
Concept explainers
Purchase-related transactions using perpetual inventory system
The following selected transactions were completed by Niles Co. during March of the current year:
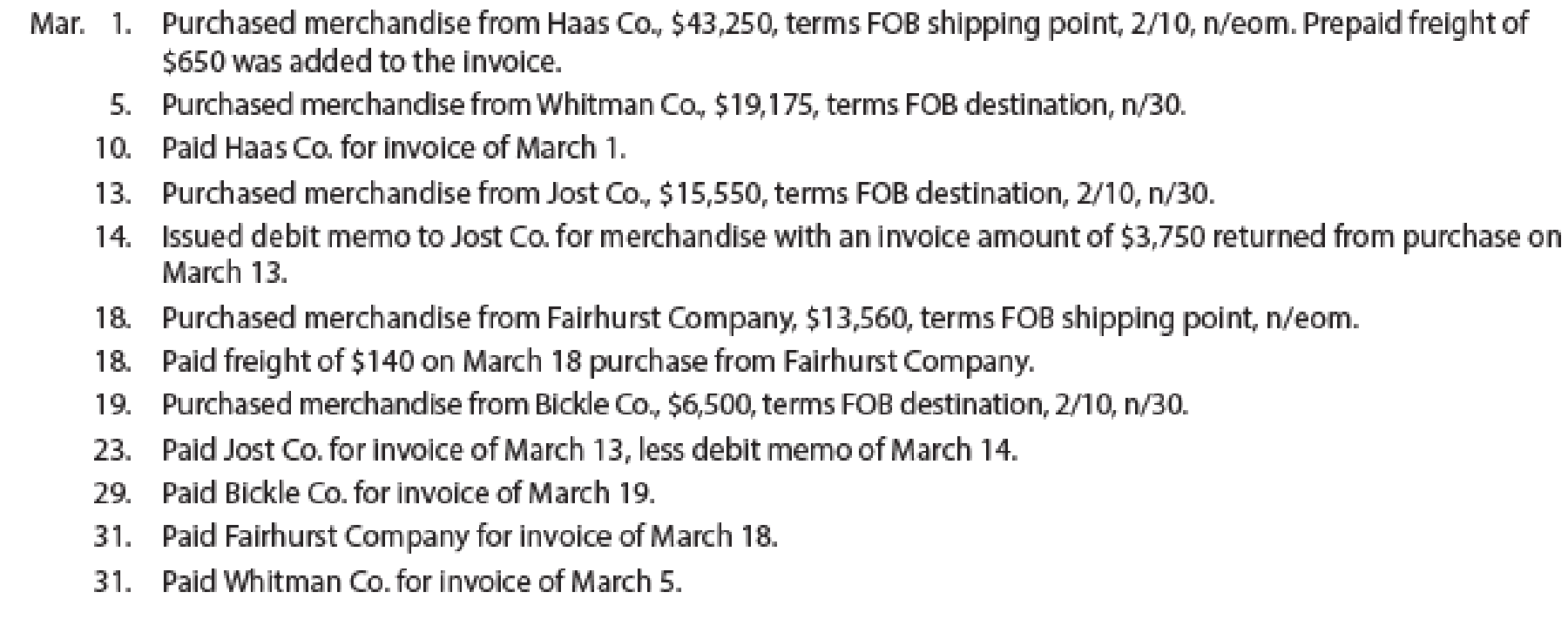
Instructions
Journal entry: Journal is the book of original entry whereby all the financial transactions are recorded in chronological order. Under this method each transaction has two sides, debit side and credit side. Total amount of debit side must be equal to the total amount of credit side. In addition, it is the primary books of accounts for any entity to record the daily transactions and processed further till the presentation of the financial statements.
The following are the rules of debit and credit:
- 1. Increase in assets and expenses accounts are debited. Decrease in liabilities and stockholders’ equity accounts are debited.
- 2. Increase in liabilities, revenues, and stockholders’ equity accounts are credited. Decreases in all asset accounts are credited.
Prepare journal entries to record the transactions of Company N during the month of March using perpetual inventory system.
Explanation of Solution
Perpetual Inventory System refers to the inventory system that maintains the detailed records of every inventory transactions related to purchases and sales on a continuous basis. It shows the exact on-hand- inventory at any point of time.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 1 | Inventory | 43,035 | ||
| Accounts payable | 43,035 (1) | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (1)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of accounts payable.
Purchases = $43,250
Discount percentage = 2%
Freight charges = $650
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $43,035. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $43,035.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $43,035. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $43,035.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 5 | Inventory | 19,175 | ||
| Accounts payable | 19,175 | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (2)
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $19,175. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $19,175.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $19,175. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $19,175.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 10 | Accounts payable | 43,035 | ||
| Cash | 43,035 | |||
| (To record the payment against accounts payable) |
Table (3)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $43,035. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $43,035.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $43,035. Therefore, credit cash account with $43,035.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 13 | Inventory | 15,239 | ||
| Accounts payable | 15,239 (2) | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (4)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of accounts payable.
Purchases = $15,550
Discount percentage = 2%
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $15,239. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $15,239.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $15,239. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $15,239.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 14 | Accounts payable | 3,675 (3) | ||
| Inventory | 3,675 | |||
| (To record purchase return) |
Table (5)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of accounts payable.
Purchases return = $3,750
Discount percentage = 2%
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $3,675. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $3,675.
- Inventory is an asset and it is decreased by $3,675. Therefore, credit Inventory account with $3,675.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 18 | Inventory | 13,560 | ||
| Accounts payable | 13,560 | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (6)
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $13,560. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $13,560.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $13,560. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $13,560.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 18 | Inventory | 140 | ||
| Cash | 140 | |||
| (To record freight charges paid) |
Table (7)
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $140. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $140.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $140. Therefore, credit cash account with $140.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 19 | Inventory | 6,370 | ||
| Accounts payable | 6,370 (4) | |||
| (To record purchase on account) |
Table (8)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of accounts payable.
Purchases = $6,500
Discount percentage = 2%
- Inventory is an asset and it is increased by $6,370. Therefore, debit Inventory account with $6,370.
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is increased by $6,370. Therefore, credit accounts payable account with $6,370.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 23 | Accounts payable | 11,564 (5) | ||
| Cash | 11,564 | |||
| (To record payment made in full settlement less discounts) |
Table (9)
Working Note:
Calculate the amount of net accounts payable.
Inventory = $15,239 (2)
Purchase returns = $3,675 (3)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $11,564. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $11,564.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $11,564. Therefore, credit cash account with $11,564.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 29 | Accounts payable | 6,370 | ||
| Cash | 6,370 | |||
| (To record payment made in full settlement less discounts) |
Table (10)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $6,370. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $6,370.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $6,370. Therefore, credit cash account with $6,370.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 31 | Accounts payable | 13,560 | ||
| Cash | 13,560 | |||
| (To record payment made in full settlement less discounts) |
Table (11)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $13,560. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $13,560.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $13,560. Therefore, credit cash account with $13,560.
Record the journal entry of Company N.
| Date | Account Title and Explanation |
Post Ref. |
Debit ($) |
Credit ($) |
| March 31 | Accounts payable | 19,175 | ||
| Cash | 19,175 | |||
| (To record payment made in full settlement less discounts) |
Table (12)
- Accounts payable is a liability and it is decreased by $19,175. Therefore, debit accounts payable account with $19,175.
- Cash is an asset and it is decreased by $19,175. Therefore, credit cash account with $19,175.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
FINANCIAL&MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING(LL)W/AC
- Estimate the cost of the merchandise destroyedarrow_forwardFairview Clinic buys $500,000 in medical supplies each year (at gross prices) from its major supplier, Consolidated Supplies, which offers the clinic terms of 5/10, net 30. What is Fairview Clinic's costly trade credit? A. $13,194 B. $39,583 C. $32,986 D. $26,389 E. $22,431arrow_forwardWhat is the return on equityarrow_forward
- Problem related to Accountingarrow_forwardIn 2013, Lisa and Fred, a married couple, have taxable income of $300,000. If they were to file separate tax returns, Lisa would have reported taxable income of $125,000 and Fred would have reported taxable income of $175,000. What is the couple s marriage penalty or benefit?arrow_forwardA company had total sales revenue of $1,100,000. The beginning accounts receivable balance was $80,000, and the ending accounts receivable balance was $250,000. How much cash was collected from customers during this reporting period? A. $1,250,000 B. $1,030,000 C. $930,000 D. $870,000arrow_forward
 Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Financial And Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337902663Author:WARREN, Carl S.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272124Author:Carl Warren, James M. Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning
College Accounting (Book Only): A Career ApproachAccountingISBN:9781305084087Author:Cathy J. ScottPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning




