
Concept explainers
1.
Ascertain the cost of goods available for sale, and the number of units available for sales.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the cost of goods available for sale, and the number of units available for sales as follows:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Beginning balance | 600 | 45 | 27,000 |
| Add: Purchases | |||
| February 10 | 400 | 42 | 16,800 |
| March 13 | 200 | 27 | 5,400 |
| August 21 | 100 | 50 | 5,000 |
| September 5 | 500 | 46 | 23,000 |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 1,800 | 77,200 |
Table (1)
Therefore, the number of units available for sales is 1,800 units, and the cost of goods available for sale is $77,200.
2.
Ascertain the number of units in ending inventory.
2.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the number of units in ending inventory as follows:
| Details | Number of Units |
| Total Goods available for Sale | 1,800 |
| Less: Sales: | |
| March 15 | 800 |
| September 10 | 600 |
| Ending Inventory | 400 |
Table (2)
Therefore, the number of units in ending inventory is 400.
3.
Ascertain the cost assigned to ending inventory under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification.
3.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual inventory system: The method or system of maintaining, recording, and adjusting the inventory perpetually throughout the year, is referred to as perpetual inventory system.
First-in-First-Out (FIFO): In this method, items purchased initially are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the recent cost for the remaining unsold items.
Last-in-First-Out (LIFO): In this method, items purchased recently are sold first. So, the value of the ending inventory consist the initial cost for the remaining unsold items.
Weighted-average Cost Method: In this method, the inventories are priced at the average rate of goods available for sales.
Specific identification method: Specific identification method identifies the cost of each item in ending inventory by separating purchases. In this method, the value of ending inventory is computed based on the lower of cost or market value.
Ascertain the cost assigned to ending inventory under (a) FIFO, (b) LIFO, (c) weighted average, and (d) specific identification as follows:
(a) FIFO
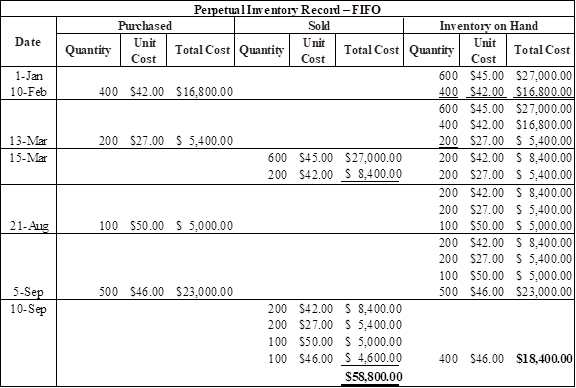
Table (3)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under FIFO is $18,400.
(b) LIFO

Table (4)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under LIFO is $18,000.
(c) Weighted average method:
Refer working note 1 and 2 for calculation of weighted average cost

Table (5)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under weighed average method is $17,760.
Working note:
Calculate the weighted average cost of inventory after March 13purchase
Calculate the weighted average cost of inventory after September 5 purchase
(d) Specific identification method:
| Details | Number of Units | Rate per Unit ($) | Total Cost ($) |
| Cost of goods available for sale (refer table 1) | 77,200 | ||
| Less: Cost of goods sold | |||
| Beginning inventory | 600 | 45 | 27,000 |
| February 10 | 300 | 42 | 12,600 |
| March 13 | 200 | 27 | 5,400 |
| August 21 | 50 | 50 | 2,500 |
| September 5 | 250 | 46 | 11,500 |
| Ending inventory | 18,200 |
Table (6)
Therefore, the cost of ending inventory under specific identification method is $18,200.
4.
Ascertain the gross profit earned by the company for the each of the given methods.
4.
Explanation of Solution
Ascertain the gross profit earned by the company for the each of the given methods as follows:
| Particulars | FIFO | LIFO | Specific Identification | Weighted Average |
| Sales | $ 105,000 | $ 105,000 | $105,000 | $ 105,000 |
| Less: Cost of goods sold | $ 58,800 | $ 59,200 | $ 59,000 | $ 59,440 |
| Gross profit | $ 46,200 | $ 45,800 | $46,000 | $ 45,560 |
Table (7)
5.
Identify the inventory method which is preferred by the manager, if company’s manger earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit.
5.
Explanation of Solution
Identify the inventory method which is preferred by the manager, if company’s manger earns a bonus based on a percent of gross profit as follows:
In this case, gross profit under FIFO method ($46,200) is more than the other three methods. Hence, the manager of Company would likely to prefer the FIFO method.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Financial Accounting Fundamentals
- Please explain the correct approach for solving this general accounting question.arrow_forwardI am trying to find the accurate solution to this financial accounting problem with appropriate explanations.arrow_forwardI need help finding the correct solution to this financial accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forward
- Can you help me solve this general accounting problem with the correct methodology?arrow_forwardI need help with this financial accounting problem using proper accounting guidelines.arrow_forwardPlease provide the solution to this general accounting question using proper accounting principles.arrow_forward
- I need help finding the accurate solution to this general accounting problem with valid methods.arrow_forwardWhen incorporating his sole proprietorship, Joe transfers all of its assets and liabilities. Included in the $30,000 of liabilities assumed by the corporation is $500 that relates to a personal expenditure. Under these circumstances, the entire $30,000 will be treated as boot. / Provide explanation please a. True b. Falsearrow_forwardIn determining whether § 357(c) applies, assess whether the liabilities involved exceed the bases of all assets a shareholder transfers to the corporation./ Provide explanation please. a. True b. Falsearrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





