
(a)
The way to obtain the graph of the function
(a)
Answer to Problem 1RE
The graph of
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Concept used:
Shifting of graphs:
“Shifting is a rigid translation because it does not change the size and shape of the curve. Shifting is used to move the curve vertically or horizontally without any change in shape and size of the curve.”
The function
The function
Scaling of graph:
Scaling is used to change the shape and size of the curve. A vertical scaling multiplies or divides ever
If
A horizontal scaling multiplies or divides ever
Calculation:
The given function is
The given function is of the form
The graph of
First obtain the graph of
The graph of
Now obtain the graph of
The graph of
Thus, the graph of
(b)
The graph of the function
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
Draw the graph of the function
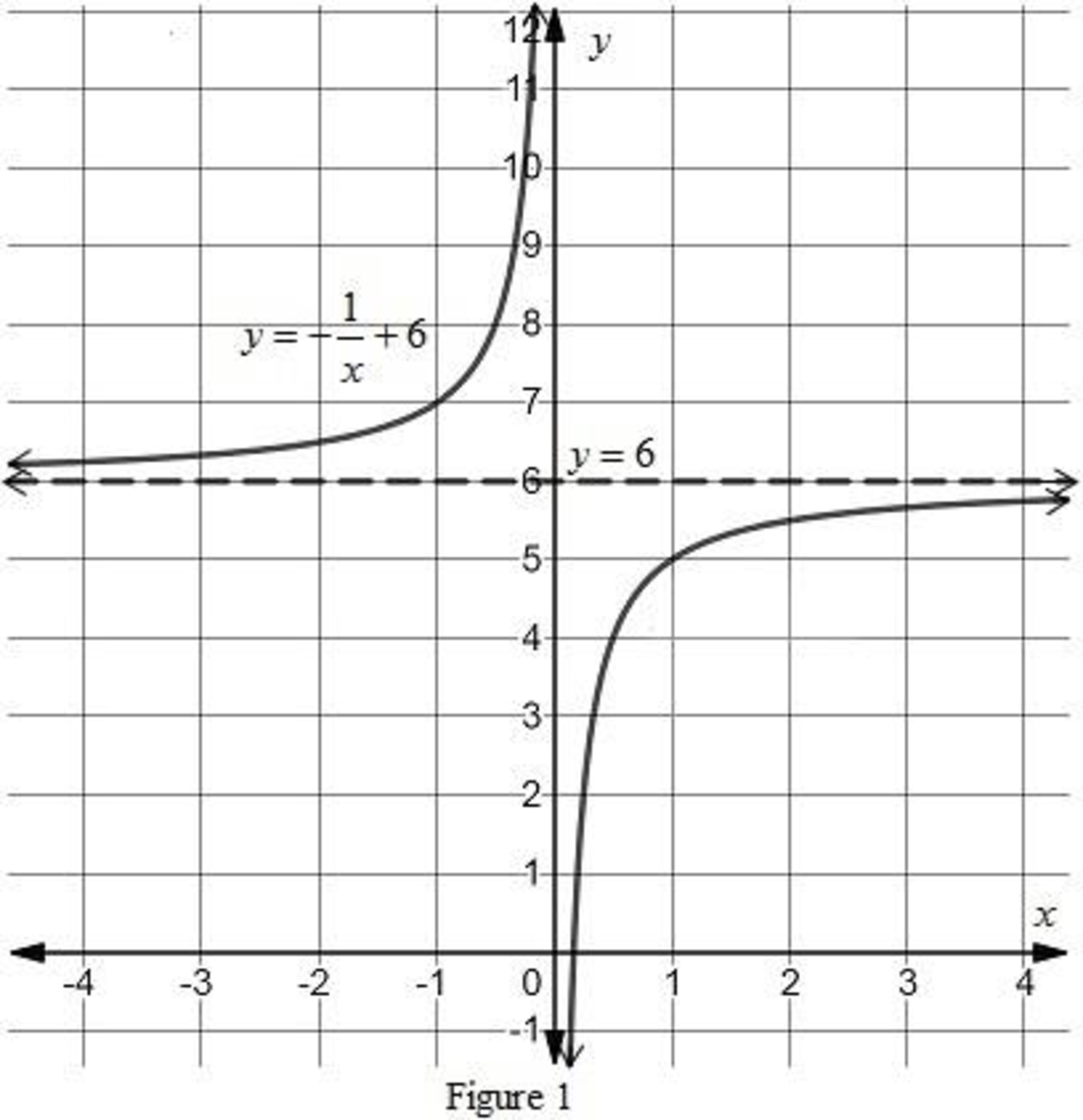
Figure
(c)
The graph of the function
(c)
Explanation of Solution
Given:
The function is
Calculation:
To graph the function
Press the button

Now press the
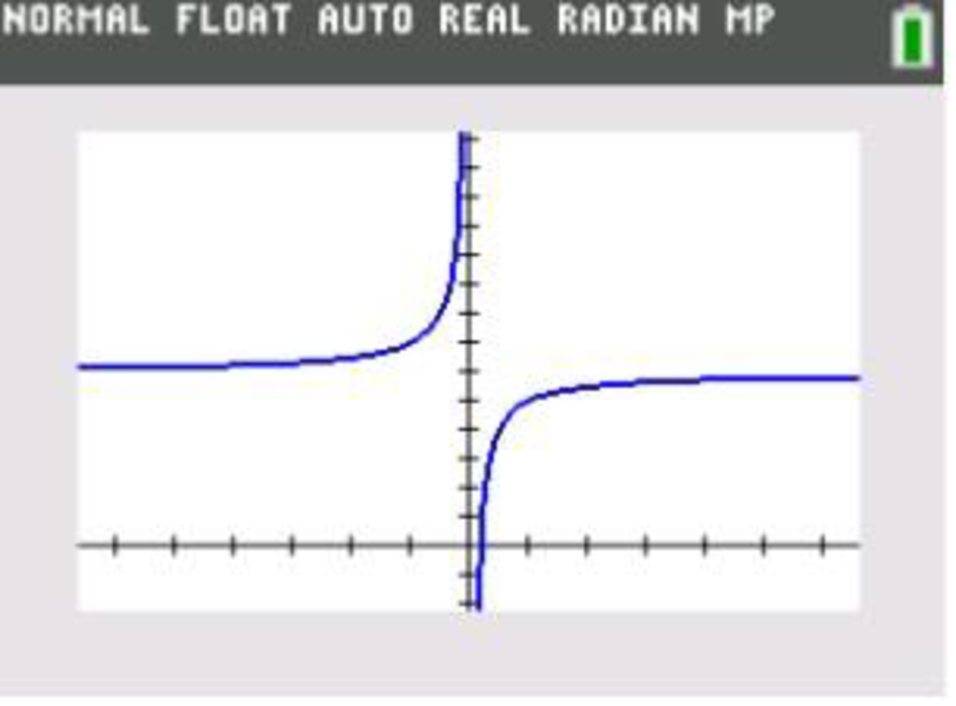
In the above screen the graph of the function
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
MyLab Math with Pearson eText -- Standalone Access Card -- for A Graphical Approach to College Algebra (7th Edition)
- In simplest way, For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. a) y = x 2 + 16 x + 39 b) y = 5 x2 - 50 x - 120arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step Write each quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = - 4( x + 6)2 + 36arrow_forwardIn simplest terms and step by step For each quadratic relation, find the zeros and the maximum or minimum. 1) y = - 2 x2 - 28 x + 64 2) y = 6 x2 + 36 x - 42arrow_forward
- Write each relation in standard form a)y = 5(x + 10)2 + 7 b)y = 9(x - 8)2 - 4arrow_forwardIn simplest form and step by step Write the quadratic relation in standard form, then fi nd the zeros. y = 3(x - 1)2 - 147arrow_forwardStep by step instructions The path of a soccer ball can be modelled by the relation h = - 0.1 d 2 + 0.5 d + 0.6, where h is the ball’s height and d is the horizontal distance from the kicker. a) Find the zeros of the relation.arrow_forward
 Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra and Trigonometry (6th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780134463216Author:Robert F. BlitzerPublisher:PEARSON Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning
Contemporary Abstract AlgebraAlgebraISBN:9781305657960Author:Joseph GallianPublisher:Cengage Learning Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON
Algebra And Trigonometry (11th Edition)AlgebraISBN:9780135163078Author:Michael SullivanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press
Introduction to Linear Algebra, Fifth EditionAlgebraISBN:9780980232776Author:Gilbert StrangPublisher:Wellesley-Cambridge Press College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
College Algebra (Collegiate Math)AlgebraISBN:9780077836344Author:Julie Miller, Donna GerkenPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





