
Concept explainers
Isomers are molecules with the same elemental composition but a different atomic arrangement. Three isomers with the formula C4H8 are shown in the models below. The enthalpy of combustion (ΔcH°) of each isomer, determined using a calorimeter, is as follows:
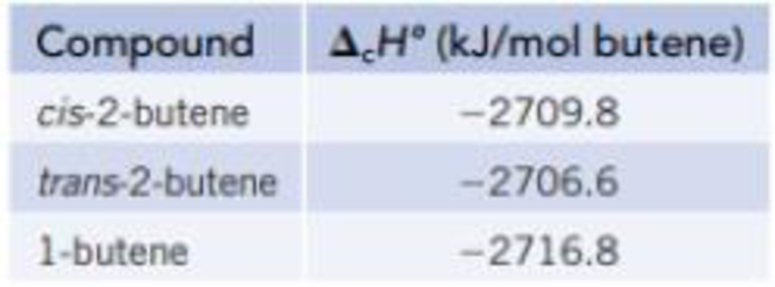
- (a) Draw an energy level diagram relating the energy content of the three isomers to the energy content of the combustion products, CO2(g) and H2O(ℓ).
- (b) Use the ΔcH° data in part (a), along with the enthalpies of formation of CO2(g) and H2O(ℓ) from Appendix L, to calculate the enthalpy of formation for each of the isomers.
- (c) Draw an energy level diagram that relates the enthalpies of formation of the three isomers to the energy of the elements in their standard states.
- (d) What is the enthalpy change for the conversion of cis-2-butene to trans-2-butene?
(a)
Interpretation:
The energy level diagram relating the energy content of the three isomers has to be determined
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1K.Energy gained or lost can be calculated using the below equation.
Where, q= energy gained or lost for a given mass of substance (m), C =specific heat capacity,
The standard molar enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change
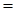
Explanation of Solution
The energy level diagram is given below
Figure 1
(b)
Interpretation:
The enthalpy of formation of
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1g substance by 1K.Energy gained or lost can be calculated using the below equation.
Where, q= energy gained or lost for a given mass of substance (m), C =specific heat capacity,
The standard molar enthalpy of formation is the enthalpy change
Explanation of Solution
Given reaction is:
For cis-2-butene
Using the formula 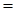
For trans-2-butene
Using the formula 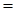
For 1-butene
Using the formula 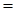
the enthalpy of formation for each of the isomers found out.
(c)
Interpretation:
The energy level diagram based on the enthalpy of formation has to be determined.
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1K. Energy gained or lost can be calculated using the below equation.
Where, q= energy gained or lost for a given mass of substance (m), C =specific heat capacity,
The standard enthalpy change of combustion of a compound is the enthalpy change which occurs when one gram of the compound is burned completely in oxygen under standard conditions, and with everything in its standard state.
Explanation of Solution
The energy level diagram based on the enthalpy of formation is:
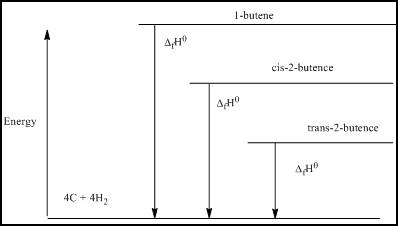
Figure 2
(d)
Interpretation:
The enthalpy change for the conversion of
Concept Introduction:
Heat energy required to raise the temperature of 1g of substance by 1K. Energy gained or lost can be calculated using the below equation.
Where, q= energy gained or lost for a given mass of substance (m), C =specific heat capacity,
The standard enthalpy change of combustion of a compound is the enthalpy change which occurs when one gram of the compound is burned completely in oxygen under standard conditions, and with everything in its standard state.
Explanation of Solution
Form the question the values given are:
Enthalpy change of cis-2-butence to trans-2-butene
So, the enthalpy change for a conversion of cis-2-butence to trans-2-butene is
Want to see more full solutions like this?
Chapter 5 Solutions
Bundle: Chemistry & Chemical Reactivity, Loose-Leaf Version, 9th + OWLv2, 4 terms (24 Months) Printed Access Card
- CI 1) n-BuLi 2) 1) 03 HH T&Cl 2) H₂O 2arrow_forwardHelp with a!arrow_forwardFor the following compound: HO -H Draw a mechanism for the tautomerization process under BASIC conditions: Mechanism A: H-O: H-OH H-O HH H-OO Mechanism B: H-Q Mechanism C: Θ OH H-O: Mechanism D: H-O H- H-OO C H-OO H- H- H-OO HH OH -H - HON H :OH H-Harrow_forward
- identify the product (or multiple products) for each of the following reactions: CI 1) NaNH2 (excess) ठ Cl 2) H₂O Hz H₂SO₂, H₂O HgSO Lindlar's catalyst 1) n-BuLi 2) 1)9-BBN 2) H₂O, NaOH ? Br H A B C afó gó H OA B O c OD E OF D E F H H Na, NHarrow_forwardIdentify the product (or multiple products) for each of the following reactions: ? or CI CI 1) NaNHz (excess) 2) H₂O OA OB O C OD OE OF H₂SO₂, H₂O Hq50. 1) n-BuLi 2) Br 1) 9-BBN 2) H₂O₂, NaOH A B H H متته D E H H H H C H H F H H H₂ Lindlar's catalyst Na NHarrow_forwardIdentify the product (or multiple products) for each of the following reactions: O A OB Oc OD OE OF CI CI 1) NaNH2 (excess) 2) H₂O H₂ H₂SO2, H₂O HgSO Lindlar's catalyst 1) n-BuLi 2) Br 1)9-BBN 2) H₂O₂, NaOH ? Na, NH3 C H A H H مننه مننه منن مننه H F H H E مند H D H Harrow_forward
- For the following compound: HO H Draw a mechanism for the tautomerization process under BASIC conditions: Mechanism A: + H-O: H-OH₂ H Mechanism B: H-Ö: HO-H H-OO -H H HH H H HH H-O: H-OO H-OO -H H e -H : OH Θ Mechanism C: Θ A : OH H-O: H H H-O-H 0. Mechanism D: e.. : OH :0 H H-O-H H-O: H-OO :O H -H H H сём H 0 :0 + H Θ H H H-arrow_forwardFor the following compound: H OH Draw a mechanism for the tautomerization process under ACIDIC conditions: Mechanism A: Θ :OH O O-H HO 0: Mechanism B: :O-H e.. Θ :OH Mechanism C: H HO-H :0: Θ 0: H H e.. : OH 0: "Θ HH O. :OH :OH O-H O-H Mechanism D: :OH H-OH₂ :OH HO-H 0: © O-H H HH 0: HHarrow_forwardHelp w c!arrow_forward
 Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and PracticeChemistryISBN:9780534420123Author:Daniel L. Reger, Scott R. Goode, David W. Ball, Edward MercerPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry for Engineering StudentsChemistryISBN:9781337398909Author:Lawrence S. Brown, Tom HolmePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning
General Chemistry - Standalone book (MindTap Cour...ChemistryISBN:9781305580343Author:Steven D. Gammon, Ebbing, Darrell Ebbing, Steven D., Darrell; Gammon, Darrell Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon, Darrell D.; Gammon, Ebbing; Steven D. Gammon; DarrellPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry & Chemical ReactivityChemistryISBN:9781337399074Author:John C. Kotz, Paul M. Treichel, John Townsend, David TreichelPublisher:Cengage Learning Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: The Molecular ScienceChemistryISBN:9781285199047Author:John W. Moore, Conrad L. StanitskiPublisher:Cengage Learning





