
Concept explainers
A.
Cycles per element (CPE):
- The CPE denotes performance of program that helps in improving code.
- It helps to understand detailed level loop performance for an iterative
program. - It is suitable for programs that use a repetitive calculation.
- The processor’s activity sequencing is measured by a clock that provides signal of some frequency.
A.
Explanation of Solution
Diagram for instruction sequence:
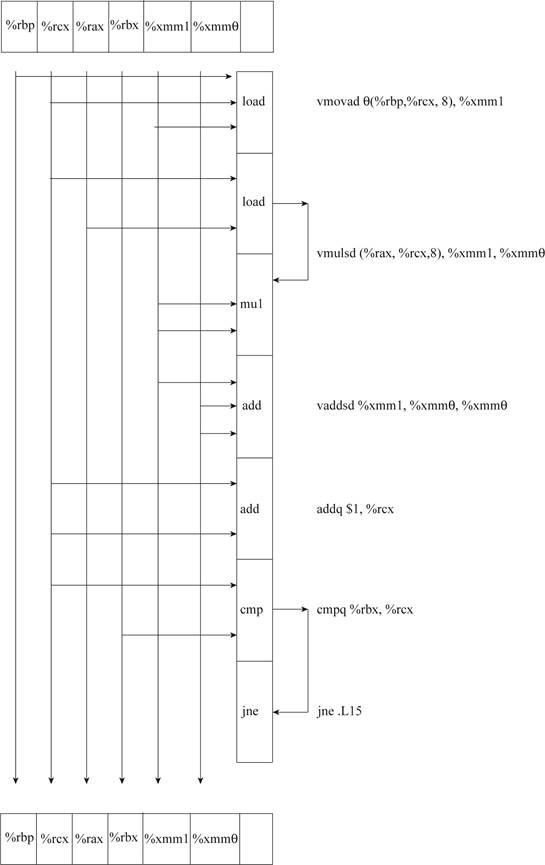
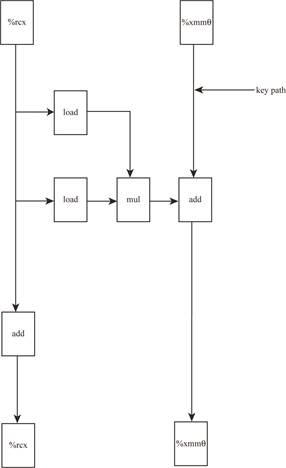
Explanation:
- The data dependencies between instructions are been depicted in diagram.
- The given instruction sequence is been decoded into operations.
- It creates a critical path of operations.
- The data flow between instructions is been shown in diagram.
B.
Cycles per element (CPE):
- The CPE denotes performance of program that helps in improving code.
- It helps to understand detailed level loop performance for an iterative program.
- It is suitable for programs that use a repetitive calculation.
- The processor’s activity sequencing is measured by a clock that provides signal of some frequency.
B.
Explanation of Solution
Lower bound on CPE:
- The lower bound on CPE is been determined by critical path.
- For data type “double”, it denotes the float add cell.
- The lower bound on CPE is 3.0 based on the architecture.
C.
Cycles per element (CPE):
- The CPE denotes performance of program that helps in improving code.
- It helps to understand detailed level loop performance for an iterative program.
- It is suitable for programs that use a repetitive calculation.
- The processor’s activity sequencing is measured by a clock that provides signal of some frequency.
C.
Explanation of Solution
Lower bound on CPE:
- The lower bound on CPE is been determined by critical path.
- For data type “integer”, it denotes the long add cell.
- The lower bound on CPE is 1.0 based on the architecture.
D.
Cycles per element (CPE):
- The CPE denotes performance of program that helps in improving code.
- It helps to understand detailed level loop performance for an iterative program.
- It is suitable for programs that use a repetitive calculation.
- The processor’s activity sequencing is measured by a clock that provides signal of some frequency.
D.
Explanation of Solution
Given C Code:
// Define method inner4
void inner4(vec_ptr u, vec_ptr v, data_t *dest)
{
// Declare variable
long i;
//Compute length of
long length = vec_length(u);
//Get first vector
data_t *udata = get_vec_start(u);
//Get second vector
data_t *vdata = get_vec_start(v);
//Initialize variable
data_t sum = (data_t) 0;
//Loop
for (i = 0; i < length; i++)
{
//Compute product and add
sum = sum + udata[i] * vdata[i];
}
//Store result
*dest = sum;
}
CPE value for floating-point versions:
- The inner product computed is been accumulated in temporary.
- The float add operation is only on key path.
- The multiplication operation takes 5 clock cycles.
- The overall operation takes 3 cycles to complete on average.
- Hence, CPE value for floating-point versions is 3.0.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Computer Systems: A Programmer's Perspective Plus Mastering Engineering With Pearson Etext -- Access Card Package (3rd Edition)
- what is a feature in the Windows Server Security Compliance Toolkit, thank you.arrow_forwardYou will write a program that allows the user to keep track of college locations and details about each location. To begin you will create a College python class that keeps track of the csollege's unique id number, name, address, phone number, maximum students, and average tuition cost. Once you have built the College class, you will write a program that stores College objects in a dictionary while using the College's unique id number as the key. The program should display a menu in this order that lets the user: 1) Add a new College 2) Look up a College 4) Delete an existing College 5) Change an existing College's name, address, phone number, maximum guests, and average tuition cost. 6) Exit the programarrow_forwardShow all the workarrow_forward
- Show all the workarrow_forward[5 marks] Give a recursive definition for the language anb2n where n = 1, 2, 3, ... over the alphabet Ó={a, b}. 2) [12 marks] Consider the following languages over the alphabet ={a ,b}, (i) The language of all words that begin and end an a (ii) The language where every a in a word is immediately followed by at least one b. (a) Express each as a Regular Expression (b) Draw an FA for each language (c) For Language (i), draw a TG using at most 3 states (d) For Language (ii), construct a CFG.arrow_forwardQuestion 1 Generate a random sample of standard lognormal data (rlnorm()) for sample size n = 100. Construct histogram estimates of density for this sample using Sturges’ Rule, Scott’s Normal Reference Rule, and the FD Rule. Question 2 Construct a frequency polygon density estimate for the sample in Question 1, using bin width determined by Sturges’ Rule.arrow_forward
- Generate a random sample of standard lognormal data (rlnorm()) for sample size n = 100. Construct histogram estimates of density for this sample using Sturges’ Rule, Scott’s Normal Reference Rule, and the FD Rule.arrow_forwardCan I get help with this case please, thank youarrow_forwardI need help to solve the following, thank youarrow_forward
 C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning
C++ Programming: From Problem Analysis to Program...Computer ScienceISBN:9781337102087Author:D. S. MalikPublisher:Cengage Learning C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr
C++ for Engineers and ScientistsComputer ScienceISBN:9781133187844Author:Bronson, Gary J.Publisher:Course Technology Ptr Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning
Systems ArchitectureComputer ScienceISBN:9781305080195Author:Stephen D. BurdPublisher:Cengage Learning- Programming Logic & Design ComprehensiveComputer ScienceISBN:9781337669405Author:FARRELLPublisher:Cengage
 New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning
New Perspectives on HTML5, CSS3, and JavaScriptComputer ScienceISBN:9781305503922Author:Patrick M. CareyPublisher:Cengage Learning Operations Research : Applications and AlgorithmsComputer ScienceISBN:9780534380588Author:Wayne L. WinstonPublisher:Brooks Cole
Operations Research : Applications and AlgorithmsComputer ScienceISBN:9780534380588Author:Wayne L. WinstonPublisher:Brooks Cole





