa as on December 31
Explanation of Solution
Cash: Cash is the money readily available in the form of currency. Since cash can be easily converted into other types of assets, it is reported as first item in the assets section as the most liquid asset.
Cash equivalents: Cash equivalents are the near-cash items, which are readily convertible into cash. Cash equivalents have a maturity period of three months, or less than 3 months. Cash equivalents are reported along with cash in the assets section of the balance sheet, as ‘Cash and cash equivalents’.
Cash and cash equivalents:
| Cash and Cash Equivalents | |
| Cash | $5,480 |
| Petty cash | 120 |
| Total cash and cash equivalents | $5,600 |
Table (9)
Note: $1,000 of Treasury bills are bought 4 months ago (August) and do not qualify as cash equivalents, but short-term investments. So, do not include this item in cash and cash equivalents.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fundamentals of Financial Accounting
- I am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with the correct explanation.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardHow can I solve this financial accounting problem using the appropriate financial process?arrow_forward
- Principles of Accounting Volume 1AccountingISBN:9781947172685Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax CollegeCentury 21 Accounting Multicolumn JournalAccountingISBN:9781337679503Author:GilbertsonPublisher:Cengage
 College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
College Accounting, Chapters 1-27AccountingISBN:9781337794756Author:HEINTZ, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Pkg Acc Infor Systems MS VISIO CDFinanceISBN:9781133935940Author:Ulric J. GelinasPublisher:CENGAGE L
Pkg Acc Infor Systems MS VISIO CDFinanceISBN:9781133935940Author:Ulric J. GelinasPublisher:CENGAGE L




