
1.
Prepare rate of change analyses for the income statements and balance sheets of Company C for 2016 and 2017 using the year to year approach.
1.
Explanation of Solution
Income statement: The financial statement which reports revenues and expenses from business operations and the result of those operations as net income or net loss for a particular time period is referred to as income statement.
Prepare rate of change analyses for the income statements of Company C for 2016 and 2017 using the year to year approach:
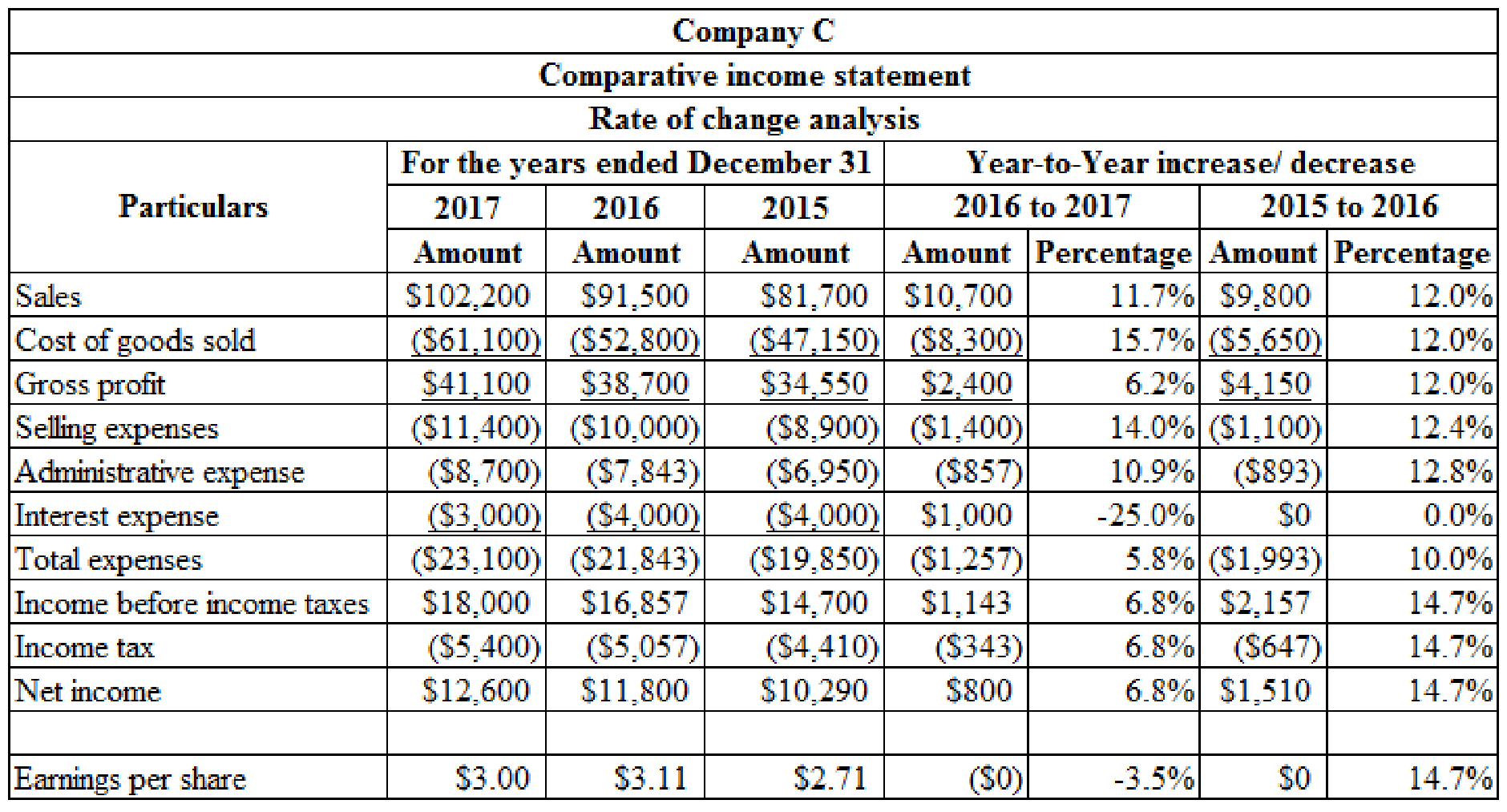
Table (1)
Prepare rate of change analyses for the
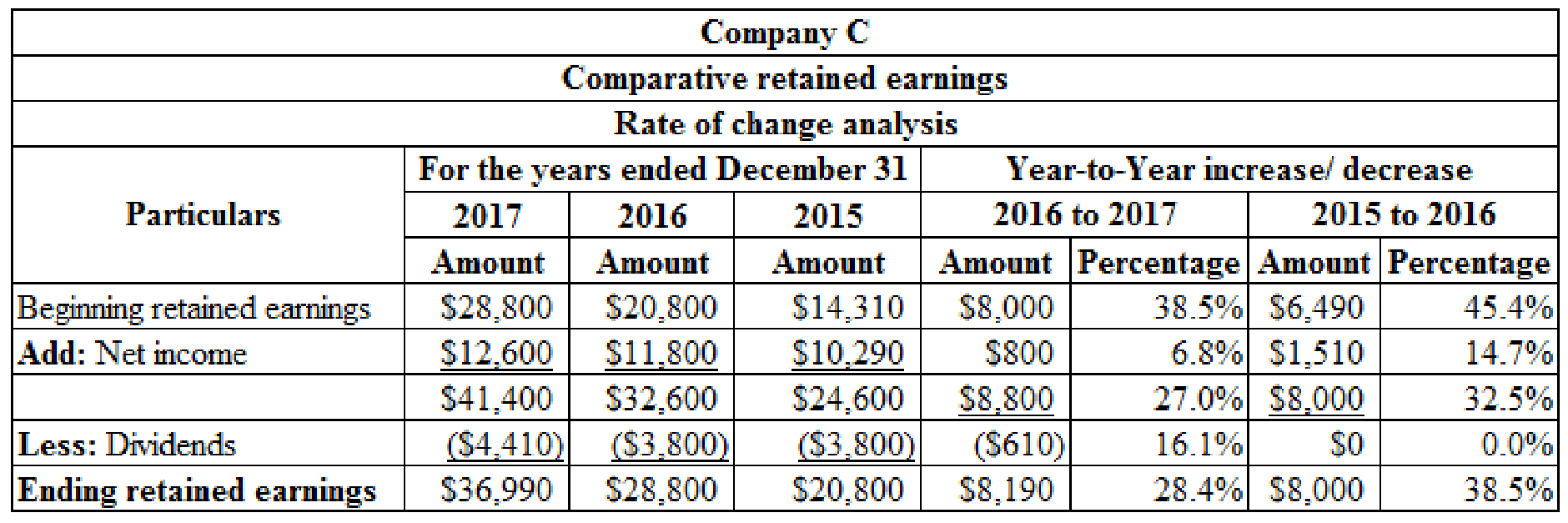
Table (2)
Prepare rate of change analyses for the balance sheets of Company C for 2016 and 2017 using the year to year approach:
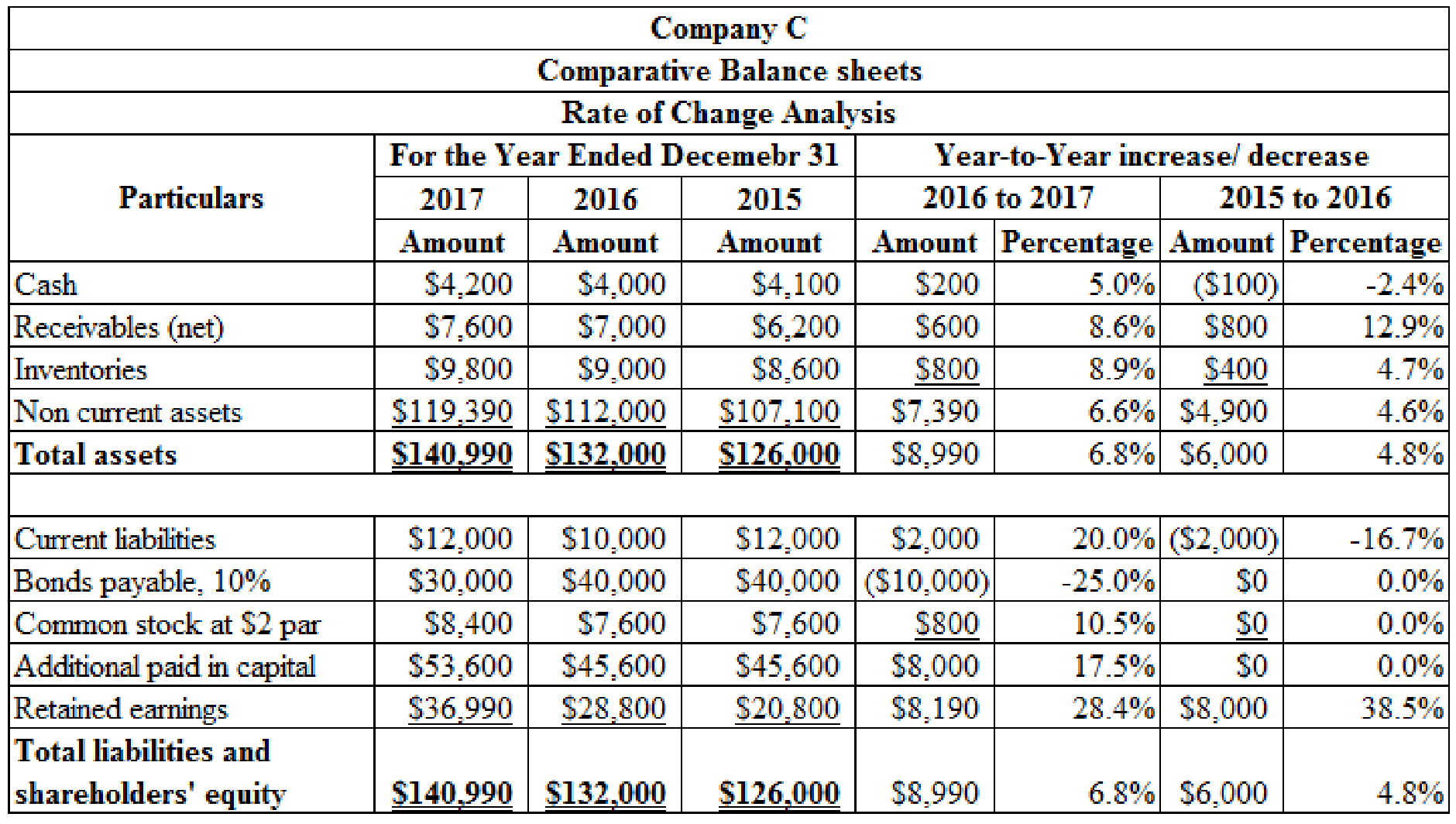
Table (3)
2. (a)
Compute
2. (a)
Explanation of Solution
Current ratio: Current ratio is one of the
Compute current ratio for 2016 and 2017:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
Current ratio: |
Table (4)
2. (b)
Compute inventory turnover for 2016 and 2017.
2. (b)
Explanation of Solution
Inventory Turnover Ratio: This ratio is a financial metric used by a company to quantify the number of times inventory is used or sold during the accounting period. It is calculated by using the formula:
Compute inventory turnover for 2016 and 2017:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
Inventory turnover: Average inventory: |
|
|
Table (5)
2. (c)
Compute receivable turnover for 2016 and 2017.
2. (c)
Explanation of Solution
Receivables turnover ratio: Receivables turnover ratio is mainly used to evaluate the collection process efficiency. It helps the company to know the number of times the
Compute receivable turnover for 2016 and 2017:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
Receivables turnover: Average accounts receivable: |
|
|
Table (6)
2. (d)
Compute net profit margin for 2016 and 2017.
2. (d)
Explanation of Solution
Net profit margin: It is one of the profitability ratios. Profit margin ratio is used to measure the percentage of net income that is being generated per dollar of revenue or sales.
Compute net profit margin for 2016 and 2017:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
Net profit margin: |
Table (7)
2. (e)
Compute earnings per share for 2016 and 2017.
2. (e)
Explanation of Solution
Earnings per Share: Earnings per share help to measure the profitability of a company. Earnings per share are the amount of profit that is allocated to each share of outstanding stock.
Compute earnings per share for 2016 and 2017:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
Earnings per share: |
Table (8)
2. (f)
Compute return on total assets ratio for 2016 and 2017.
2. (f)
Explanation of Solution
Return on total assets: Return on investments (assets) is the financial ratio which determines the amount of net income earned by the business with the use of total assets owned by it. It indicates the magnitude of the company’s earnings with relative to its total assets.
Compute return on total assets for 2016 and 2017:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
Return on total assets: Average total assets: |
|
|
Table (9)
Working note: 1 Determine the after tax rate:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
After tax rate: |
Table (10)
2. (g)
Compute return on common
2. (g)
Explanation of Solution
Return on common stockholders’ equity ratio: It is a profitability ratio that measures the profit generating ability of the company from the invested money of the shareholders. The formula to calculate the return on equity is as follows:
Compute return on common stockholders’ equity for 2016 and 2017:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
Return on common stockholders’ equity: Average stockholders’ equity: |
|
|
Table (11)
2. (h)
Compute debt to assets for 2016 and 2017.
2. (h)
Explanation of Solution
Debt to assets ratio: The debt to asset ratio shows the relationship between total asset and the total liability of the company. Debt ratio reflects the financial strategy of the company. It is used to measure the percentage of company’s assets that are financed by long term debts. Debt to assets ratio is calculated by using the formula:
Compute debt to assets for 2016 and 2017:
| Ratios and Formula | 2017 | 2016 |
|
Debt to assets ratio: |
Table (12)
3.
Explain the possible reasons for the decrease in the market price per share in 2017.
3.
Explanation of Solution
The probable reason for the decrease in the market price per share in 2017:
- The current ratio, receivable turnover ratio, net profit margin ratio, return on total assets, return on shareholders’ equity and earnings per share ratio in year 2017 are less than the result provided in the year of 2016.
- The financial condition of the company is not as strong as it was in 2016 because earnings per share of Company C have decreased from $3.11(2016) to $3 (2017) and the debt to assets ratio has also decreased from 37.9% (2016) to $29.8% (2017).
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting and Analysis (Looseleaf)
 Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning
Intermediate Accounting: Reporting And AnalysisAccountingISBN:9781337788281Author:James M. Wahlen, Jefferson P. Jones, Donald PagachPublisher:Cengage Learning Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning
Financial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781305088436Author:Carl Warren, Jim Reeve, Jonathan DuchacPublisher:Cengage Learning

