
Concept explainers
Core Skill: Connections In what other organ is a brush border found (refer back to Figure 46.6)? What general conclusions can you draw about the function of such specialized epithelia?
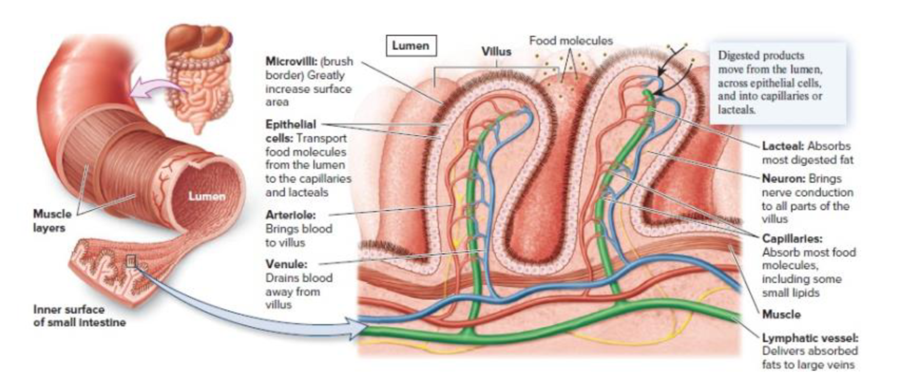
Figure 46.6 The specialized arrangement of tissues in the small intestine. The inner surface of the small intestine is folded into numerous villi, which increase the surface area for digestion and absorption. Within each villus are capillaries and a lymphatic vessel called a lacteal, into which absorbed nutrients are transported. The epithelial cells of the villi have extensions from their surface called microvilli. The microvilli constitute the brush border of the intestine and greatly add to the total surface area.
Want to see the full answer?
Check out a sample textbook solution
Chapter 49 Solutions
Biology
Additional Science Textbook Solutions
Chemistry
Fundamentals of Physics Extended
Biological Science (6th Edition)
Chemistry: Structure and Properties (2nd Edition)
Campbell Biology in Focus (2nd Edition)
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
- Molecular Biology Explain/discuss how “slow stop” and “quick/fast stop” mutants wereused to identify different protein involved in DNA replication in E. coli.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology Question A gene that codes for a protein was removed from a eukaryotic cell and inserted into a prokaryotic cell. Although the gene was successfully transcribed and translated, it produced a different protein than it produced in the eukaryotic cell. What is the most likely explanation?arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of origins of replicationarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology Question Please help. Thank you For E coli DNA polymerase III, give the structure and function of the b-clamp sub-complex. Describe how the structure of this sub-complex is important for it’s function.arrow_forwardMolecular Biology LIST three characteristics of DNA Polymerasesarrow_forwardMolecular Biology RNA polymerase core enzyme structure contains what subunits? To form holo enzyme, sigma factor is added to core. What is the name of the structure formed? Give the detailed structure of sigma factor and the function of eachdomain. Please help. Thank youarrow_forward
- Molecular Biology You have a single bacterial cell whose DNA is labelled with radioactiveC14. After 5 rounds of cell division, how may cells will contain radioactive DNA? Please help. Thank youarrow_forward1. Explain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forward1. In the Sentinel Cell DNA integrity is preserved through nanoscopic helicase-coordinated repair, while lipids in the membrane are fortified to resist environmental mutagens. also provide pictures for this question.arrow_forward
- Explain the structure and properties of atoms and chemical bonds (especially how they relate to DNA and proteins). Also add some pictures.arrow_forwardIn the Sentinel Cell DNA integrity is preserved through nanoscopic helicase-coordinated repair, while lipids in the membrane are fortified to resist environmental mutagens. also provide pictures for this question.arrow_forward1. Explain how genetic information is stored, copied, transferred, and expressed. Also add some pictures for this question.arrow_forward
 Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning
Biology (MindTap Course List)BiologyISBN:9781337392938Author:Eldra Solomon, Charles Martin, Diana W. Martin, Linda R. BergPublisher:Cengage Learning Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781938168130Author:Kelly A. Young, James A. Wise, Peter DeSaix, Dean H. Kruse, Brandon Poe, Eddie Johnson, Jody E. Johnson, Oksana Korol, J. Gordon Betts, Mark WomblePublisher:OpenStax College Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning
Human Physiology: From Cells to Systems (MindTap ...BiologyISBN:9781285866932Author:Lauralee SherwoodPublisher:Cengage Learning





