
(a)
The equation and definition of unit circle.
(a)
Explanation of Solution
A unit circle is a circle with radius one unit whose centre lies on the origin
The equation of a unit circle is shown below.
Therefore, a unit circle is a circle with radius 1 unit whose equation is
(b)
To explain: The term terminal point determined by t with the help of a diagram.
(b)
Explanation of Solution
Consider a unit circle with the starting point
Consider a point
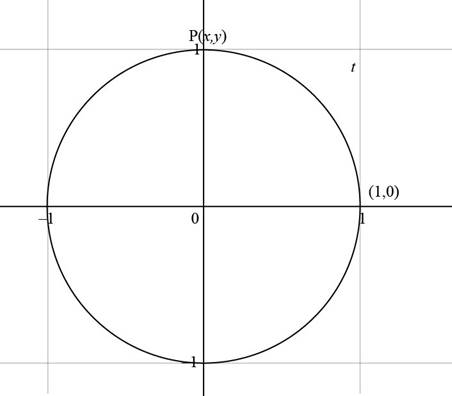
Figure (1)
It is clearly seen from the above figure that the terminal point is
Therefore, the term used for the end point after covering t distance in counterclockwise direction of a unit circle is terminal point.
(c)
The terminal point for
(c)
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The terminal point determined by
Explanation of Solution
Consider a unit circle with the starting point
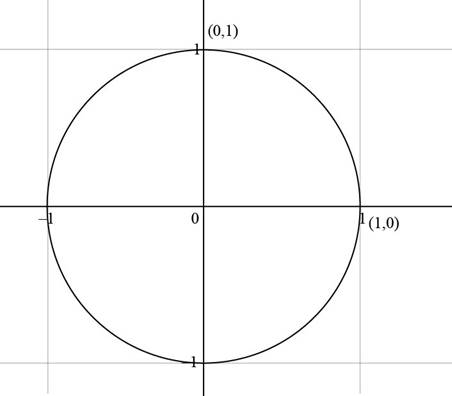
Figure (2)
Therefore, the terminal point determined by
(d)
To explain: The reference point associated with t.
(d)
Explanation of Solution
Let t is a real number.
The reference number
To obtain the reference, it is very important to know the position of t in the quadrant.
If the terminal point lies on first or fourth quadrant, where x is positive then
Thus, the reference number
(e)
The reference number and terminal point for
(e)
Answer to Problem 1RCC
The reference number for
Explanation of Solution
The reference point
The reference number for
The reference number is
Since the terminal point determined by t is in fourth quadrant therefore, x coordinate is positive and y coordinate is negative.
Hence the terminal point is
Thus, the reference number for
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
PRECALCULUS: MATHEMATICS FOR CALCULUS
- Find the effective rate corresponding to the given nominal rate. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) (a) 9.5%/year compounded monthly % (b) 9.5%/year compounded daily % Need Help? Read It Watch It SUBMIT ANSWER -/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES TANAPCALC10 5.3.007. ASK YOUR TEACHE Find the present value of $90,000 due in 7 years at the given rate of interest. (Round your answers to the nearest cent.) (a) 9%/year compounded semiannually (b) 9%/year compounded quarterly LAarrow_forwardFind the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $160,000, r = 7%, t = 4, compounded daily A = $211113.60 Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER --/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES TANAPCALC10 5.3.005. Find the effective rate corresponding to the given nominal rate. (Round your answers to three decimal places.) (a) 8%/year compounded semiannually % (b) 9%/year compounded quarterly %arrow_forwardFind the derivative of the function. g'(t) = 9t g(t) = In(t) (9ln(t) - 1) [In(t)] 2 × Need Help? Read It Watch Itarrow_forward
- Find the accumulated amount A, if the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) P = $3800, r = 4%, t = 10, compounded semiannually A = $ 5645.60 × Need Help? Read It SUBMIT ANSWER [3.33/6.66 Points] DETAILS MY NOTES REVIOUS ANSWERS ASK YOUR TEACHER TANAPCALC10 5.3.001.EP. PRACTICE ANOTHER Consider the following where the principal P is invested at an interest rate of r per year for t years. P = $3,100, r = 4%, t = 10, compounded semiannually Determine m, the number of conversion periods per year. 2 Find the accumulated amount A (in dollars). (Round your answer to the nearest cent.) A = $ 4604.44arrow_forwardForce with 800 N and 400 N are acting on a machine part at 30° and 60°, respectively with a positive x axis, Draw the diagram representing this situationarrow_forwardI forgot to mention to you to solve question 1 and 2. Can you solve it using all data that given in the pict i given and can you teach me about that.arrow_forward
 Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL
Holt Mcdougal Larson Pre-algebra: Student Edition...AlgebraISBN:9780547587776Author:HOLT MCDOUGALPublisher:HOLT MCDOUGAL Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal LittellAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage
Algebra: Structure And Method, Book 1AlgebraISBN:9780395977224Author:Richard G. Brown, Mary P. Dolciani, Robert H. Sorgenfrey, William L. ColePublisher:McDougal LittellAlgebra & Trigonometry with Analytic GeometryAlgebraISBN:9781133382119Author:SwokowskiPublisher:Cengage Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
 College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Algebra (MindTap Course List)AlgebraISBN:9781305652231Author:R. David Gustafson, Jeff HughesPublisher:Cengage Learning





