
Estimated Time: 25–30 minutes
Group Size: 2
Right
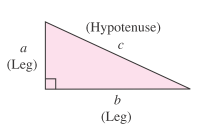
Right triangles have an important property that the sum of the squares of the two legs of a right triangles have an important property that the sum of the squares of the two legs of a right triangle equals the square of the hypotenuse. This fact is referred to as the Pythagorean theorem. In symbols, the Pythagorean theorem is stated as:
Now equate the two expressions representing the area of the large outer square:
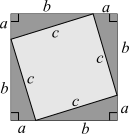
To calculate: The expression representing the area of large outer square. The figure is as follows:
Answer to Problem 3GA
Solution:
Equating the area of large outer square to the sum of area of Inner Square and area of four right triangle gives
Explanation of Solution
Given Information:
The area of Inner Square is

Formula Used:
The area of square is
The area of right-angle triangle is
Calculation:
Consider the given figure.
Steps to determine the area of large outer square:
Step1: First determine the area of Inner Square and area of four right triangles.
Step2: Then add both areas which is equal to area of large outer square.
Area of Inner Square is
Now, add these two areas and equate it to the area of large outer square.
Clear the parenthesis on both sides of the equation.
Subtract
Thus, equating the area of large outer square to the sum of area of Inner Square and area of four right triangle gives
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
ALEKS 360 ONLINE ACCESS (6 WEEKS) FOR B
- Solve questions by Course Name (Ordinary Differential Equations II 2)arrow_forwardplease Solve questions by Course Name( Ordinary Differential Equations II 2)arrow_forwardInThe Northern Lights are bright flashes of colored light between 50 and 200 miles above Earth. Suppose a flash occurs 150 miles above Earth. What is the measure of arc BD, the portion of Earth from which the flash is visible? (Earth’s radius is approximately 4000 miles.)arrow_forward
- e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardSuppose you flip a fair two-sided coin four times and record the result. a). List the sample space of this experiment. That is, list all possible outcomes that could occur when flipping a fair two-sided coin four total times. Assume the two sides of the coin are Heads (H) and Tails (T).arrow_forwarde). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forward
- Evaluate the following expression and show your work to support your calculations. a). 6! b). 4! 3!0! 7! c). 5!2! d). 5!2! e). n! (n - 1)!arrow_forwardAmy and Samiha have a hat that contains two playing cards, one ace and one king. They are playing a game where they randomly pick a card out of the hat four times, with replacement. Amy thinks that the probability of getting exactly two aces in four picks is equal to the probability of not getting exactly two aces in four picks. Samiha disagrees. She thinks that the probability of not getting exactly two aces is greater. The sample space of possible outcomes is listed below. A represents an ace, and K represents a king. Who is correct?arrow_forwardConsider the exponential function f(x) = 12x. Complete the sentences about the key features of the graph. The domain is all real numbers. The range is y> 0. The equation of the asymptote is y = 0 The y-intercept is 1arrow_forward
 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal Littell Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill





