
To check
If any of the anions of the homonuclear diatomic molecules formed by B, C, N, O and F have shorter bond lengths than those of the corresponding neutral molecules.
Answer to Problem 5.112QA
Solution:
The bond lengths of the anions of the homonuclear diatomic molecules formed by B and C have shorter bond lengths than those of the corresponding neutral molecules.
Explanation of Solution
Bond order and bond length are inversely proportional to each other. When bond order increases the bond length decreases. When bond order decreases the bond length increases. We will find out the bond order of neutral diatomic molecules and their 1- and 2- anions. From the molecular orbital diagram we can find out number of bonding and antibonding electrons. The formula to calculate bond order is as below.
The molecular orbital diagram for the given molecules with the gain of one and two electrons forming the corresponding 1- and 2- anion is as shown below. With the help of this diagram we will calculate bond order of each molecule and ion.
Bond order of B2 and B21- and B22-.
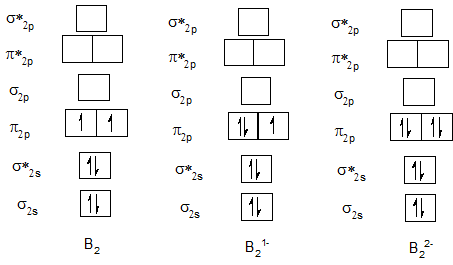
Bond order of C2, C21- and C22-.
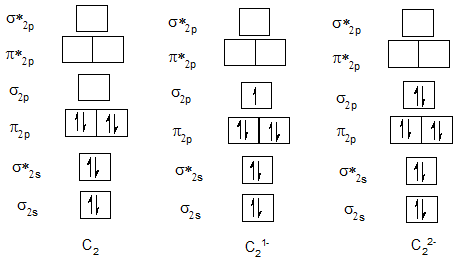
Bond order of N2, N21- and N22-.
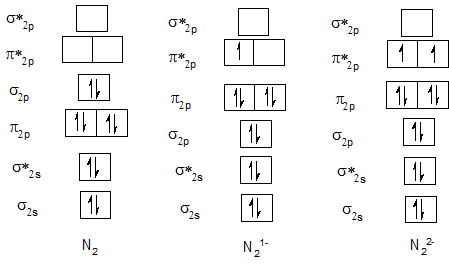
Bond order of O2, O21- and O22-.
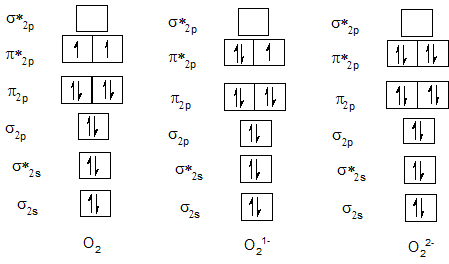
Bond order of F2, F21- and F22-.
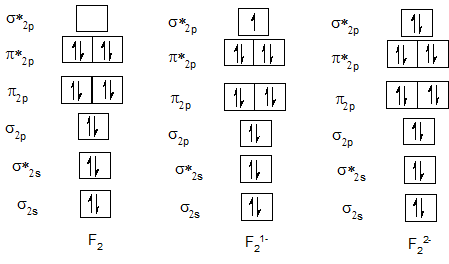
| Neutral diatomic molecule | Bond order of neutral molecule | Molecular anion | Bond order of anion | Molecular anion | Bond order of anion |
| B2 | 1 | B21- | 1.5 | B22- | 2 |
| C2 | 2 | C21- | 2.5 | C22- | 3 |
| N2 | 3 | N21- | 2.5 | N22- | 2 |
| O2 | 2 | O21- | 1.5 | O22- | 1 |
| F2 | 1 | F21- | 0.5 | F22- | 0 |
From the data in the table we can say that bond order of B2 is smaller than B21- and bond order of B21- is smaller than B22-. Therefore bond length of B2 is larger than B21-. Also bond length of B21- is larger than B22-. Similarly bond length of C2 is larger than C21-. Also bond length of C21- is larger than C22-. Therefore the bond lengths of the anions of the homonuclear diatomic molecules formed by B and C have shorter bond lengths than those of the corresponding neutral molecules.
Conclusion:
Bond order is inversely proportional to bond length. From bond order of each molecule and corresponding anion, the bond lengths of the anions of the homonuclear diatomic molecules formed by B and C have shorter bond lengths than those of the corresponding neutral molecules.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
CHEMISTRY ATOM FOCUSED EBK W/ A.C. >I<
- For each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new CC bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. དྲ。 ✗MgBr ? O CI Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new C-C bond? Yes No • ? Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No × : ☐ Xarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: OH NaBH4 H ? CH3OH Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. ☐ : Sarrow_forwardPredict the major products of this organic reaction: 1. LIAIHA 2. H₂O ? Note: be sure you use dash and wedge bonds when necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. X : ☐arrow_forward
- For each reaction below, decide if the first stable organic product that forms in solution will create a new C - C bond, and check the appropriate box. Next, for each reaction to which you answered "Yes" to in the table, draw this product in the drawing area below. Note for advanced students: for this problem, don't worry if you think this product will continue to react under the current conditions - just focus on the first stable product you expect to form in solution. NH2 tu ? ? OH Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No Will the first product that forms in this reaction create a new CC bond? Yes No C $ ©arrow_forwardAs the lead product manager at OrganometALEKS Industries, you are trying to decide if the following reaction will make a molecule with a new C-C bond as its major product: 1. MgCl ? 2. H₂O* If this reaction will work, draw the major organic product or products you would expect in the drawing area below. If there's more than one major product, you can draw them in any arrangement you like. Be sure you use wedge and dash bonds if necessary, for example to distinguish between major products with different stereochemistry. If the major products of this reaction won't have a new CC bond, just check the box under the drawing area and leave it blank. Click and drag to start drawing a structure. This reaction will not make a product with a new CC bond. G marrow_forwardIncluding activity coefficients, find [Hg22+] in saturated Hg2Br2 in 0.00100 M NH4 Ksp Hg2Br2 = 5.6×10-23.arrow_forward
- give example for the following(by equation) a. Converting a water insoluble compound to a soluble one. b. Diazotization reaction form diazonium salt c. coupling reaction of a diazonium salt d. indacator properties of MO e. Diazotization ( diazonium salt of bromobenzene)arrow_forward2-Propanone and ethyllithium are mixed and subsequently acid hydrolyzed. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward(Methanesulfinyl)methane is reacted with NaH, and then with acetophenone. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forward
- 3-Oxo-butanenitrile and (E)-2-butenal are mixed with sodium ethoxide in ethanol. Draw and name the structures of the products.arrow_forwardWhat is the reason of the following(use equations if possible) a.) In MO preperation through diazotization: Addition of sodium nitrite in acidfied solution in order to form diazonium salt b.) in MO experiment: addition of sodium hydroxide solution in the last step to isolate the product MO. What is the color of MO at low pH c.) In MO experiment: addition of sodium hydroxide solution in the last step to isolate the product MO. What is the color of MO at pH 4.5 d.) Avoiding not cooling down the reaction mixture when preparing the diazonium salt e.) Cbvcarrow_forwardA 0.552-g sample of an unknown acid was dissolved in water to a total volume of 20.0 mL. This sample was titrated with 0.1103 M KOH. The equivalence point occurred at 29.42 mL base added. The pH of the solution at 10.0 mL base added was 3.72. Determine the molar mass of the acid. Determine the Ka of the acid.arrow_forward
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY





