
Concept explainers
a)
Calculate the predetermined
a)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of total labor hours:
Hence, the total labor hours are $48,000.
Calculation of allocation rate:
Hence, the allocation rate per labor hour is $21.
b)
Calculate the total overhead cost allocated by the company to each product.
b)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of overhead cost allocated to each type of product:
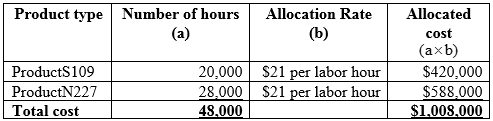
Table (1)
Hence, the total allocated cost is $1,008,000.
c)
Determine the cost per unit and total cost of products when direct labor hour is the base of overheads.
c)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of total cost of each product line and combined cost of the products:
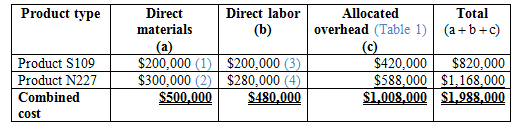
Table (2)
Hence, the total combined cost is $2,088,000.
Calculation of cost per unit using traditional cost method:
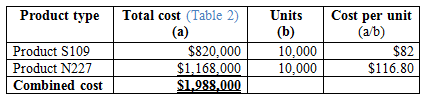
Table (3)
Hence, the costs per unit of product S109 and product N227 are $82 and $116.80.
Working notes:
Calculation of direct material cost for product S109:
Hence, the direct material cost for product S109 is $200,000.
…… (1)
Calculation of direct material cost for product N227:
Hence, the direct material cost for product N227 is $300,000.
…… (2)
Calculation of direct labor cost for product S109:
Hence, the direct labor cost for product S109 is $200,000.
…… (3)
Calculation of direct labor cost for product N227:
Hence, the direct labor cost for product N227 is $280,000.
…… (4)
d)
Calculate the price of each product using mark-up value.
d)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of price for each product:
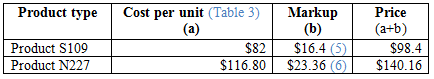
Table (4)
Hence, the prices of each product using markup are $98.4 and 140.16.
Working notes:
Calculation of mark-up value for Product S109:
Hence, the mark-up value for Product S109 is 16.4.
…… (5)
Calculation of mark-up value for Product N227:
Hence, the mark-up value for Product N227 is 23.36.
…… (6)
e)
Calculate the overhead rate of each product.
e)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of overhead cost under ABC system:
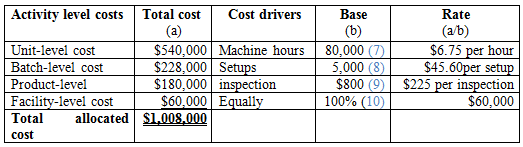
Table (5)
Working notes:
Calculation of base rate for unit-level cost:
Hence, the base rate for unit-level cost is 80,000 hours.
…… (7)
Calculation of base rate for batch-level cost:
Hence, the base rate for batch-level cost is 5,000 setups.
…… (8)
The calculation of base rate for product-level cost:
Hence, the base rate for product-level cost is 800 inspections.
…… (9)
Calculation of base rate for facility-level cost:
Hence, the base rate for facility-level cost is 100%.
…… (10)
f)
Calculate the total and per unit cost of each product using ABC system.
f)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of total allocated cost for the product S109:
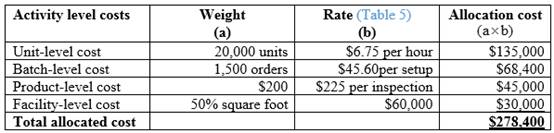
Table (6)
Hence, the total allocated cost for product S109 is $278,000.
Calculation of total allocated cost for the product N227:
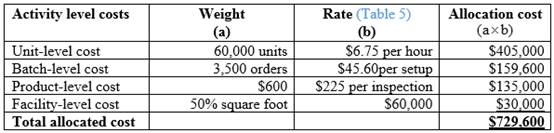
Table (7)
Hence, the total allocated cost for product N227 is $729,600.
Calculation of total cost of each product line and combined cost of the products using ABC system:
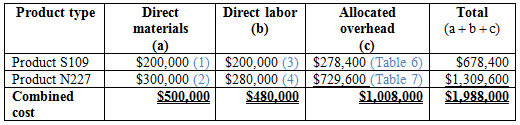
Table (8)
Hence, the total combined cost is $1,988,000.
Calculation of cost per unit using ABC method:
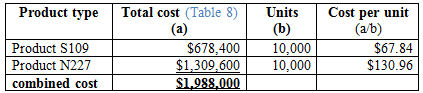
Table (9)
Hence, the costs per unit of product S109 and product N227 are $67.84 and $130.96.
g)
Calculate the revised price for the given products.
g)
Explanation of Solution
Calculation of revised price for given products:
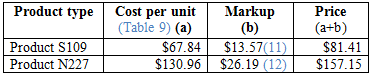
Table (10)
Hence, the prices of each product using markup are $81.41 and $157.15.
Working notes:
Calculation of mark-up value for Product S109:
Hence, the mark-up value for Product S109 is 13.57.
…… (11)
Calculation of mark-up value for Product N227:
Hence, the mark-up value for Product N227 is 26.19.
…… (12)
h
Based on the results from requirements f and g, discuss the reason product N227 costs more and reason for adjusting sales price.
h
Explanation of Solution
Manufacturing the product N227 is more costly because it requires more machine setups, inspection cost, and machine hours than Product S109. However, the ABC system reveals the accurate cost of the product. Laboratory I need to adjust its prices in order to sustain in the market for a long term.
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Fundamental Managerial Accounting Concepts with Access
- Kindly help me with this General accounting questions not use chart gpt please fast given solutionarrow_forwardPlease provide the accurate answer to this general accounting problem using appropriate methods.arrow_forwardI am looking for the correct answer to this financial accounting problem using valid accounting standards.arrow_forward
- Cooper Industries disposed of an asset at the end of the sixth year of its estimated life for $12,500 cash. The asset's life was originally estimated to be 8 years. The original cost was $76,000 with an estimated residual value of $6,000. The asset was being depreciated using the straight-line method. What was the gain or loss on the disposal? Helparrow_forwardCooper Industries disposed of an asset at the end of the sixth year of its estimated life for $12,500 cash. The asset's life was originally estimated to be 8 years. The original cost was $76,000 with an estimated residual value of $6,000. The asset was being depreciated using the straight-line method. What was the gain or loss on the disposal?arrow_forwardI need guidance with this general accounting problem using the right accounting principles.arrow_forward

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





