
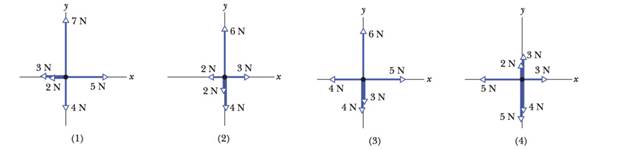
Figure 5-19 gives the free-body diagram for four situations in which an object is pulled by several forces across a frictionless floor, as seen from overhead. In which situations does the acceleration
To Find
a) Which situation have x component of acceleration.
b) Which situation have y component of acceleration.
c) Direction of acceleration for each situation.
Answer to Problem 1Q
Solution
a) 2, 3 and 4.
b) 1, 3 and 4.
c) 1 – Along + y-axis, 2- Along + x-axis, 3- In 4th quadrant and 4- In 3rd quadrant.
Explanation of Solution
1) Concept:
Using the concept of net force from the Newton’s second law of motion, we can find the net force acting on the given object for given conditions.
2) Calculations:
a) According to Newton’s second law net force is product of mass and acceleration.
If we want x component acceleration there must be net force in x direction
So, For situation 1
Net force in x direction
So, there is no x component of acceleration.
For Situation 2
Net Force in x direction
As net force is 1N, x component of acceleration is present.
For Situation 3
Net Force in x direction
As net force is 1N, x component of acceleration is present.
For Situation 4
Net Force in x direction
As net force is 1N, x component of acceleration is present.
b)
For situation 1
Net force in y direction
So, there is y component of acceleration.
For Situation 2
Net Force in y direction
As net force is no y component of acceleration is present.
For Situation 3
Net Force in y direction
As net force is -1N, y component of acceleration is present.
For Situation 4
Net Force in y direction
As net force is -4N, y component of acceleration is present.
c) Direction of acceleration is in direction of net force.
For situation 1 there is only net force is only in +y direction so acceleration is also in +y direction.
For situation 2 there is only net force is only +x direction so acceleration is also +x direction.
For situation 3 as there is net force both in x and y direction and total net force is in fourth quadrant.
For situation 4 as there is net force both in x and y direction and total net force is in third quadrant.
Conclusion: Using the equations from the Newton’s second law of motion and vector algebra, it is possible to find the net force acting on the system.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fundamentals Of Physics
- 6. As the distance between two charges decreases, the magnitude of the electric potential energy of the two-charge system: a) Always increases b) Always decreases c) Increases if the charges have the same sign, decreases if they have the opposite signs d) Increases if the charges have the opposite sign, decreases if they have the same sign 7. To analyze the motion of an elastic collision between two charged particles we use conservation of & a) Energy, Velocity b) Momentum, Force c) Mass, Momentum d) Energy, Momentum e) Kinetic Energy, Potential Energyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forwardpls help on all asked questions kindlyarrow_forward
- 17. Two charges, one of charge +2.5 × 10-5 C and the other of charge +3.7 × 10-6 C, are 25.0 cm apart. The +2.5 × 10−5 C charge is to the left of the +3.7 × 10−6 C charge. a. Draw a diagram showing the point charges and label a point Y that is 20.0 cm to the left of the +3.7 × 10-6 C charge, on the line connecting the charges. (Field lines do not need to be drawn.) b. Calculate the net electric field at point Y.arrow_forward3arrow_forwardSet ба ||Axl 49.32 6b 71 Ay 22 Magnitude of A Angle of A 24.04 Angle of -A 22 54 155.96 ° (pos Ax) 204.04 ° (neg Ax) 335.96 ° (pos Ax) ° (neg Ax) 115.77 ° (pos Ax) 295.77 ° (pos Ax) -39 81 208.78 ° (neg Ax) 28.78 ° (neg Ax)arrow_forward
 Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning
Classical Dynamics of Particles and SystemsPhysicsISBN:9780534408961Author:Stephen T. Thornton, Jerry B. MarionPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers with Modern ...PhysicsISBN:9781337553292Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning





