
Concept explainers
The graph here represents the distribution of molecular speeds of hydrogen and neon at 200 K.
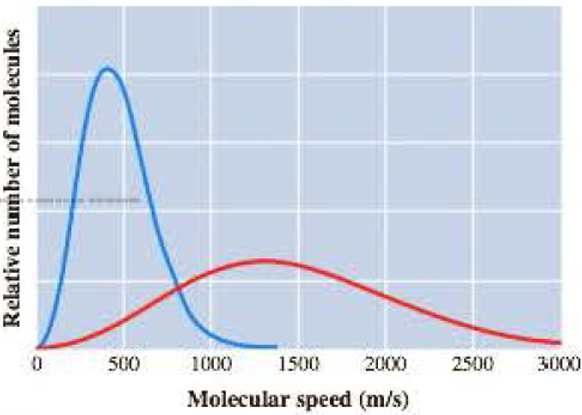
- a Match each curve to the appropriate gas.
- b Calculate the rms speed (in m/s) for each of the gases at 200 K.
- c Which of the gases would you expect to have the greater effusion rate at 200 K? Justify your answer.
- d Calculate the temperature at which the rms speed of the hydrogen gas would equal the rms speed of the neon at 200 K.
(a)
Interpretation:
The curve in the given graph must be matched with the appropriate gas.
Answer to Problem 5.136QP
The taller and narrow curve represents neon atoms
The flatter and wider curve represents hydrogen molecules
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The given graph represents the distribution of molecular speeds of hydrogen and neon at
Matching of given curves with appropriate gases:
In the given graph, the taller and narrow curve whose maximum falls near
The flatter and wider curve whose maximum falls near
The taller and narrow curve matches with neon atoms
The flatter and wider curve matches with hydrogen molecules
(b)
Interpretation:
The rms speed (in
Concept Introduction:
Root-mean-square (rms):
The root-mean-square molecular speed (
Where,
Answer to Problem 5.136QP
The rms speed of neon gas at
The rms speed of hydrogen gas at
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The given graph represents the distribution of molecular speeds of hydrogen and neon at
Calculation of rms speed:
The rms speed of neon is calculated as follows,
The rms speed of hydrogen gas is calculated as follows,
The rms speed of neon gas at
The rms speed of hydrogen gas at
(c)
Interpretation:
The gas that has greater effusion rate at
Concept Introduction:
Graham’s law of effusion:
Answer to Problem 5.136QP
The gas that has greater effusion rate at
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The given graph represents the distribution of molecular speeds of hydrogen and neon at
Gas possessing greater effusion rate:
The rates of effusion are directly related to the rms speed.
Greater the rms speed, greater is the rate of effusion.
Since the rms speed of hydrogen is greater than neon, hydrogen gas will have greater effusion rate.
In the container, the fast moving molecules collide with the holes of the container more often and hence have a higher effusion probability.
The gas that has greater effusion rate at
(d)
Interpretation:
The temperature at which the rms speed of the hydrogen gas equals the rms speed of neon gas at
Concept Introduction:
Root-mean-square (rms):
The root-mean-square molecular speed (
Where,
Answer to Problem 5.136QP
The temperature at which the rms speed of the hydrogen gas equals the rms speed of neon gas at 200 K is
Explanation of Solution
Given,
The given graph represents the distribution of molecular speeds of hydrogen and neon at
Temperature calculation:
The temperature equaling the rms speed of neon is calculated from root mean square equation as follows,
The temperature at which the rms speed of the hydrogen gas equals the rms speed of neon gas at
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
General Chemistry
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Campbell Biology: Concepts & Connections (9th Edition)
Organic Chemistry
General, Organic, and Biological Chemistry - 4th edition
Organic Chemistry (8th Edition)
- Draw the stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardDraw a structural formula of the principal product formed when benzonitrile is treated with each reagent. (a) H₂O (one equivalent), H₂SO₄, heat (b) H₂O (excess), H₂SO₄, heat (c) NaOH, H₂O, heat (d) LiAlH4, then H₂Oarrow_forwardDraw the stepwise mechanism for the reactionsarrow_forward
- Draw stepwise mechanismarrow_forwardPart I. Draw reaction mechanism for the transformations of benzophenone to benzopinacol to benzopinaco lone and answer the ff: a) Give the major reason for the exposure of benzophenone al isopropyl alcohol (w/acid) to direct sunlight of pina colone Mechanism For b) Pinacol (2,3-dimethy 1, 1-3-butanediol) on treatment w/ acid gives a mixture (3,3-dimethyl-2-butanone) and 2, 3-dimethyl-1,3-butadiene. Give reasonable the formation of the productsarrow_forwardwhat are the Iupac names for each structurearrow_forward
- What are the IUPAC Names of all the compounds in the picture?arrow_forward1) a) Give the dominant Intermolecular Force (IMF) in a sample of each of the following compounds. Please show your work. (8) SF2, CH,OH, C₂H₂ b) Based on your answers given above, list the compounds in order of their Boiling Point from low to high. (8)arrow_forward19.78 Write the products of the following sequences of reactions. Refer to your reaction road- maps to see how the combined reactions allow you to "navigate" between the different functional groups. Note that you will need your old Chapters 6-11 and Chapters 15-18 roadmaps along with your new Chapter 19 roadmap for these. (a) 1. BHS 2. H₂O₂ 3. H₂CrO4 4. SOCI₂ (b) 1. Cl₂/hv 2. KOLBU 3. H₂O, catalytic H₂SO4 4. H₂CrO4 Reaction Roadmap An alkene 5. EtOH 6.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 7. Mild H₂O An alkane 1.0 2. (CH3)₂S 3. H₂CrO (d) (c) 4. Excess EtOH, catalytic H₂SO OH 4. Mild H₂O* 5.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH An alkene 6. Mild H₂O* A carboxylic acid 7. Mild H₂O* 1. SOC₁₂ 2. EtOH 3.0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/E:OH 5.1.0 Equiv. NaOEt 6. NH₂ (e) 1. 0.5 Equiv. NaOEt/EtOH 2. Mild H₂O* Br (f) i H An aldehyde 1. Catalytic NaOE/EtOH 2. H₂O*, heat 3. (CH,CH₂)₂Culi 4. Mild H₂O* 5.1.0 Equiv. LDA Br An ester 4. NaOH, H₂O 5. Mild H₂O* 6. Heat 7. MgBr 8. Mild H₂O* 7. Mild H₂O+arrow_forward
- Li+ is a hard acid. With this in mind, which if the following compounds should be most soluble in water? Group of answer choices LiBr LiI LiF LiClarrow_forwardQ4: Write organic product(s) of the following reactions and show the curved-arrow mechanism of the reactions. Br MeOH OSO2CH3 MeOHarrow_forwardProvide the correct IUPAC name for the compound shown here. Reset cis- 5- trans- ☑ 4-6- 2- 1- 3- di iso tert- tri cyclo sec- oct but hept prop hex pent yl yne ene anearrow_forward
 General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781133949640Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: An Atoms First ApproachChemistryISBN:9781305079243Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. ZumdahlPublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning





