
Concept explainers
(a)
To plot:
The data given in the table and suggest the type of
(a)
Answer to Problem 5.14P
Beta and gamma radiation
Explanation of Solution
Calculation:
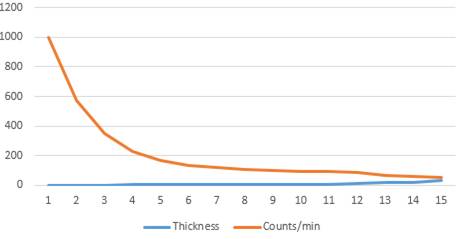
The graph is plotted for counting per min to the thickness of the absorber. The count for beta particle decreases rapidly and then after certain range it decreases slowly. The counts for beta particle approach zero. But, in the above diagram the count is not approaching zero because of gamma radiations.
Thus, the types of radiation according to the above curve is Beta and gamma radiation.
Conclusion:
The type of radiation suggested by the curve is Beta radiation.
(b)
The energy of the beta radiations.
(b)
Answer to Problem 5.14P
The energy of the beta radiations is,
Explanation of Solution
Given:
Range of beta particle,
Formula used:
The Energy of beta particle is,
Where,
Calculation:
From the graph plotted between the thickness and the count per min curve. The range can be estimated as,
The Energy of beta particle is,
Conclusion:
From the above graph the energy of beta radiation is
(c)
Whether gamma rays are present, the energy of gamma rays if present.
(c)
Answer to Problem 5.14P
Yes, the energy is 1.5 MeV.
Explanation of Solution
The attenuation of gamma ray can be described as,
As intensity observed initially is 1000. So,
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
For
So, mean is,
Thus, the energy corresponding to it is 1.5 MeV.
(d)
The isotope compatible with absorption data.
(d)
Answer to Problem 5.14P
The isotope compatible with above absorption data is 198Au.
Explanation of Solution
The isotope compatible with above absorption data is 198Au.
(e)
The equation fits the absorption data.
(e)
Answer to Problem 5.14P
Explanation of Solution
The equation fits the absorption data is,
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
EBK INTRODUCTION TO HEALTH PHYSICS, FIF
- (a) For a spherical capacitor with inner radius a and outer radius b, we have the following for the capacitance. ab C = k₂(b- a) 0.0695 m 0.145 m (8.99 × 10º N · m²/c²)( [0.145 m- 0.0695 m × 10-11 F = PF IIarrow_forwardA pendulum bob A (0.5 kg) is given an initialspeed of vA = 4 m/s when the chord ishorizontal. It then hits a stationary block B (1kg) which then slides to a maximum distanced before it stops. Determine the value of d.The coefficient of static friction between theblock and the plane is μk = 0.2. The coefficientof restitution between A and B is e = 0.8.Ans: d=1.0034 marrow_forwardFigure 29-43 Problem 12. ••13 In Fig. 29-44, point P₁ is at distance R = 13.1 cm on the perpendicular bisector of a straight wire of length L = 18.0 cm carrying current i = 58.2 mA. (Note that the wire is not long.) What is the magnitude of the magnetic field at P₁ due to i? P2° R R Larrow_forward
- Checkpoint 1 The figure shows the current i in a single-loop circuit with a battery B and a resistance R (and wires of neg- ligible resistance). (a) Should the emf arrow at B be drawn pointing leftward or rightward? At points a, B C R b, and c, rank (b) the magnitude of the current, (c) the electric potential, and (d) the electric potential energy of the charge carriers, greatest first.arrow_forwardPls help ASAParrow_forwardPls help asaparrow_forward
 Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781938168000Author:Paul Peter Urone, Roger HinrichsPublisher:OpenStax College University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax
University Physics Volume 3PhysicsISBN:9781938168185Author:William Moebs, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





