
a.(1)
To prepare: Time line for a $100 lump sum cash flow at the end of the year 2.
Introduction:
Time Line: A line representing the cash flow of a company over a period of time is called time line. It shows the cash flow by representing them diagrammatically.
a.(1)
Explanation of Solution
Time line is drawn representing lump sum cash flow,
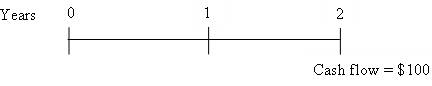
Fig 1
Time line shows cash flow at the end of the year is $100.
(2)
To prepare: Time line for ordinary
(2)
Explanation of Solution
Time line is drawn representing lump sum cash flow,
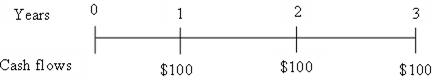
Fig 2
Time line shows annuity of $100 per year for 3 years.
(3)
To prepare: Time line for an uneven cash flow stream of $50, $100, $75 and, $50 at the end of years 0 through 3.
(3)
Explanation of Solution
Time line is drawn to show uneven cash flow stream.
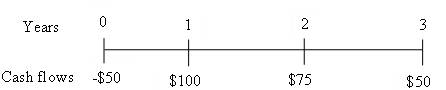
Fig 3
Time line represents an uneven cash flow stream at the end of years 0 through 3.
b.1.
To calculate:
Future Value of Cash Flow:
The future value of cash flow is the value of cash which it gains after receiving interest for a number of periods. It is also known as the terminal value.
b.1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of future value,
Given,
Original investment is $100.
Number of years is 3.
Interest rate is 4%.
Formula to calculate future value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, 4% for interest rate and 3 for number of years.
The future value of the original investment is $112.49.
2.
To calculate: The present value of $100 if after 3 years at 4% annual compounding.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute present value.
Given,
Original Investment is $100.
Number of years is 3.
Interest rate is 4%.
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, 4% for interest rate and 3 for number of years.
The present value of the original investment is $88.90.
c.
To calculate: Annual interest rate to grow $100 to $119.10 in 3 years.
c.
Explanation of Solution
Compute interest rate.
Given,
Future value is $119.10.
Original investment is $100.
Formula to calculate interest rate,
Substitute $100 for original investment, $119.10 for Future value and 3 for number of years.
Simplify the above equation to get interest rate,
Annual interest rate to grow $100 to $119.10 is 6%.
d.
To calculate: The time period to grow sales double at 10% annually growth rate.
d.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation is solved in spreadsheet by “NPER” formula.
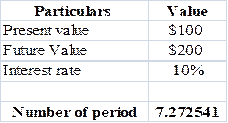
Table (1)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “NPER” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “NPER” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
- Final answer will be shown by the formula that is 7.27years.
So,it will take 7.27 years for a sale to get double with 10% annual interest rate.
e.
To explain: Difference between annuity and ordinary annuity, type of annuity shown in table line and changed it to other type of annuity.
Annuity:
It is an agreement under which a person pays the lump sum payment or the number of small transactions and in return he gets the amount at later date or upon annuitization. The purpose of the annuity is not to break the flow of income after retirement.
e.
Answer to Problem 42IC
- In ordinary annuity, payment is made at the end of every period while in annuity due, payment is made at the beginning of every period.
- The time line is representing the ordinary annuity.
- It can be converted by changing their periods.
Explanation of Solution
- In ordinary annuity the payment is made at the end of the period while in annuity due the payment is made at the beginning of period so investments done in annuity have better chances to grow as it has more time to compound.
- The timing of cash flows indicates the difference between the types of
annuities (ordinary annuity and annuity due). The calculation of ordinary annuity is always done at the end of the period and calculation of annuity due is always done at the beginning of the period. - Annuity due is calculated at the beginning of period as there is no beginning value so the time line is representing the ordinary annuity.
- Ordinary annuity is calculated at the end of period while annuity due at the beginning of period so the ordinary annuity can be transformed to annuity due by swapping its payments to the beginning of period.
f. 1.
To calculate: Future value of $100 ordinary annuity in 3 years at 4% annual interest rate.
Future value of cash flow:
The future value of cash flow is that value of cash which it gains after receiving interest for a number of periods. It is also known as the terminal value.
f. 1.
Explanation of Solution
Compute future value of ordinary annuity.
Given,
Annual payment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 3.
Formula to calculate future value,
Substitute $100 for annual payment, 4% for interest rate and 3 for number of years.
The future value will be $312.16 for $100 after 3 years at 4% interest rate.
2.
To calculate: Present value of $100 ordinary annuity in 3 years at 4% annual interest rate.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute future value of ordinary annuity.
Given,
Annual payment $100
Interest rate 4%
Number of years 3
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for annual payment, 4% for interest rate and 3 for number of years.
The present value will be $277.51 for $100 after 3 years at 4% interest rate.
3.
To calculate: Present and futurevalue of $100 annuity due in 3 years at 4% annual interest rate.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Compute future value of annuity due.
Given,
Original investment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 3.
Formula to calculate future value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, 4% for interest rate and 3 for number of years.
So, the future value of annuity due is $112.49.
Compute future value of annuity due.
Given,
Original investment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 2.
Formula to calculate future value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, 4% for interest rate and 2 for number of years.
So, the future value of annuity due is $108.16.
Compute future value of annuity due.
Given,
Original investment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 1.
Formula to calculate future value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, 4% for interest rate and 1 for number of years.
So the future value of annuity due is $104.
Compute present value of annuity due.
Given,
Original investment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 3.
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, 4% for interest rate and 3 for number of years.
So, the present value of annuity due is $88.90.
Compute present value of annuity due.
Given,
Original investment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 2.
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, 4% for interest rate and 2 for number of years.
So the present value of annuity due is $92.46.
Calculation of present value of annuity due
Given,
Original investment $100
Interest rate 4%
Number of years 1
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, 4% for interest rate and 1 for number of years.
So the present value of annuity due is $96.15.
The future value of annuity due is $324.65 while the present value is $277.51.
g.1.
To calculate: Present value of ordinary annuity with an annual interest rate of 4% for 5 years.
g.1.
Explanation of Solution
Compute present value of ordinary annuity.
Given,
Annual payment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 5.
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for annual payment, 4% for interest rate and 5 for number of years.
Present value of ordinary annuity is $445.18
2.
To calculate: Present value of ordinary annuity with an annual interest rate of 4% for 10 years.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Compute present value of ordinary annuity.
Given,
Annual payment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 10.
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for annual payment, 4% for interest rate and 10 for number of years.
Present value of ordinary annuity for 10 years is $811.09.
3.
To calculate: Present value of ordinary annuity with an annual interest rate of 4% for 25 years.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Compute present value of ordinary annuity.
Given,
Annual payment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Number of years is 25.
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for annual payment, 4% for interest rate and 25 for number of years.
Present value of ordinary annuity for 25 years is $1,562.21.
4.
To calculate: Present value of ordinary annuity with an annual interest rate of 4% with perpetuity.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Compute present value of ordinary annuity.
Given,
Original investment is $100.
Interest rate is 4%.
Formula to calculate present value,
Substitute $100 for original investment, and 4% for interest rate.
Present value of ordinary annuity with 4% interest rate with perpetuity is $2500.
h.1.
To calculate: Future value of $5 daily after 45years with 8% annual returns.
h.1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation is solved in spreadsheet by “FV” formula,

Table (2)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “FV” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “FV” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
- Final answer will be shown by the formula that is $58,254.82.
The future value of $1,825 after 45 years at 8% interest rate will be $58,254.82
2.
To calculate: Future value of $5 daily after 25 years with 8% annual returns.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation is solved in spreadsheet by “FV” formula,

Table (3)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “FV” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “FV” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
- Final answer will be shown by the formula that is $12,498.47.
The future value of $1,825 after 25 years at 8% interest rate will be $12,498.47.
3.
To calculate: Amount to be saved in by 40 years old to get the return of $58,254.82.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation is solved in spreadsheet by “PMT” formula,
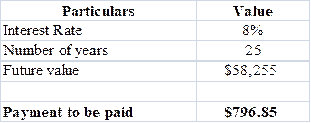
Table (4)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “PMT” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “PMT” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
- Final answer will be shown by the formula that is $796.85.
Amount to be saved by 40 years old to get the return of $58,254.82 is $796.85.
i.
To calculate: The present value of uneven cash flow with annual interest rate 4%.
i.
Explanation of Solution
Present value of uneven cash flow is shown in table.
| Years |
Cash Flows ($) (A) |
Discount Factor at 4% (B) |
Present Value ($)
|
| 1 | 100 | 0.9615 | 96.15 |
| 2 | 300 | 0.9246 | 277.37 |
| 3 | 300 | 0.8890 | 266.70 |
| 4 | -50 | 0.8548 | -42.74 |
| Total | 597.48 |
Table (5)
Working note:
Calculation of discount factor for year 1 is,
Calculation of discount factor for year 2 is,
Calculation of discount factor for year 3 is,
Calculation of discount factor for year 4 is,
Present value of uneven cash flows with annual interest rate of 4% is 597.48.
j.1.
To calculate: Future value with an initial amount more often than annually.
j.1.
Explanation of Solution
If the annual rate is 4% and cash flow is $50 for 5 years compounded annually.
Calculation is solved in spreadsheet by “FV” formula,

Table (5)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “FV” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “FV” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
- Final answer will be shown by the formula that is $60.83.
So, $50 after 5 years will be $60.83 at 4% annual rate.
If the annual rate is 4% and cash flow is $50 for 5 years compounded semiannually.
Calculation is solved in spreadsheet by “FV” formula,

Table (6)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “FV” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “FV” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
- Final answer will be shown by the formula that is $55.20.
So, $50 after 5 years will be $55.20 at 4% semiannual rate.
$50 after 5 years with 4% annual rate is $60.83 while with semiannual rate is $55.20.
2.a.
To explain: Nominal interest rate.
2.a.
Answer to Problem 42IC
Credit card companies generally charge an annual percentage rate for giving money on credit that charge is called nominal interest rate.
Explanation of Solution
Nominal interest rate is a rate for a particular period; it is converted into the effective rate to get the difference between the nominal rates of two banks.
b.
To Explain: Periodic interest rate
b.
Answer to Problem 42IC
It is a rate charge on investment.
Explanation of Solution
Periodic interest rate is the interest rate charged on loan or an investment for a particular period of time it can be charged on monthly, semiannually or annual basis.
c.
To Explain: Effective annual rate
c.
Answer to Problem 42IC
It is an investment’s annual rate.
Explanation of Solution
If an individual wants to get true annual rates which can be compared with other banks then the nominal rate is converted into effective annual rate.
Nominal interest rate and effective rate is charged by bank annually while the periodic interest rate is charged on loan and investment and it can be monthly,semiannually, or annually.
3
To calculate: Effective annual rate correspondingto a nominal rate of 4% compounded semiannually, quarterly and daily.
3
Explanation of Solution
Calculation to get effective annual rate semiannually
Given,
Nominal interest rate 4%
Compounding Semiannually
Formula to calculate effective annual rate,
Where,
- EAR is the effective annual rate.
- APR is the annual percentage rate.
- M is the number of periods.
Substitute 4% for APR and M for 2
So, the effective annual rate for semiannually is 4.04%.
Compute effective annual rate quarterly.
Given,
Nominal interest rate is 4%.
Compounding is quarterly.
Formula to calculate effective annual rate,
Where,
- EAR is the effective annual rate.
- APR is the annual percentage rate.
- M is the number of periods.
Substitute 4% for APR and M for 4
So, the effective annual rate for quarterly is 4.06%.
Compute effective annual rate daily.
Given,
Nominal interest rate is 4%.
Compounding is daily.
Formula to calculate effective annual rate,
Where,
- EAR is the effective annual rate.
- APR is the annual percentage rate.
- M is the number of periods.
Substitute 4% for APR and M for 365
So the effective annual rate for daily is 4.06%.
The effective annual rate for semiannually is 4.04%, for quarterly is 4.06%and for daily is 4.08%
4.
To calculate: Future value of $100 after 3 years under 4% semiannual and quarterly compounding.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation is solved in spreadsheet by “FV” formula,

Table (7)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “FV” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “FV” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
- Final answer will be shown by the formula that is $112.62
So, $100 will be $112.62 at 4% annual rate.
Future value of $100 after 3 years under 4% quarterly
Calculation is solved in spreadsheet by “FV” formula,

Table (7)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “FV” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “FV” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
- Final answer will be shown by the formula that is $112.62
So, $100 will be $112.68 at 4% annual rate.
Thus, $100 will be $112.62 after 3 years at 4% annual interest rate for semiannually and it will be $112.68 after 3 years at 4% annual interest rate for quarterly.
k.
To explain: When the effective annual rate will equal nominal rate.
k.
Answer to Problem 42IC
Effective annual rate and nominal rate become equal when the interest calculation is considered.
Explanation of Solution
Investment’s annual rate is effective annual rate while nominal interest rate are generally charged by the credit card companies for particular period. They can only be equal when simple interest calculation is considered; they will never be same for
Effective annual rate and nominal interest rate can only be equal during simple interest consideration.
l.1.
To calculate: The future value of cash flow stream at the end of 3 year at 4 % compounded annually.
l.1.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of ordinary annuity at 2% interest rate after 3 years which earn 4% compounded semiannually.
| Periods |
Cash Flows ($) (A) |
Future Value factor at 2% (B) |
Future Value ($)
|
| 2 | 100 | 1.0824 | 108.2432 |
| 4 | 100 | 1.0404 | 104.0400 |
| 6 | 100 | 1 | 100.0000 |
| Total | 312.2832 |
Table (8)
Working note:
Calculation of discount factor for year 2 is,
Calculation of discount factor for year 4 is
The future value of annuity is $312.2832.
2.
To calculate: The present value of cash flow stream at the end of 3 year at 4 % compounded annually.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of ordinary annuity at 2% interest rate after 3 years which earn 4% compounded semiannually.
| Periods |
Cash Flows ($) (A) |
Present Value factor at 2% (B) |
Future Value ($)
|
| 2 | 100 | 0.9612 | 96.1169 |
| 4 | 100 | 0.9238 | 92.3845 |
| 6 | 100 | 0.8880 | 88.7971 |
| Total | 277.2986 |
Table (9)
Working note:
Calculation of present value factor for year 2,
Calculation of present value factor for year 4,
Calculation of present value factor for year 6,
Present value of cash flow stream at the end of 3 year at 4 % compounded annually is $277.2986.
3.
To explain: The answer, if instead of 4%/2 or 2%/2 it is 4% or 2%.
3.
Answer to Problem 42IC
The answer will be incorrect.
Explanation of Solution
It is used 4% when compounding is done annually but for semiannually if 4% is to be taken it will give the incorrect result, so 2% is to be used instead of 4%.
To get the correct answer 2% is used instead of 4%.
m.
To prepare: Amortization schedule for a $1,000 at 4% annual interest loan with three equal installments
m.
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of annual installment is done by using “PMT” formula in spreadsheet at the amortization schedule.
Amortization Schedule is prepared below.
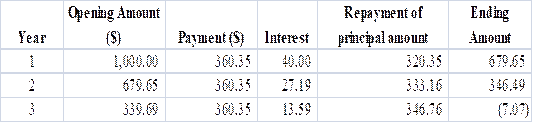
Table (10)
Steps required to calculate present value by using “PMT” function in excel are given,
- Select ‘Formulas’ option from Menu Bar of excel sheet.
- Select insert Function that is (fx).
- Choose category of Financial.
- Then select “PMT” and then press OK.
- A window will pop up.
- Input data in the required field.
Payment for period 1 and period 2 is $360.35.
2.
To explain: Annual interest expense and annual interest income during year 2.
2.
Answer to Problem 42IC
Annual interest expense and annual interest income for lender during year 2 is $27.19
Explanation of Solution
Annual interest expense is an expense for borrower while it is an income for lender which is calculated in part 1 and that is $27.19.
Annual interest expense for borrower and annual interest income for lender during year 2 is $27.19.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Financial Management
- What is the finance ? tell about its significant.arrow_forwardTake value of 1.01^-36=0.699 . step by steparrow_forwardsolve this question.Pat and Chris have identical interest-bearing bank accounts that pay them $15 interest per year. Pat leaves the $15 in the account each year, while Chris takes the $15 home to a jar and never spends any of it. After five years, who has more money?arrow_forward
 Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College
Excel Applications for Accounting PrinciplesAccountingISBN:9781111581565Author:Gaylord N. SmithPublisher:Cengage LearningPrinciples of Accounting Volume 2AccountingISBN:9781947172609Author:OpenStaxPublisher:OpenStax College





